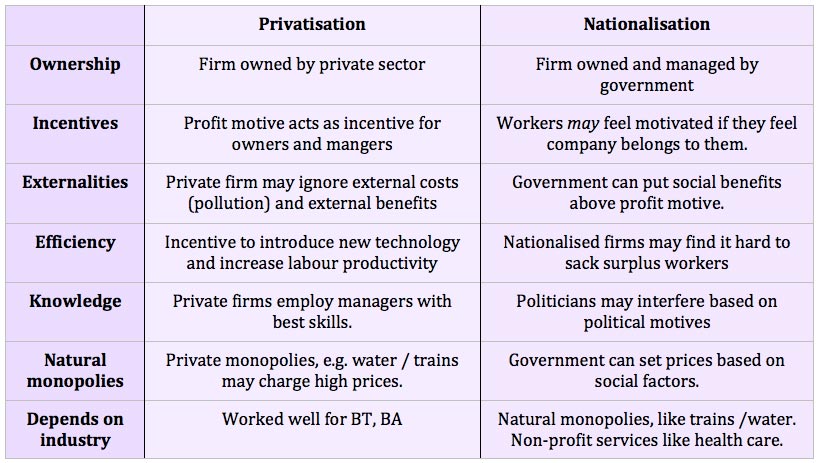
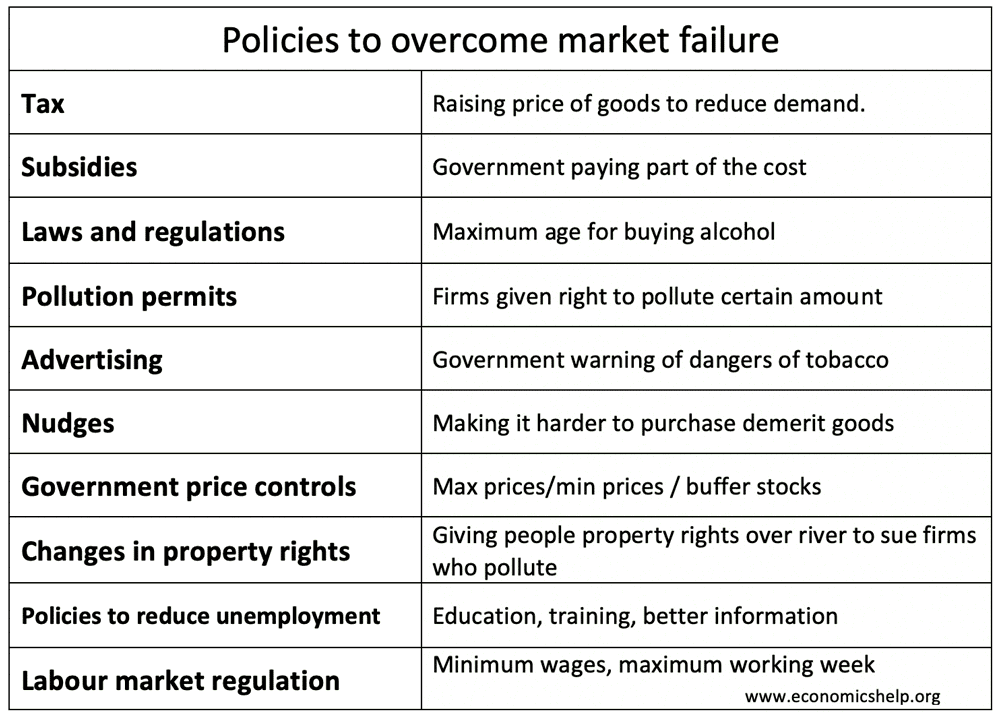
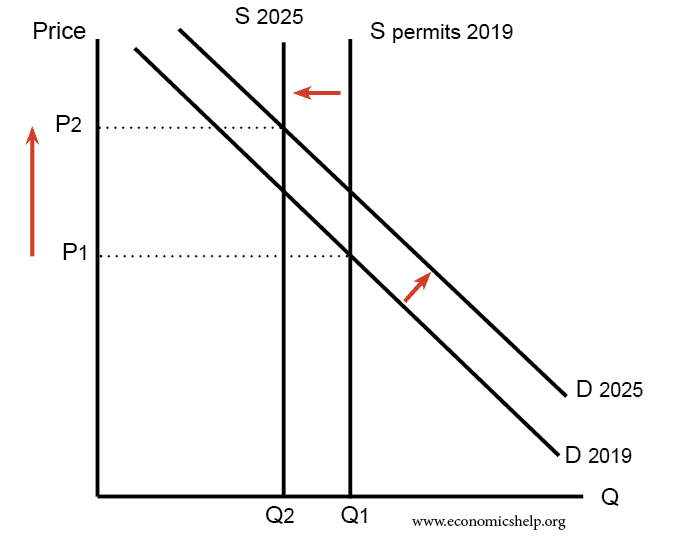
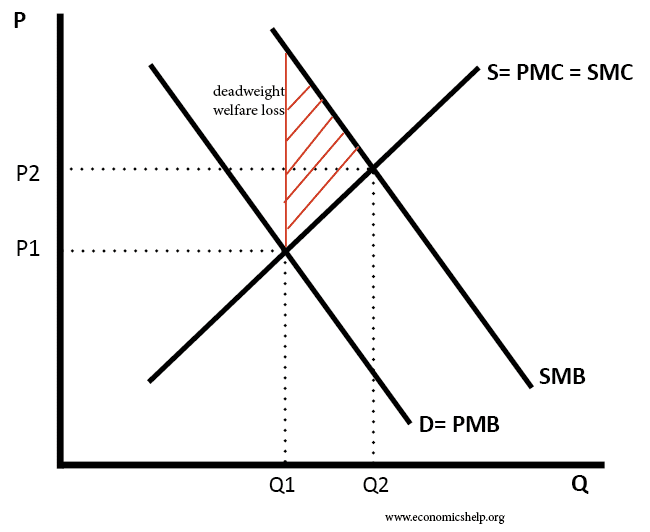
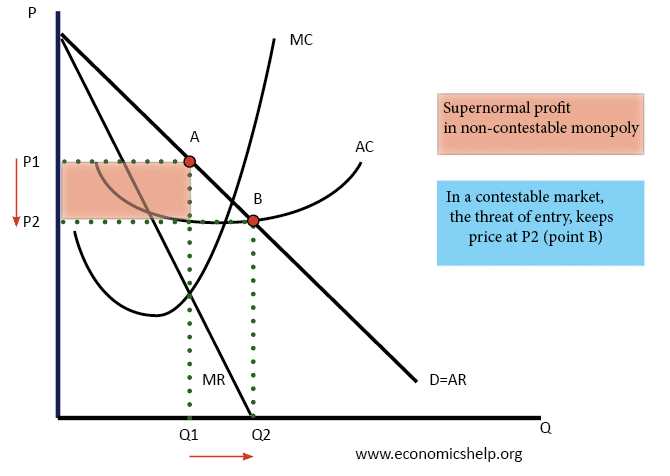
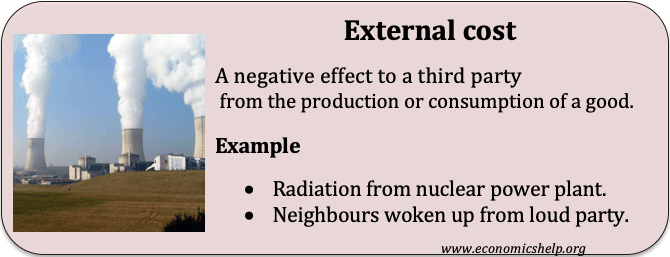
Arguments for nationalisation
Nationalisation occurs when the government take control of an industry previously owned by private firms. For example, after 1945, the Labour government nationalised key industries, such as railways, steel and electricity. The argument was that the government would be able to run the industries in the best interests of society. Arguments for Nationalisation include 1. …