A Carbon tax is a specific tax on the consumption of goods which cause carbon dioxide emissions. C02 emissions have been identified as a major source of global warming and therefore, governments have been keen to reduce carbon emissions.
Advantages of Carbon Taxes
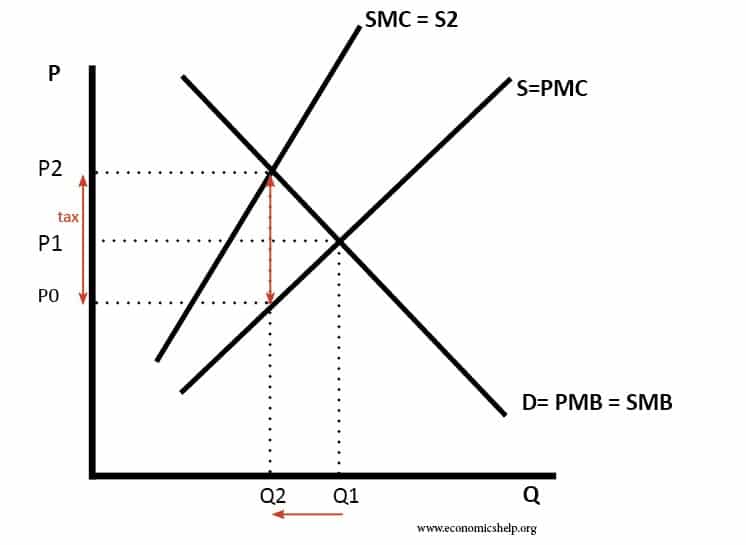
The market price is P1 – but this ignores the external cost of pollution. A carbon tax of P2-P0 would raise the price to P2 and cause a more socially efficient level of output.
- Carbon taxes have been suggested as a way to internalise the negative externality of carbon emissions. This means that consumers/producers will pay the full social cost of consumption. For example, the private cost of an aeroplane may be £400. However, the external cost of pollution from that air flight might be estimated at £120. Therefore, the carbon tax would add £120 onto the flight, and the final price would be £520. This would discourage some from flying – leading to a reduction in air-travel and a reduction in pollution. If people pay the full social cost – it will lead to a more socially efficient level of consumption.
- Carbon taxes provide an incentive for firms to use and develop more environmentally friendly production processes. If we tax carbon emissions, then it may change the balance and make solar power relatively more competitive than burning fossil fuels like carbon. This will encourage investment in renewable energy and lead to further technological developments. In recent years, investment and new technology have made solar energy more effective and efficient. A carbon tax can accelerate this switch to renewable energy which has lower pollution costs.
- They can also raise money to be spent on environmental initiatives. The revenue raised from a carbon tax can be used to fund investment in alternatives. For example, the government can subsidies more environmentally friendly public transport.
Problems with Carbon Taxes
- It can be difficult to measure how much carbon is produced, and therefore difficult to know what level of carbon tax to charge.
- It is difficult to know the true cost of carbon emissions on the environment and future generations.
- Carbon taxes can cause the possibility of tax evasion. For example, firms try to mask the true level of pollution. Alternatively, we could outsource production to countries with less stringent tax systems – in effect exporting pollution to poorer countries. Carbon taxes may need global agreements.
- Discourage investment. An argument made by business is that carbon taxes will discourage investment and reduce profitability.
- Countries may free ride on others making efforts to reduce carbon emissions and reduce the impact of global warming. For example, under President Trump, the US left the Paris agreement on global warming.
Related