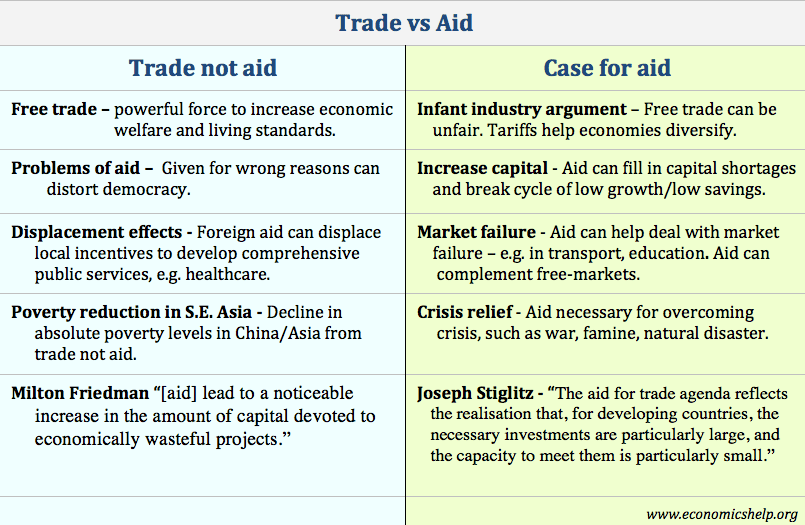
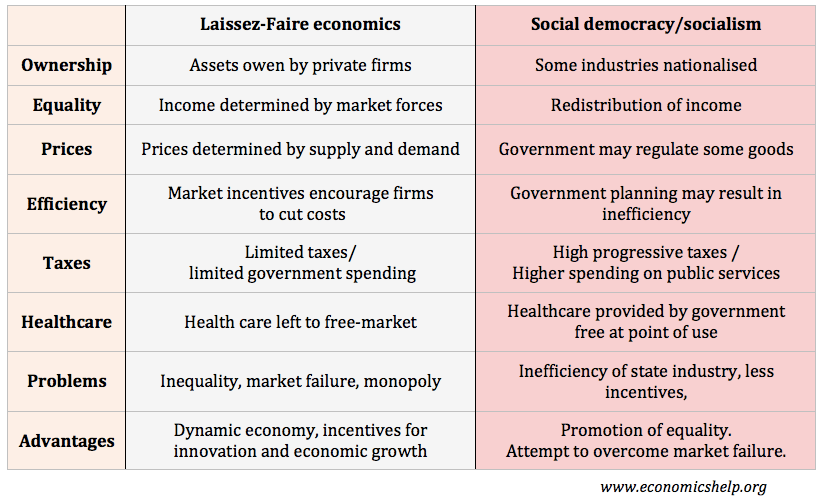
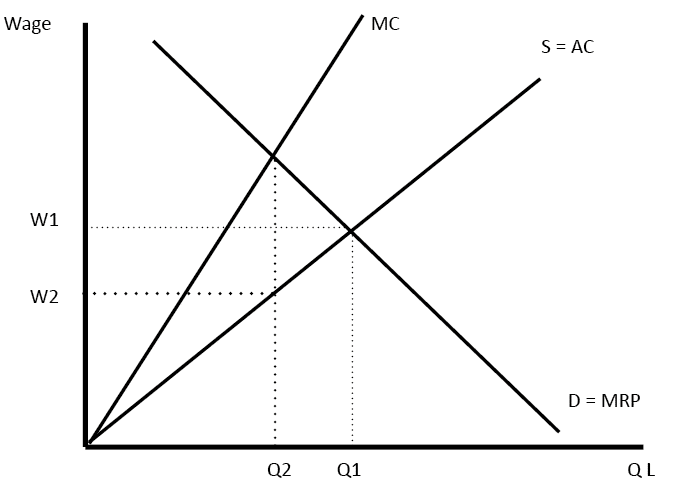
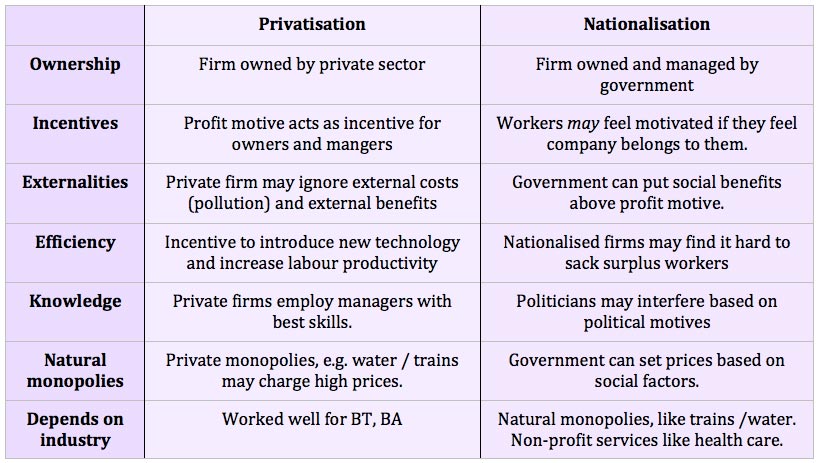
Trade not Aid
Definition of ‘Trade not aid’ This is the economic idea that the best way to promote economic development is through promoting free trade and not providing direct foreign aid. Logic of ‘Trade not Aid’ A culture of dependency. Foreign aid to developing economies is invariably wasteful and can create a culture of dependency. Also, recipients of …