A capitalist economic system is one characterised by free markets and the absence of government intervention in the economy.
In practice a capitalist economy will need some government intervention, primarily to protect private property. (This is important to distinguish capitalism from anarchism, where there is absolutely no government present)
Features of a capitalist economic system
- Economic freedom. Individuals free to set up business and provide the goods and services they want.
- Consumer sovereignty. Consumers free to decide which goods and services to purchase.
- Limited government. Government intervention limited to the protection of private property and provision of public goods.
- Finance sector. Capitalism requires a developed banking and financial system which can provide loans to companies and banking services to households.
- Profit motive is seen as important for enabling an efficient distribution of resources and encouraging innovation and responsive markets.
- Market forces. Goods and services are distributed according to ‘the invisible hand of the market’ – in other words, the allocation of goods is determined by market forces. For example, if demand rises, firms have an incentive to increase supply.
- Flexible labour markets – easy to hire and fire workers.
- Free trade. Low tariff barriers to encourage international trade.
Friedman on Capitalism
“There is one and only one social responsibility of business – to use it resources and engage in activities designed to increase its profits so long as it stays within the rules of the game, which is to say, engages in open and free competition without deception or fraud”
― Milton Friedman, Capitalism and Freedom (1962)
Examples of capitalist economies
According to this rank of countries by ‘economic freedom’. The US is ranked 12th. The UK ranked 13th. Source: Global Finance
- Hong Kong
- Singapore
- New Zealand
- Australia
- Canada
In the real world, many economies which are viewed to have a capitalist economic system may have government spending taking up to 35% of GDP. This is because the government pays for welfare, health, education and national defence. However, the economy is still viewed as capitalist because in the area of private enterprise, firms are free to decide what to produce and for whom.
Economists who advocate capitalism
- Friedrich Hayek – The Road to Serfdom (1944)
- Milton Friedman – Capitalism and Freedom (1962)
- Adam Smith – The Wealth of Nations (1776)
Alternatives to capitalism
A capitalist economic system is often contrasted to a socialist or communist economic system where economic decisions are made centrally by government agencies. In a communist economy, the means of production are owned collectively and the government has more say in what to produce, how to produce and how to distribute resources.
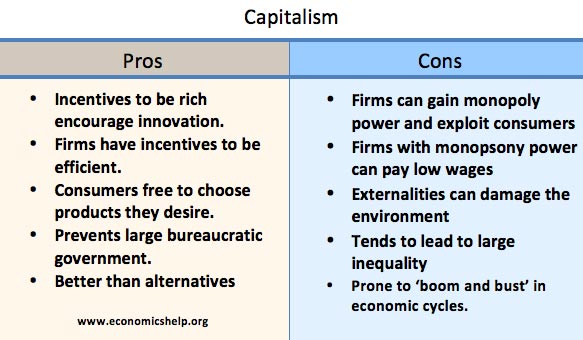
Advantage and disadvantages of capitalism
Advantages of a capitalist economic system
- More efficient
- Less bureaucratic
- More innovation
- Discourages discrimination and forces people to trade with each other – breaking down barriers.
Problems of a capitalist economic system
- Inequality. Capitalist economic systems invariably lead to inequalities of wealth and income. However, it is argued that this inequality provides an incentive for wealth generation and economic growth.
- Monopoly. In a capitalist society, firms could gain monopoly power over consumers and workers.
- Environmental problems. A capitalist society driven by the profit motive may take decisions to maximise economic income in the short term but at a cost of environmental problems in the long-term.
Different types of Capitalism
- Turbo-capitalism – free-market capitalism with little government regulation
- Responsible capitalism – Free markets but also a social welfare net. More reflective of European economies with private markets, but strong government intervention
Related