A list of the major recessions in UK and US.
List of Recessions in UK
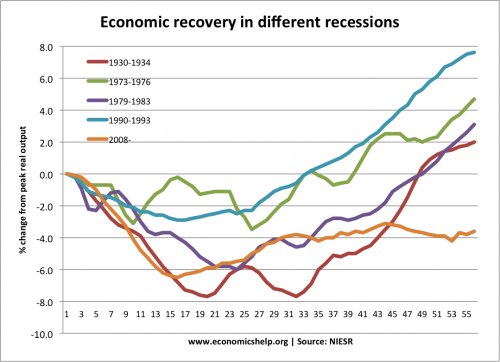
Comparing different recessions
1919-21 Recession
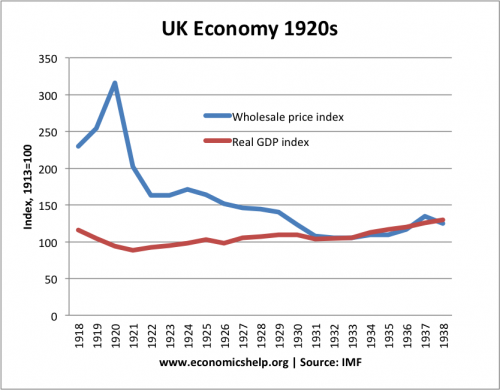
- GDP fell 25% during the three years following the end of the First World War.
- Unemployment rose to 20%
- UK experienced deflation of 10% in 1921, and 14% in 1922
Causes of fall in GDP
- End of First World War led to sharp fall in government spending which accounted for a large part of the fall in GDP
- UK’s return to the gold standard made UK exports expensive leading to lower demand.
- Trade slow to recover in the aftermath of First World War and reparations on Germany. (Keynes opposed Versailles Treaty on ground crippling reparations would harm European trade)
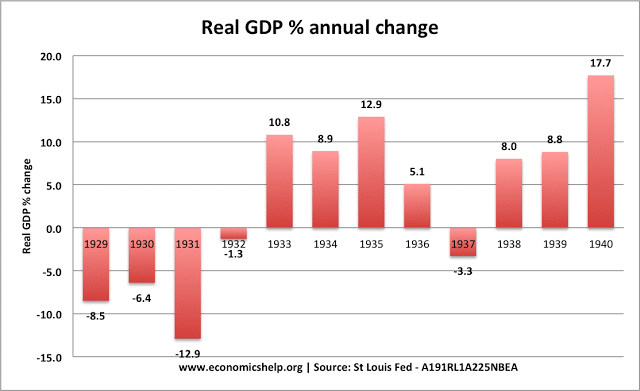
Great Depression 1930-33
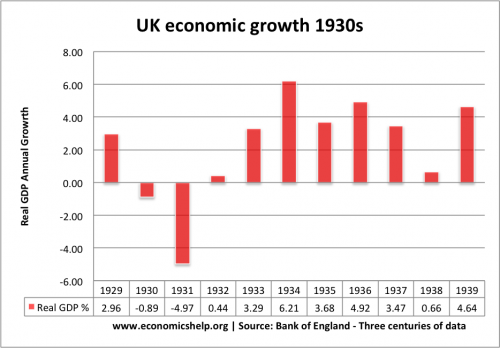
- GDP fell 5.1% in 1930-31.
- GDP fell less in the UK than other countries. But, this was against a backdrop of the poor economic performance of the 1920s. Leaving the gold standard in 1931, helped the UK recover quicker than other countries.
- Unemployment rose to over 22%
- The effects of the great depression were highly geographical. Manufacturing heartlands in north and Wales much more affected than the South and London.
Causes of Great Depression
- Causes of Great Depression
- Ongoing deflation which discouraged spending
- Fall in global trade due to the global depression and higher tariffs.
