Definition of Competition Policy: Government policies to prevent and reduce the abuse of monopoly power.
Abuse of monopoly power can lead to market failure and be against the public interest. Therefore Governments are concerned to intervene and protect the interests of the consumers.
1998 Competition Act sought to bring the UK into line with EU competition policy
The OFT is responsible for investigating suspected abuses of monopoly power and engaging in prohibited practices. There are two main types of behaviour they investigate:
- Collusive Behaviour
- Abuse of Market Power
Collusive Behaviour
This occurs when firms enter into agreements to fix prices and or output. This enables firms to make higher profits at the expense of consumers.
Collusive tendering. This occurs when firms enter into agreements to fix the bid at which they will tender for projects. Firms will take it in turns to get the contract and enable a much higher price for the contract.
Collusive behaviour is illegal and can be investigated by the OFT.
Abuse of Market Power
If a firm has more than 40% of market share, it is considered to have market power. The OFT is more likely to investigate firms with a dominant market position. Though they can also investigate people with less market share. Abuse of Market Power may include:
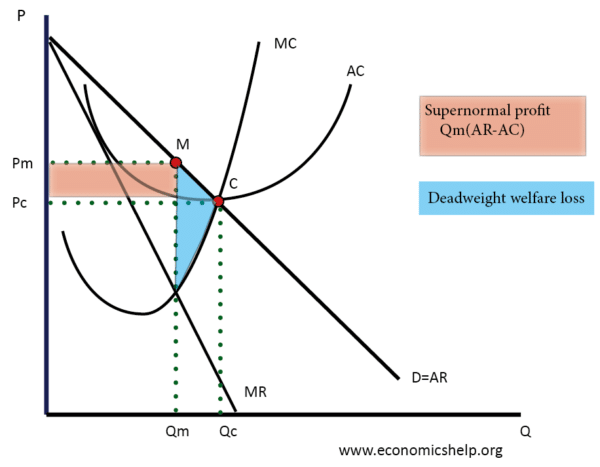
- Charging Higher prices – a Monopoly is able to set high prices. This is a theoretical diagram of a firm with monopoly power. They can increase prices from Pc to Pm. The OFT may consider this abuse of monopoly power if it leads to excess prices and profits.
- Predatory Pricing – selling below cost with the intention of forcing a rival firm out of business
- Vertical restraints – Firms may use market power to pay lower prices to suppliers (e.g. Supermarkets have been criticised for paying low prices to farmers. Also, firms may limit competition by preventing competitors from being sold in a shop. For example, an ice-cream manufacturer may give a free freezer to a shop – but on the condition, they only sell their ice-cream
- Tie in Sales. E.g. A printer which makes people may its own brand very expensive ink.
Competition and Markets Authority
UK competition policy is regulation by CMA (Competition and Markets Authority). This used to be managed by the OFT and Competition Commission.
The CMA area of influence includes:
- Regulation of Cartels/Collusion. Based on the Competition Act 1998
- Education of business so that they comply with relevant competition act
- Consumer bodies can make ‘super complaints’ to the CMA for investigation of unfair practices.
- Mergers – The CMA must be notified of mergers and they can investigate if they think they might be against public interest.
- Investigate particular industries and see whether they are run in the public interest.
Examples of Competition Policy
The merger between HP foods and Heinz accepted by Competition Commission
The report “concluded that the acquisition may not be expected to result in a substantial lessening of competition within the markets for the supply of tomato ketchup, brown sauce, barbecue sauce, tinned baked beans and tinned pasta products in the UK.”(March 2006)
- The investigation into the grocery market – largely cleared big supermarkets of unfair practices. (April 2008) However, it did recommend a test regarding the level of competition in particular local areas. Sometimes an incumbent firm could gain a local monopoly. The CMA recommended rules to encourage more local competition.
- Merger between Hungry House and Just Eat – allowed by CMA (Dec 2017)
- Referral of merger between soft drink manufacturers Refresco and Cott to an in-depth investigation (Dec 2017) The CMA were concerned this merger could increase prices due to increased market share. The Case Study for this merger is here.
- An investigation into the care home sector by CMA found they had two concerns (Summary of report).
- The industry required more public sector funding.
- Those choosing a care home need greater help in choosing which care home. The vulnerable residents also require protection when staying.
Related
- Competition and Markets Authority (External link)