The Baltic Dry Index is a measure of the international price for sending commodities by sea. It is calculated by combining the price of different shipping sizes for dry commodities. Commodities include metals, grains, crude oil.
The Baltic Dry Index developed in the mid-eighteenth century. It gained the name Baltic Dry index partly because at the time the main shipping routes were between London and the Baltic States around Germany.
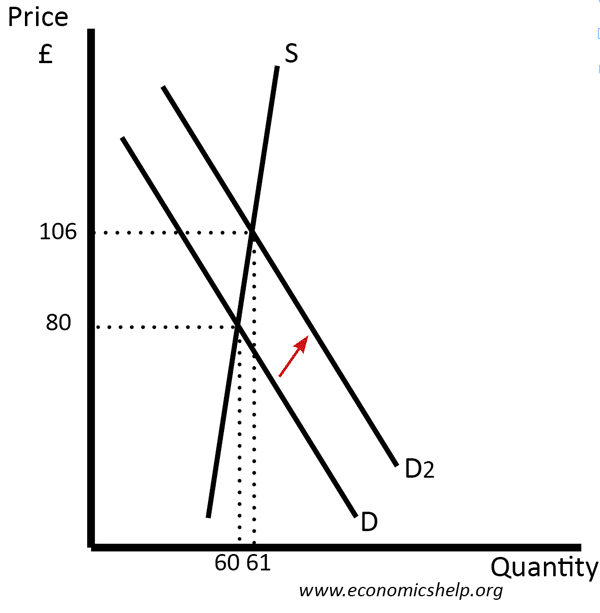
Baltic Dry Index Volatility
The price of moving commodities by sea tends to be volatile. This is because
- Supply of shipping vessels is inelastic. To build a new ship could take 2 years. Therefore, if there is a rise in the prices, shipping owners cannot easily increase the supply of ships.
- Ships have a large fixed cost so when bought, the owners will try to use them unless the price falls below the marginal cost of taking cargo.
Therefore a small change in demand for shipping goods means a relatively large change in price.
Diagram showing how inelastic Supply causes a large rise in price
The Baltic Dry Index as Economic Indicator
- The Baltic Dry Index provides a useful role as a forward looking economic indicator.
- A fall in economic growth would lead to lower demand for commodities and transporting commodities. This will be reflected in a fall in the price of the Baltic Dry index.
- Unlike many indexes, it is not subject to speculation. You would only buy a ship if you wanted to actually transport goods. Whereas people may buy gold due to speculation of rising prices.
In 2008, the Baltic Dry Index plummeted as the global economy slowed down. In 2009, the index has slowly picked up suggesting demand for raw materials is being revived.