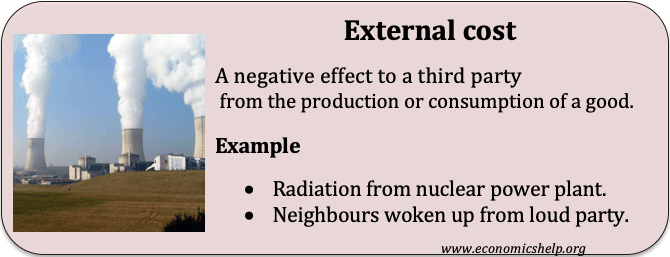
External costs
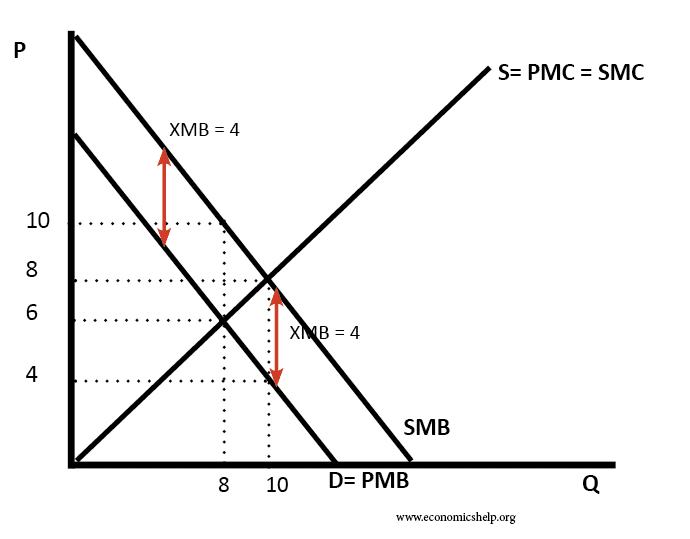
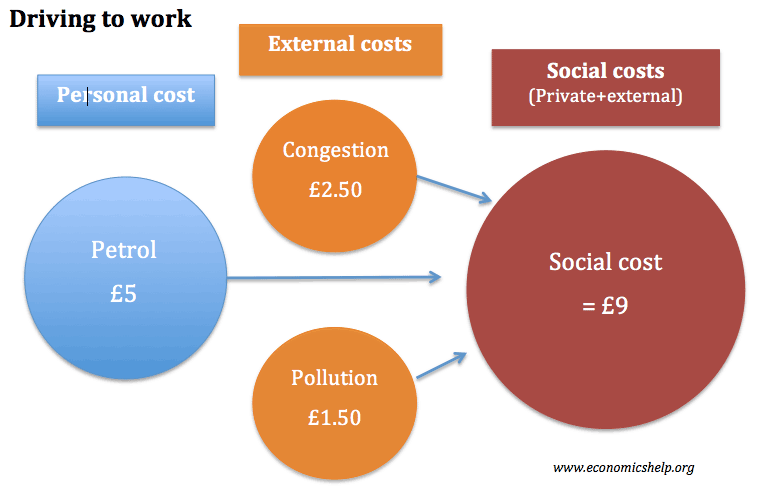
Definition of External costs An external cost occurs when producing or consuming a good or service imposes a cost (negative effect) upon a third party. If there are external costs in consuming a good (negative externalities), the social costs will be greater than the private cost. The existence of external costs can lead to market …