- Budget of 1931 increasing taxes and cutting unemployment benefits
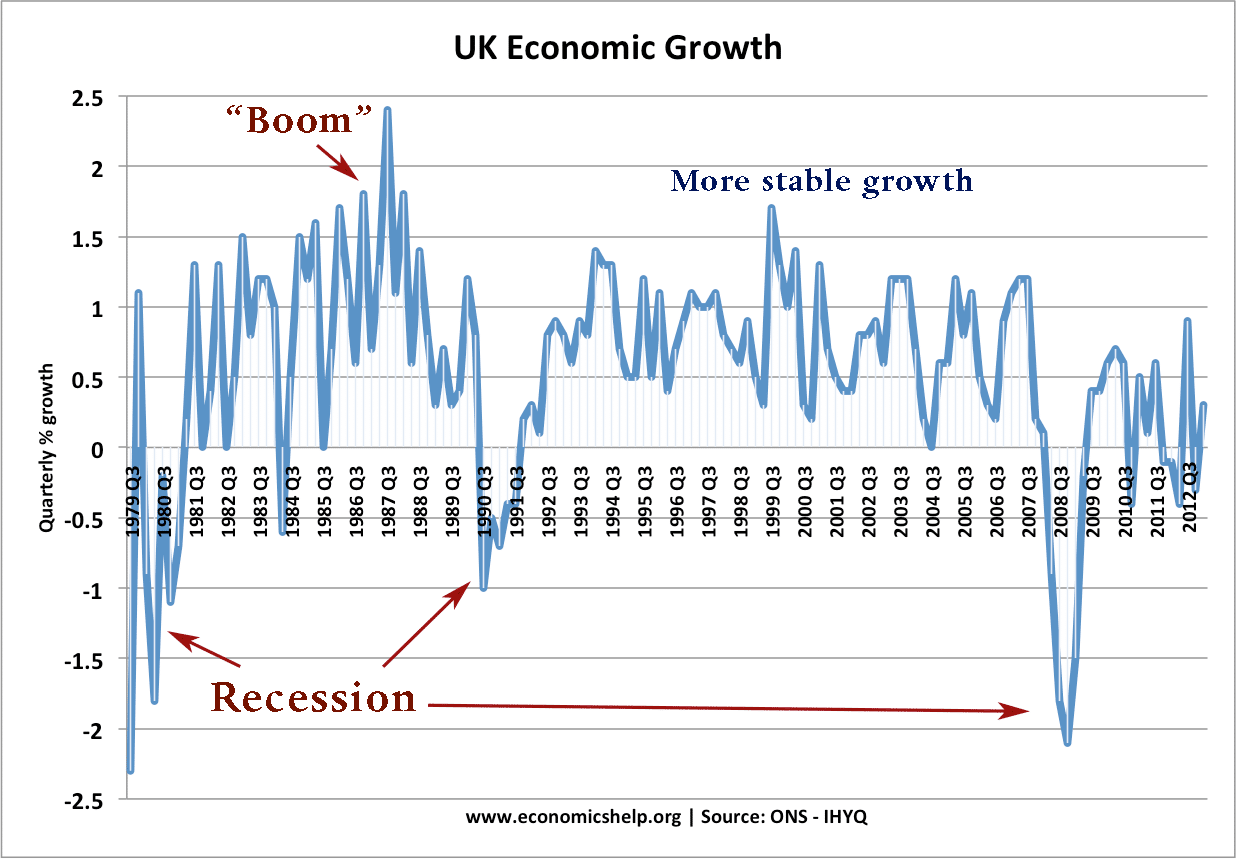
Recessions Post War
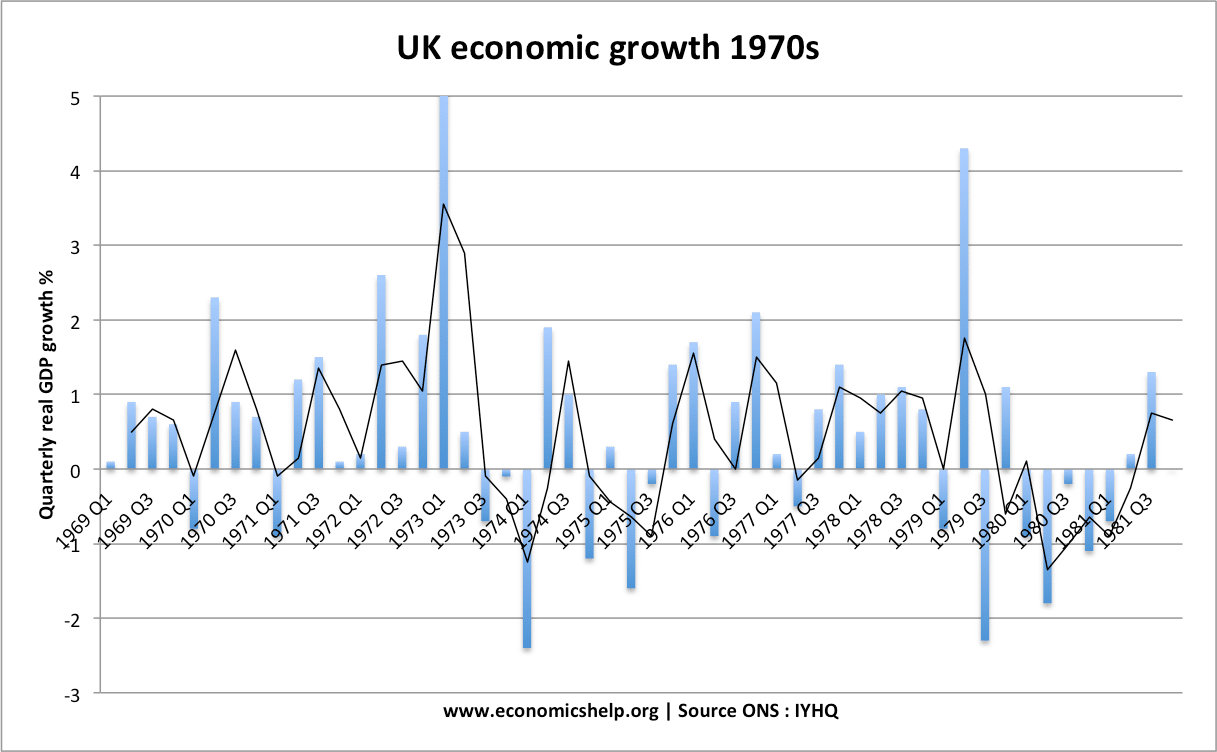
1973-75 Recession
- GDP fell 3.9%.
