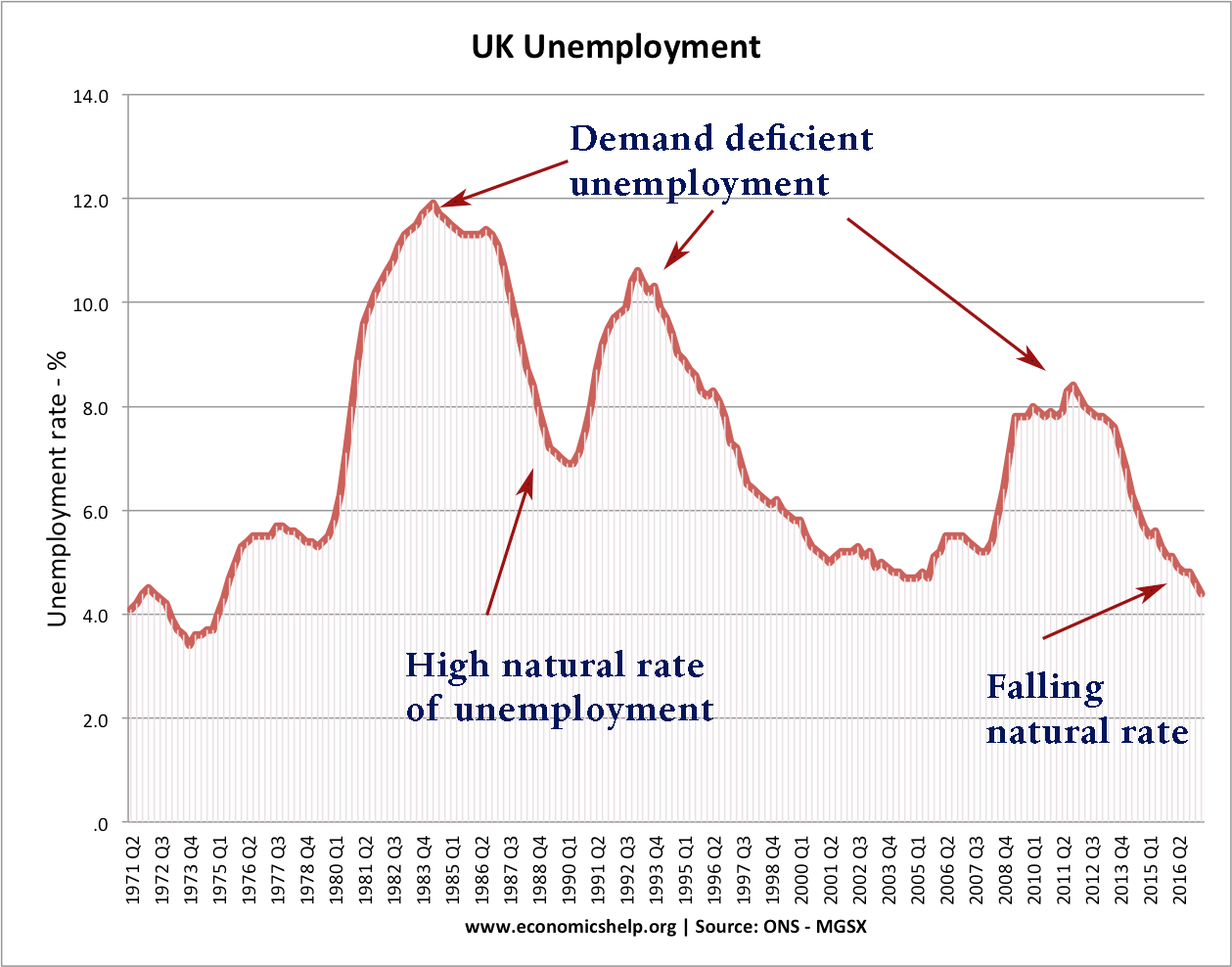
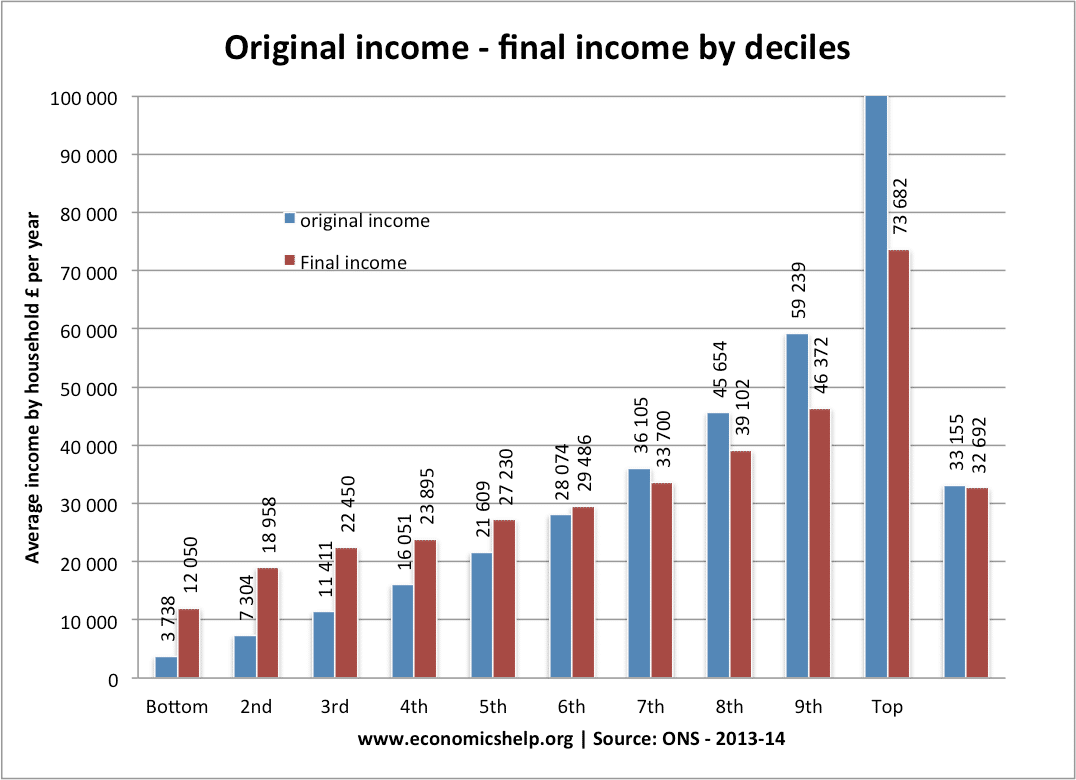
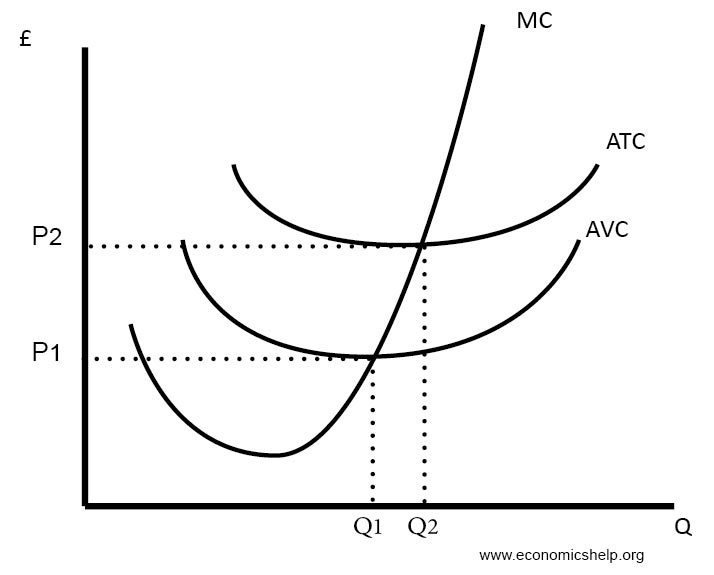
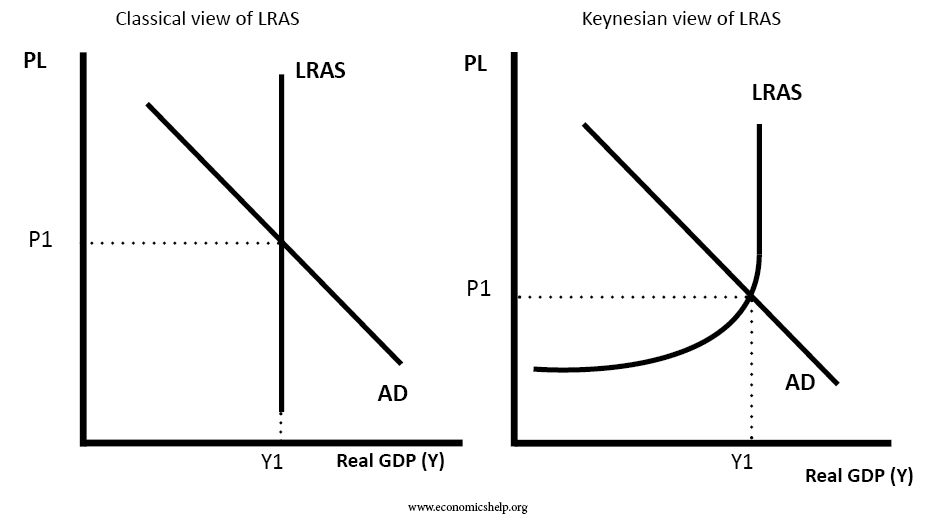
Labour Markets
Basics of Labour Markets Demand for Labour Supply of Labour Wage Determination Marginal revenue product of labour Labour market imperfections Monopsony diagram Labour Market Imperfections Monopsony Trades unions Geographical immobiliities Discrimination in the labour market Government intervention in labour markets Minimum wages Minimum wages Minimum Wages for 16-18 year olds Disadvantages of minimum wages Would …