What factors enable a firm to grow in size?
- Internal expansion When a firm increases size through increasing production and sales.
- External expansion – When the firm grows through a merger with another firm.
Internal expansion can involve
- Cutting price to increase sales and gain more market share. This may make the firm less profitable in the short-term but it can increase the size of the firm. A shift from profit maximisation to sales maximisation can be aimed at increasing the size of the firm.
- Using profits for investment. If the firm is in a profitable industry, then it gains the revenue and confidence to expand production. Investment enables the firm to provide more of the good or service. For a coffee chain, the quickest way to grow is to open more establishments in new cities and locations.
- Borrowing to fund investment. If a firm does not have surplus profit and savings, it can borrow from banks to fund investment in increasing capacity.
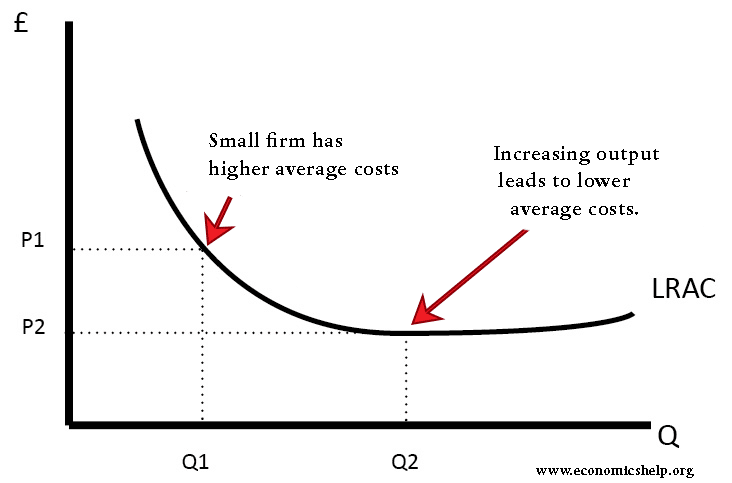
- Economies of scale. As a firm grows it can create a positive feedback loop. As it expands it gets lower average costs and greater efficiency. This enables it to undercut rivals and gain more market share. Economies of scale are important for industries with high fixed costs – such as car manufacture or supermarkets. It is difficult to survive as a small car firm. Therefore, there is an incentive to grow and gain economies of scale or go out of business.
- Reaching into new markets – e.g. overseas markets. For many niche product firms, once a national market is saturated, expanding overseas is an effective way to continue to grow sales
- Product diversification – introducing new models and types of service. For IT firms, it is easy to reach the end of a product life-cycle. CDs, tape players are all no longer in demand. Therefore, firms need to keep introducing new technology which enables them to develop new product lines. Firms can also try and be innovative and develop new types of products and services. For example, firms are finding that offering greater product customisation is a good way to attract new demand. 3D printing and online purchase gives firms the opportunity to develop a greater range of products, which can appeal to particular preferences of consumers.
- Non-price competition A firm can grow through methods of non-price competition. This can involve advertising campaigns, loyalty cards and better after sales service.
- Offering free/subsidised services. A firm like Amazon has concentrated on shifting consumer habits to make shopping at Amazon an instinctive purpose. For example, Amazon Prime (free next day delivery) has been heavily encouraged with a cheap price and free tv services. Once customers have an Amazon Prime account, it creates a strong basis for long-term growth as they have a captive market base.
Barriers to growth of firms
- Some firms may have a unique niche. e.g. expensive clothing labels may lose their aura of ‘exclusivity’ if they grow.
- Growing the firm may require issuing shares and listing the firm on the stock market. This means that the original founder has a greater danger of losing control and being more answerable to shareholders who want short-term profitability.
- Lack of focus if there is too much diversification.
- It becomes harder to retain high standards of service if the firm grows. The original founder has to do more delegation; it depends whether he can find good people to delegate to.
- It depends on the industry. Cafes do not share same economies of scale as airline industry
- Competition regulation. The government may block mergers which gain more than 25% market share. Some firms may even be forced to de-merge if they abuse their dominant market position.
Related
