Liquidity Trap – definition, examples and explanation
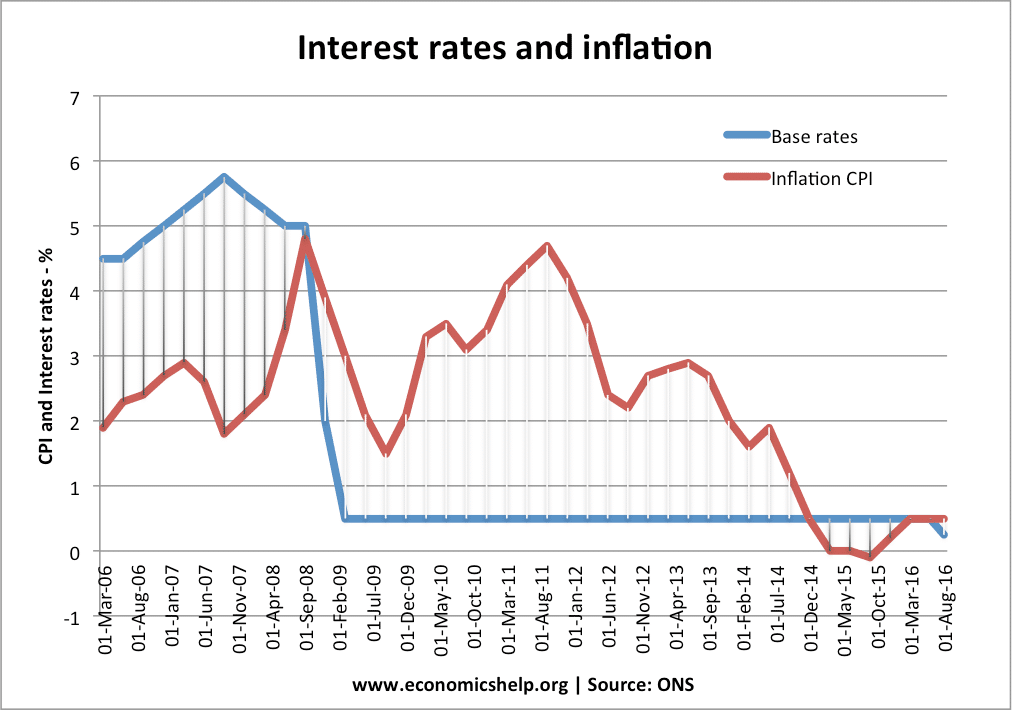
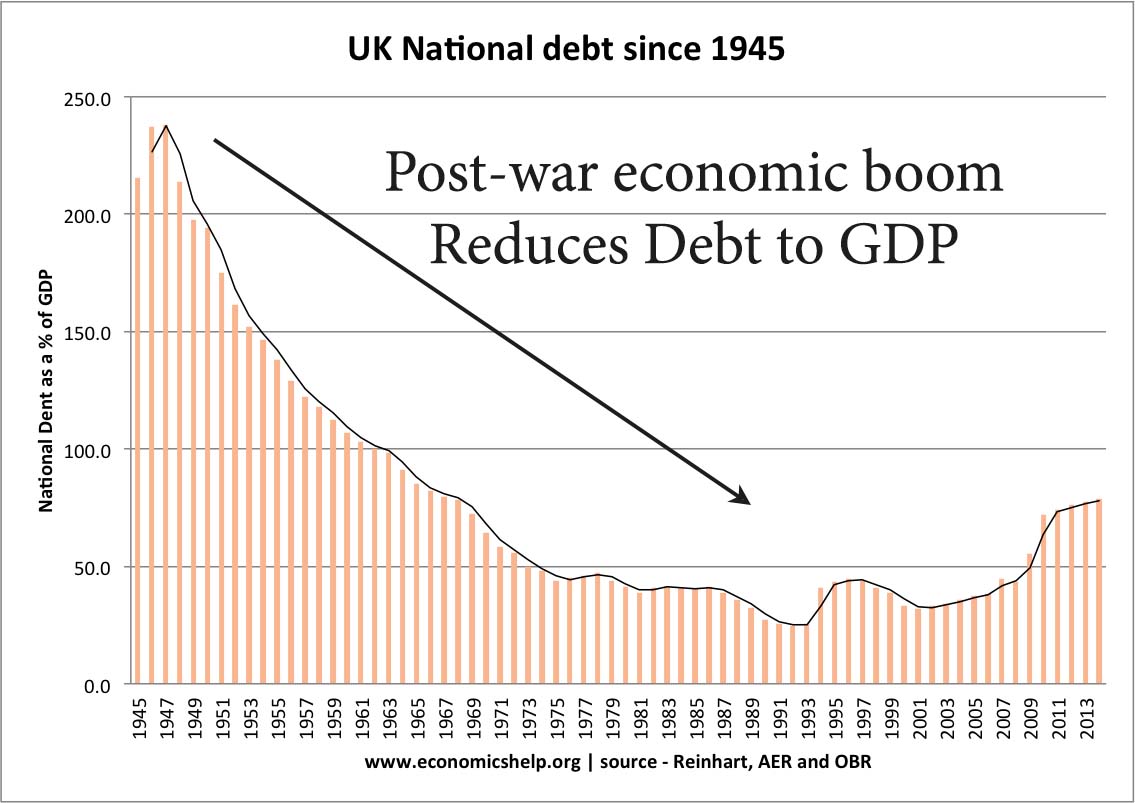
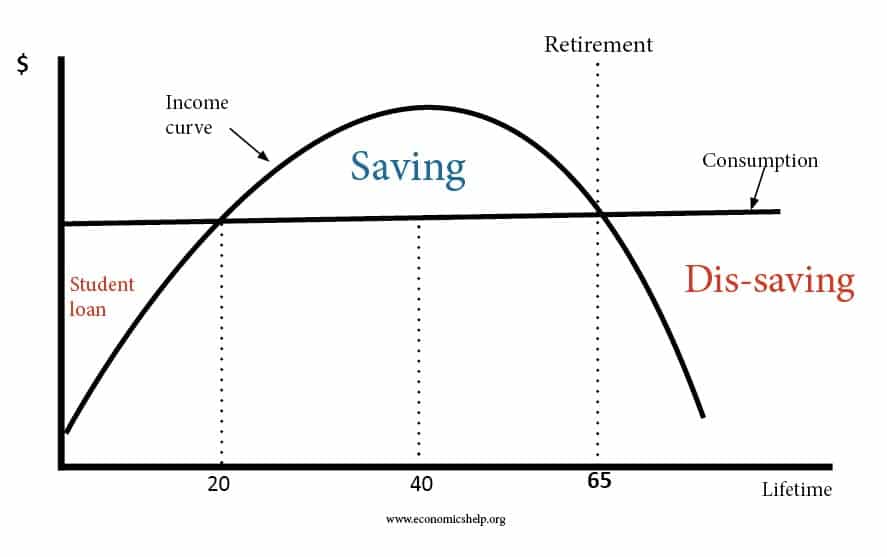
