Factor immobility occurs when it is difficult for factors of production (e.g. labour and capital) to move between different areas of the economy. Factor immobility could involve:
- Geographical immobility – When it is difficult to move from one geographical area to another.
- Occupational immobility – difficult to move from one type of work to another.
Geographical immobility
Unemployment in South Wales may be very high, but there could still be job vacancies in London. Why is it difficult for the unemployed in South Wales to move to London and South East of England?
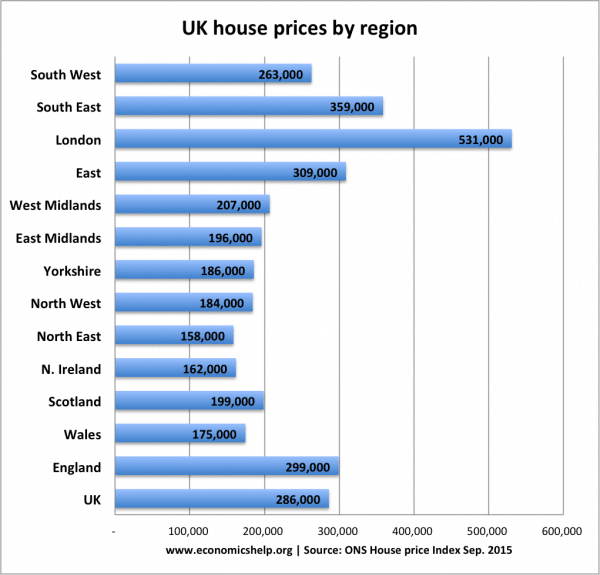
- Cost of moving/difficulty in finding accommodation. If you sold a house in Wales for £175,000, you wouldn’t be able to afford anything in London because of the higher house prices. Therefore the cost of buying or even renting may prohibit a worker from moving to areas with higher demand for workers.
- Lack of information. It may be difficult for the unemploymed to know about available jobs and available accommodation.
- Personal ties. An unemployed worker may have family and social ties in his place of birth. He may have children in school or partner in employment. All this makes it difficult to move.
- Within the Eurozone, there is even greater geographical immobility because of the difficulties in moving between countries, where different languages are spoken.
Policies to overcome geographical immobility
- Improve the quality and quantity of rented accommodation in employment hotspots. For example, building more council houses in London and the south. However, this may be difficult because there is limited space in London and there is already congestion and overcrowding.
- Move jobs out of London. The government has moved many public agencies out of London, for example, DVLA was moved to Swansea. The idea is to move jobs out of London – creating jobs in Wales and shifting demand from London.
- Improved transport links. High-speed railway lines into London may enable people to commute from longer distances.
Reasons for occupational immobility
If coal mines or steel factories closed down in South Wales, it may be very difficult for the unemployed coal miners to find work in new industries in the service sector.
- They may lack relevant skills/confidence or motivation to work in completely new industries.
- It may be difficult to receive training in areas where jobs are available.
- People over a certain age (e.g. 55) may be pessimistic about their chances to learn new skills in higher-tech industries.
Reasons for capital immobility
- If there is a rapid structural change in the economy. It may take time to alter machines and capital to keep up to date with changing nature of the economy.
Importance of factor immobility
- Globalisation is accelerating economic changes. Companies are outsourcing production to lower labour cost economies, causing disruptions in labour markets.
- Factor immobility is causing structural unemployment and/or lower wages – especially for manual workers who lose their jobs.
- Economic inefficiency. Factor immobility leads to resources being underused and causing a Pareto inefficient outcome.
- Factor immobility is a cause of market failure. The free market fails to provide an efficient allocation of resources because of the geographical and occupational immobilities.
- Inequality. Factor immobility can lead to increased inequality. This has occurred in past three decades.
Policies to overcome factor immobility
- Improve the provision of information
- Subsidise firms to move to depressed areas.
- Education and retraining for workers who don’t have relevant skills.
Related