A third party is an individual or entity involved in a transaction but not one of the main principle actors.
In business, a third party could be an outside company who helps to complete a business transaction. For example, if a firm gets an order to produce manufactured goods, it may outsource part of the production process to an outside company.
If a bank gives a loan to a consumer. If the consumer fails to repay on time, the bank may outsource the recollection of the loan to a third party.
Third party and externalities
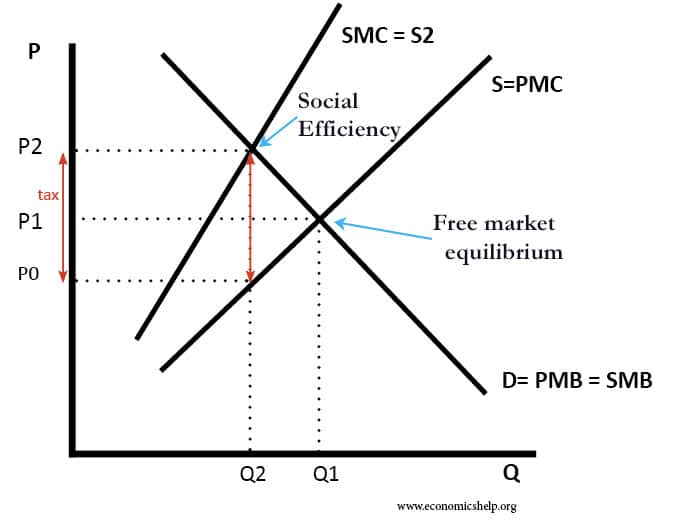
Social cost is higher than private cost because of the externality affecting a third party.
- A third party could be someone affected by pollution from a factory. In this case, the third party may never have wished to be involved but is forced to encounter the externality of the production.
- If an individual plays loud music. he may enjoy the music, but a neighbour (in this case a third party) may not enjoy to the neighbour they see as a negative externality.
- If a family decides not to get vaccinated then they are at greater risk of catching infectious diseases but also it causes an increased risk to the rest of society (third parties)
- Third parties can also benefit if it is a positive externality. If an individual gains education, then it can increase the overall knowledge of the economy and third parties benefit.
Related
