Productivity is the output per input in a period of time
- Labour productivity measures the output per worker in a period of time.
- If productivity rises, firms can produce more with the same number of workers. This enables
- Higher wages for workers
- Increased output for the economy
- A reduction in costs. A firm can produce the same quantity with fewer workers, leading to lower average costs. This can lead to lower prices or at least keep prices low.
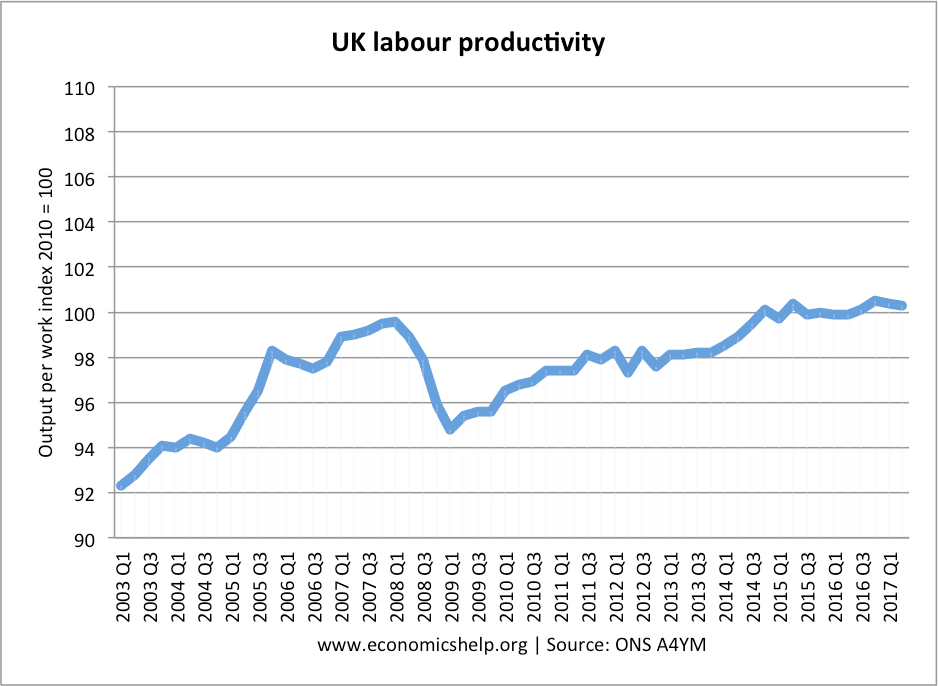
Labour productivity in the UK. From 2003 Q1 to 2008 Q1 the index of labour productivity rose from 92 to just under 100. A rise of 8.6%.
Evaluation of labour productivity
- Increasing productivity is only part of the equation. There must be demand for the product.
- Increasing labour productivity might require expensive investment in capital. The cost savings from higher productivity need to be higher than the capital investment.
- If real wages rise, it becomes more important to increase labour productivity.
- If wages are low and capital is expensive, firms may place less emphasis on labour productivity and choose more labour intensive methods of production
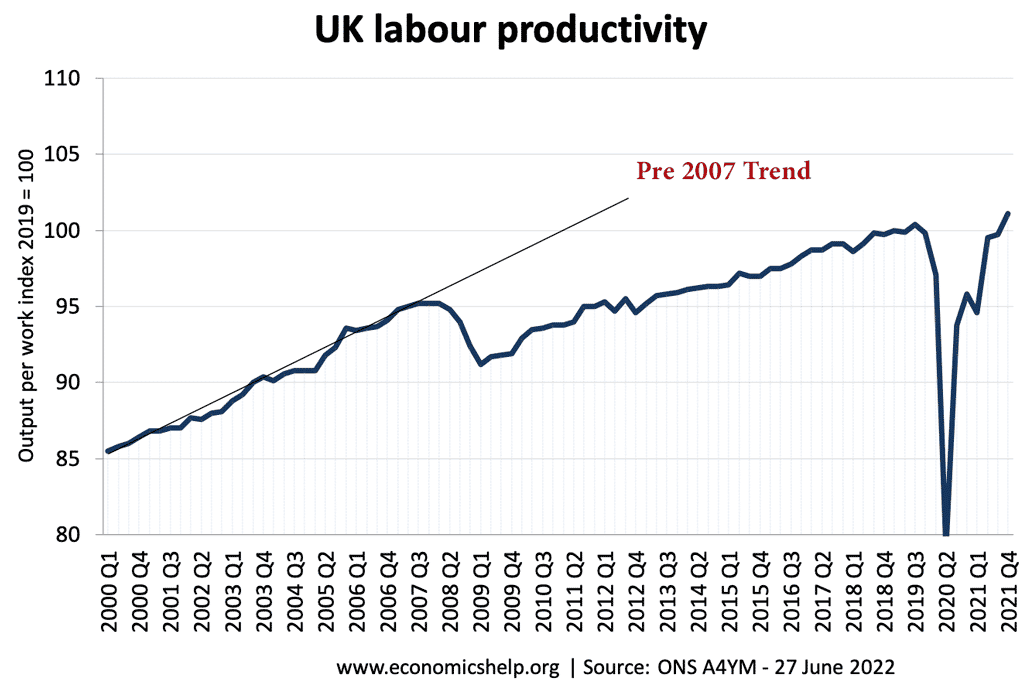
Labour productivity and trend rate
Related