- Double dip recession.
- Caused partly by rapid rise in oil prices. Also, came after ‘Barber boom’ – very rapid growth in 1973 Q1
- Took 14 months to recover to initial level of GDP
Causes of 1973-75 Recession
- Bust after the Barber boom of 1972/73.
- Oil price shock of 1973
- Falling real house prices
- See: Economy of the 1970s
1980-82 Recession
- GDP fell 5.7%.
- Unemployment 11.9% in 1984.
- Took 18 months to recover. Unemployment levels took much longer to fall
Causes of 1980-82 Recession
- Tightening of monetary and fiscal policy to reduce inflation.
- Appreciation in Pound due to North Sea oil and high interest rates.
- See: 1980-82 Recession
1990-92 Recession.
- GDP fell 2.5%
- Unemployment rose to 10%
Causes of 1990-92 Recession
- Higher interest rates attempting to reduce inflation caused by fast growth in the late 1980s
- Falling house prices
- Overvalued exchange rate.
- See: 1990-92 Recession
2008-13 Recession
- GDP fell 6.1%
- Double dip recession in 2011-12.
- See: Double dip recession of 2008
List of Recessions in US
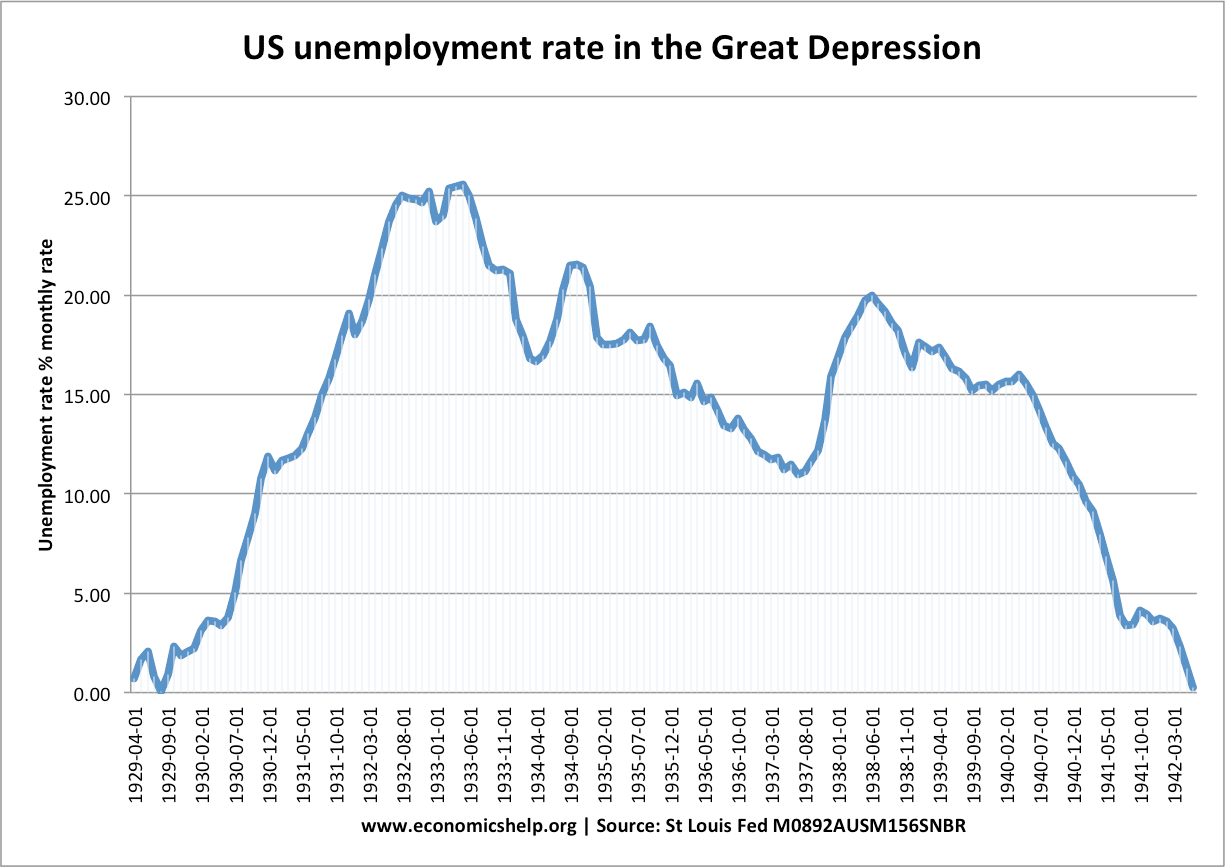
Great Depression 1929-1933.
