Definition consumption externality
This occurs when consuming a good cause either a positive or negative externality to a third party.
Positive consumption externality
When consuming a good gives a benefit to others. Examples include:
- Going to university. Your education gives benefit to rest of society (You can teach others)
- Taking medicine which prevents spread of infectious disease.
Diagram of positive consumption externality
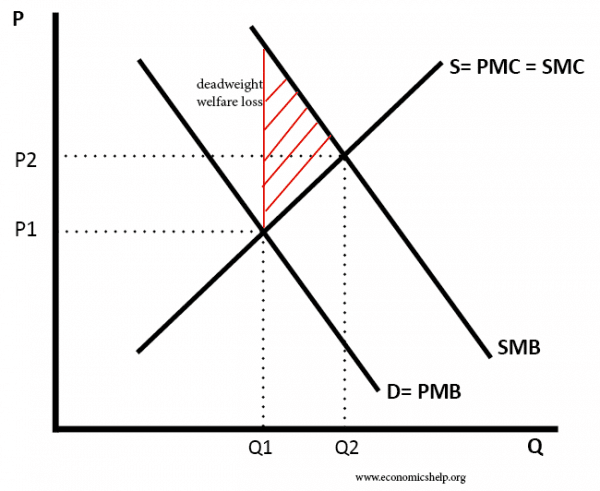
Because there is a benefit to others from your consumption, the social marginal benefit (SMB) is greater than private marginal benefit (PMB)
In a free market, there will be under-consumption of goods with positive consumption externalities.
Output in a free market will be at Q1, but social efficiency is at Q2 (where SMC = SMB)
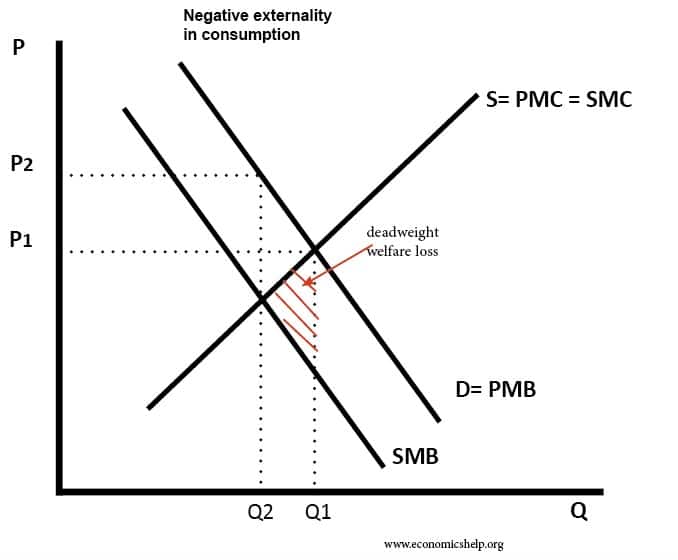
Negative consumption externality
Consuming a good causes a harmful effect on third parties.
In this case, there will be over-consumption of goods with negative consumption externalities in a free market.
Example of negative externality in consumption
- e.g. smoking causes harmful effect to those who breathe in your smoke.
Related