Definition of allocative efficiency
This occurs when there is an optimal distribution of goods and services, taking into account consumer’s preferences.
A more precise definition of allocative efficiency is at an output level where the Price equals the Marginal Cost (MC) of production. This is because the price that consumers are willing to pay is equivalent to the marginal utility that they get. Therefore the optimal distribution is achieved when the marginal utility of the good equals the marginal cost.
Example using diagram
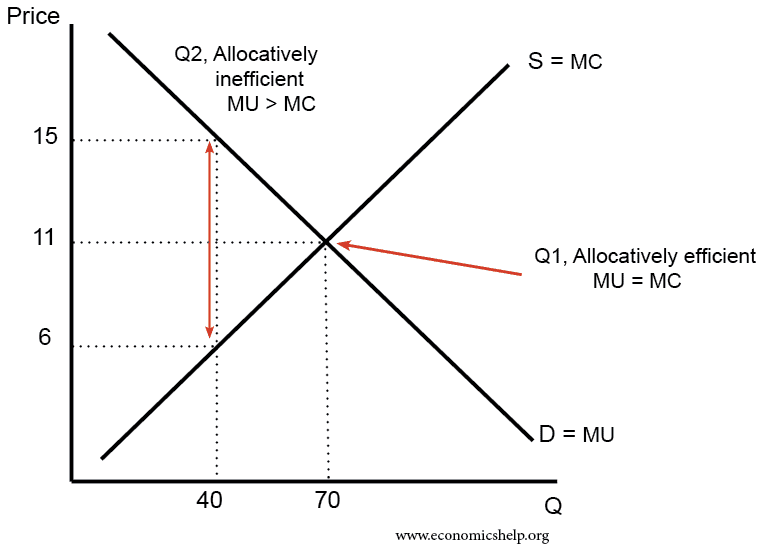
At an output of 40, the marginal cost of the good is £6, but at this output, consumers would be willing to pay a price of £15. The price (which reflects the good’s marginal utility) is greater than marginal cost – suggesting under-consumption. If output increased and price fell, society would benefit from enjoying more of the good.
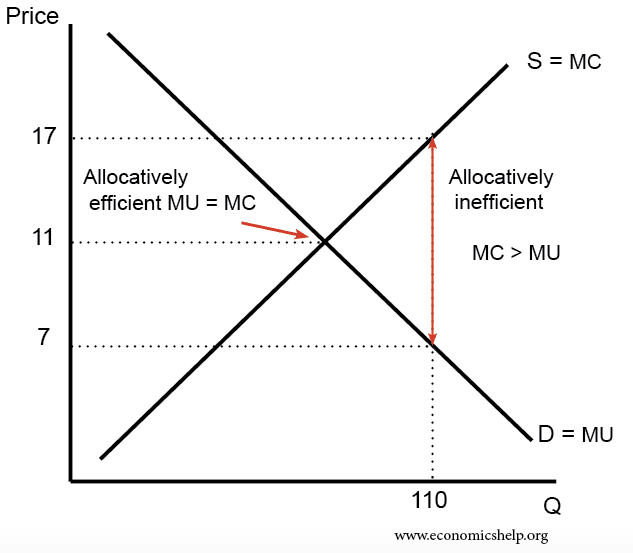
At an output of 110, the marginal cost is £17, but the price people are willing to pay is only £7. At this output, the marginal cost (£17) is much greater than the marginal benefit (£7) so there is over-consumption. Society is over-producing this good.
Allocative efficiency will occur at a price of £11. This is where the marginal cost (MC) = marginal utility.