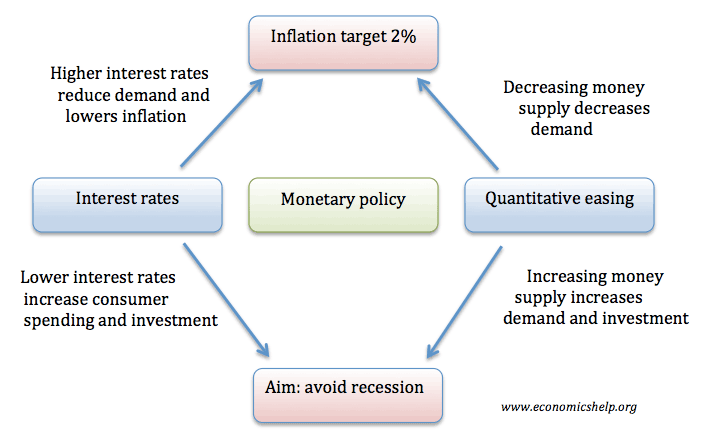
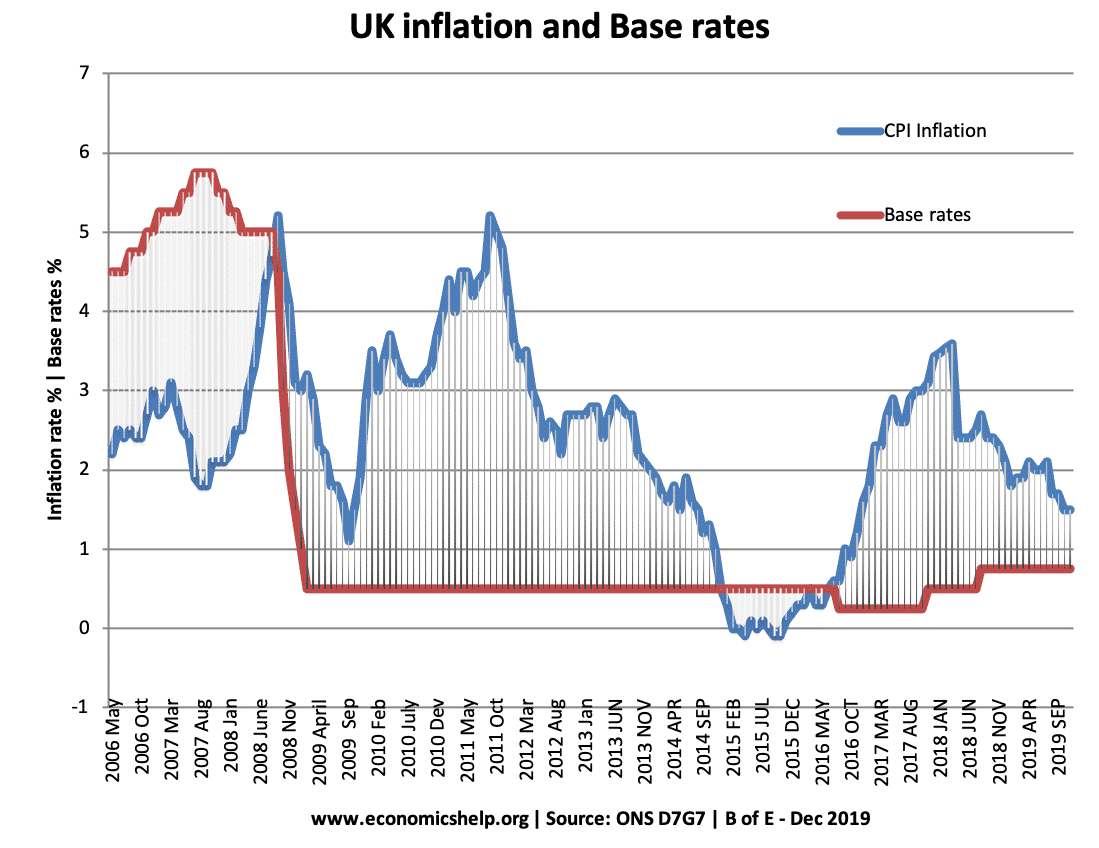
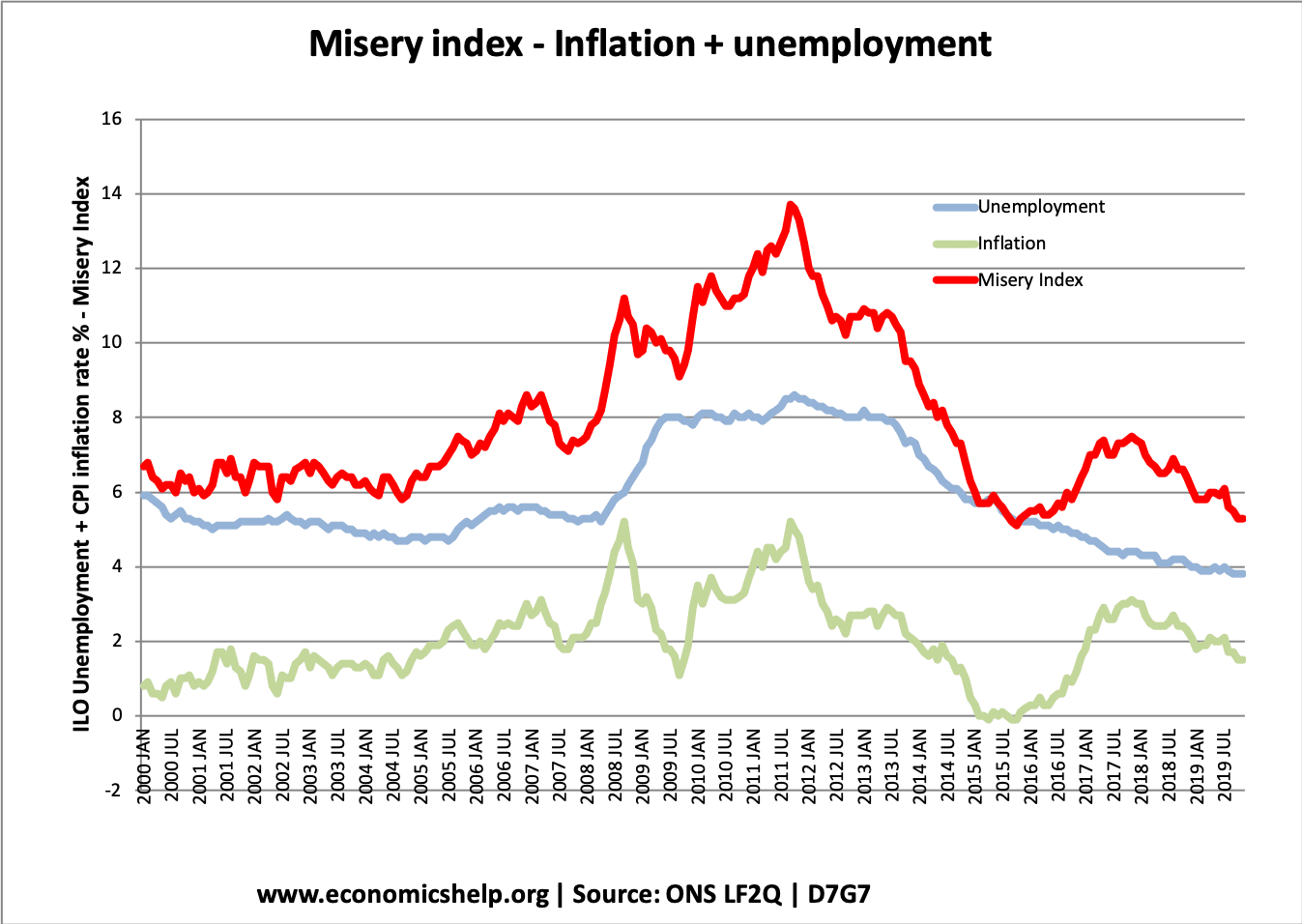
Definition of a liquidity trap: When monetary policy becomes ineffective because, despite zero/very low-interest rates, people want to hold cash rather than spend or buy illiquid assets. A liquidity trap is characterised by Very low-interest rates Low inflation Slow/negative economic growth Preference for saving rather than spending and investment Monetary policy becomes ineffective in boosting …