Definition of composite demand
Demand for a good that has multiple different uses. e.g. People may demand oil because it can be used to create either petrol or plastics.
Examples of composite demand
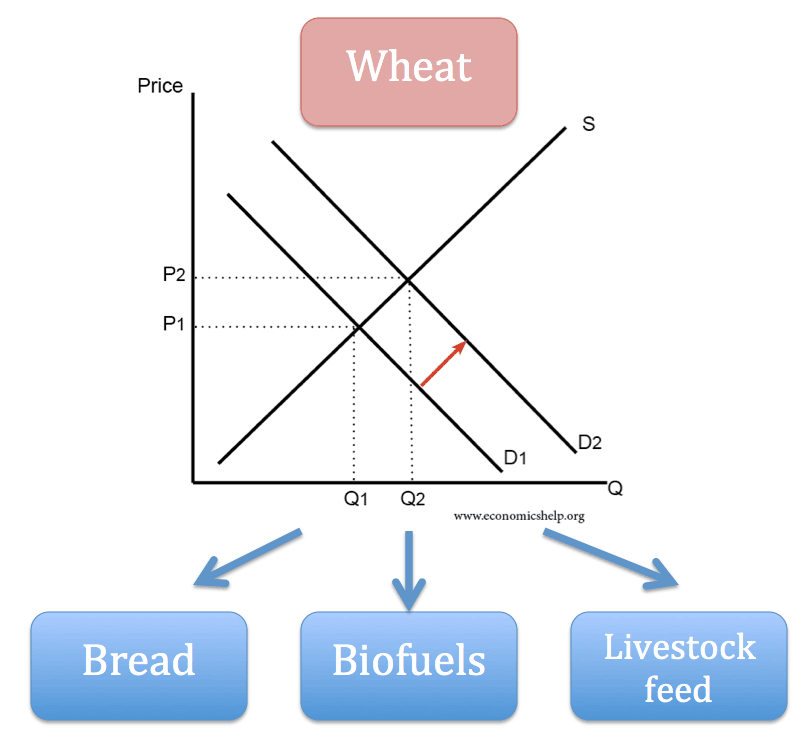
- People may demand wheat for producing bread, biofuels or feeding livestock.
- Land can be used for farming or building houses.
- Steel could be used for building tanks or it could be used for building bicycles.
- Demand for new iPhone – to use as a camera, access the internet and make phone calls.
Impact of composite demand
When a good like wheat has different uses, there can be a rationing effect. If demand for biofuel goes up, then the price of wheat for bread will also rise. More people demanding wheat for biofuels limits the availability of wheat for making bread.
If we build more houses, it leaves less land for farming and the price of farming land will tend to rise.
Related Notes
- Joint Demand – when goods are demanded together. Two complements like iPad and Application for iPad.
- Different types of goods
- Factors affecting demand