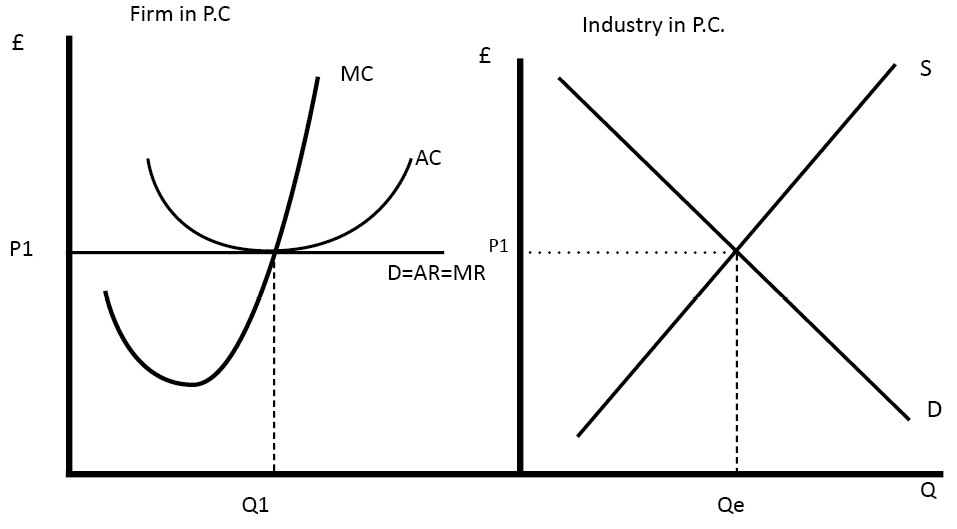
Perfect competition – allocatively efficient
- Firms in perfect competition are said to produce at an allocative efficient level because at Q1, P=MC
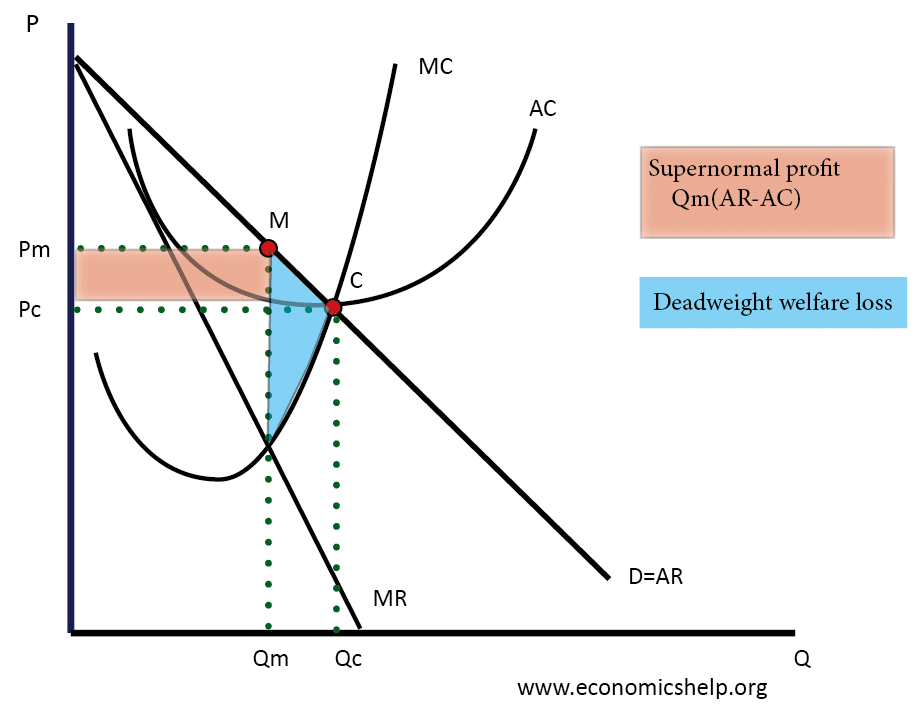
Monopolies – allocatively inefficient
- Monopolies can increase price above the marginal cost of production and are allocatively inefficient. This is because monopolies have market power and can increase price to reduce consumer surplus.
- Monopoly sets a price of Pm. This is allocatively inefficient because at this output of Qm, price is greater than MC.
- Allocative efficiency would occur at the point where the MC cuts the Demand curve so Price = MC.
- The area of deadweight welfare loss shows the degree of allocative inefficiency in the economy.
Allocative efficiency and productive efficiency
Productive Efficiency is concerned with producing goods at the lowest cost. This occurs on the production possibility frontier (PPF).
(Note producing on the production possibility frontier is not necessarily allocatively efficient because a PPF only shows the potential output. Allocative efficiency is concerned with the distribution of goods and this requires the addition of indifference curves.
Related