Readers Question: When considering national economic policy government must accept that there is a trade-off between inflation and unemployment. Discuss.
National Economic Policy will be concerned with these main macro economic objectives
- Sustained and sustainable economic growth
- Low Unemployment
- Low inflation (inflation target often 2%)
- Low current account deficit (satisfactory balance of payments)
- Stable Exchange Rate
- Low government borrowing
To achieve these macroeconomic objectives, the government will use a variety of policy tools including
- Fiscal Policy – government spending and taxation rates to influence aggregate demand
- Monetary policy – Using interest rates and controlling the supply of money to influence demand for money
- Supply side policies – government attempts to increase efficiency and productivity in the economy.
- Exchange rate policy – influencing the exchange rate to influence a countries competitiveness
To achieve low unemployment, the government can try boost aggregate demand in the economy. They can do this through expansionary fiscal and expansionary monetary policy. For example, cutting taxes and cutting interest rates. This can cause higher economic growth. However, higher economic growth may cause an increase in inflation.
Therefore, there can be a conflict between these two different macroeconomic objectives.
Evaluation
However, it is possible to achieve all the main macroeconomic objectives, in some circumstances. For example
Depends on the situation of the economy. If the economy is in a recession, increasing aggregate demand will not be inflationary because there is so much spare capacity in the economy. Therefore, in some cases, attempts to reduce demand deficient unemployment will not cause inflation.
However, in the future, the current policy of quantitative easing (increasing the money supply) could well reduce demand deficient unemployment but cause inflation.
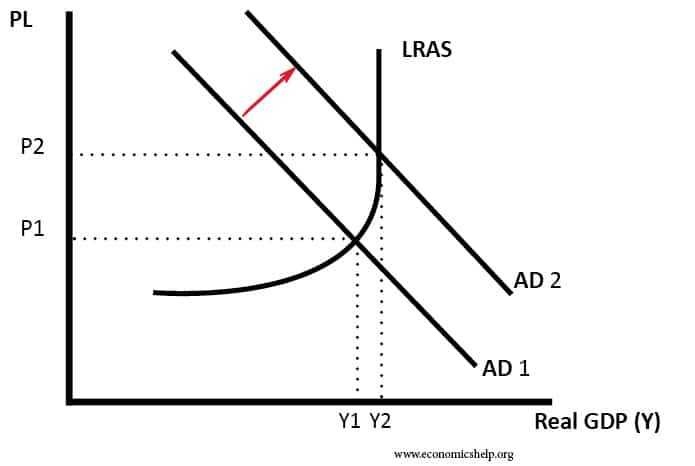
Depends How Much You increase Aggregate Demand. If the economy is in a recession and the government use demand-side policies to boost growth. Inflation is likely to occur if economic growth exceeds the long run trend rate – if aggregate demand increases faster than aggregate supply.
However, if aggregate demand increases at the same rate as AS (in the UK this tends to be 2.5% a year), then inflation shouldn’t be a problem.
Natural Rate of Unemployment It depends how the government seeks to reduce unemployment. If you can reduce the natural rate of unemployment (frictional and structural unemployment), then these policies will not be inflationary. Inflation is a threat when using demand-side policies. Therefore, national economic policy should involve both demand-side and supply-side policies.
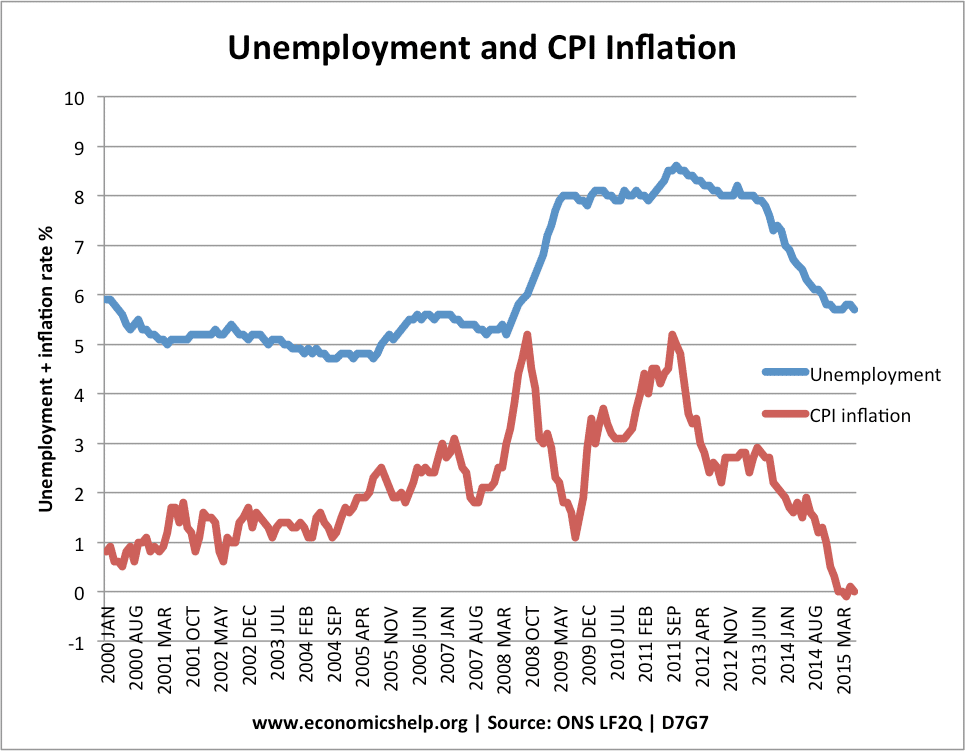
From 1994-2007, the government reduced unemployment without causing inflation.
See Previous Essays