- GDP fell 26.7%. Peak unemployment 24.9% (1933)
1937 Recession.
- GDP fell 18.2%. Peak unemployment 19%.
1945 Recession
- GDP fell 12.7% as a result of fall in government spending at the end of the Second World War. Not as bad as statistics suggest due to technical nature of cuts in government spending on the military.
- Only 5.2% unemployment
1948-40 Recession
- GDP fell 1.7%.
1953-54 Recession.
- GDP fell 2.6%. Duration 10 months.
- Unemployment 6.1%
1960-61 Recession.
- GDP fell 1.6%. Duration 10 months. Unemployment 7.1%
1969-70 Recession.
- GDP fell 0.6%. Duration 11 months. Unemployment 6.1%
1973-75 Recession
- GDP fell 3.2%. Duration 1 year 4 months. unemployment 9%
1980 Recession.
- GDP fell 2.2%. Duration 6 months. Unemployment 7.8%
1981-82 Recession
- GDP fell 2.7%. Unemployment 10.8%
1990-91 Recession
- GDP fell 1.4%. Duration 8 months. Unemployment 7.8%
2001 Recession
- GDP fell 0.5%. Duration 8 months. Unemployment 6.3%
2007-09 Recession
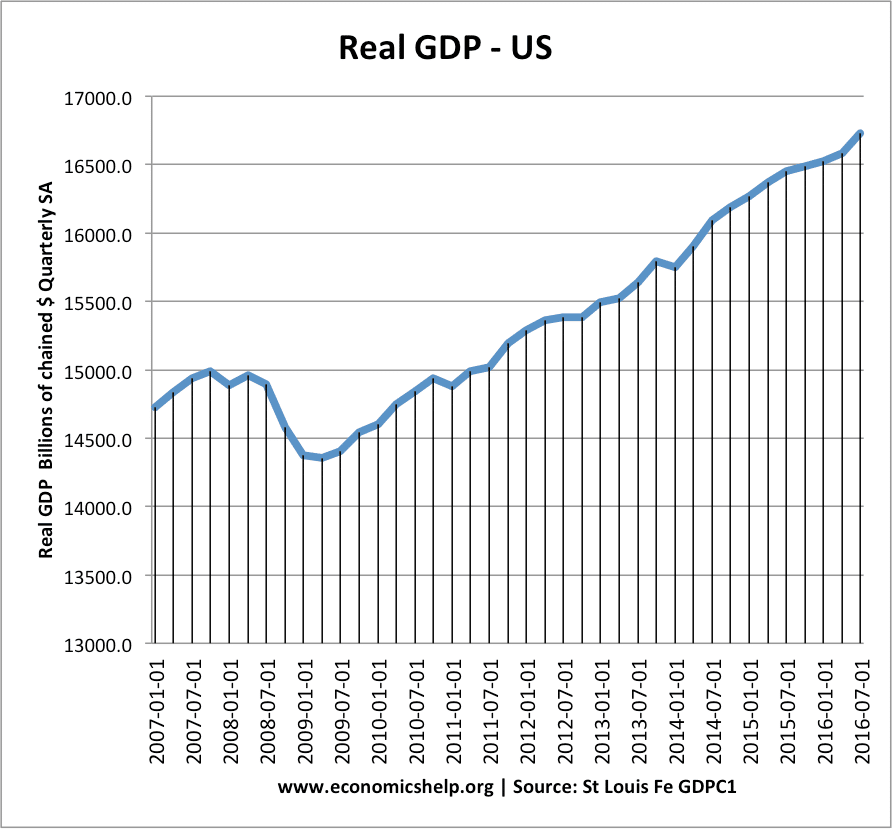
- GDP fell 5.1%. duration 1 year 6 months. Unemployment 10.1% – Deepest recession since Great Depression.
- Slow recovery in 2010-11 led to continued rise in unemployment
Related