In economics, utility refers to the amount of satisfaction that a consumer gains from a particular good or service.
- Total utility refers to the complete amount of satisfaction gained.
- Marginal utility refers to the satisfaction gained from an extra unit consumed.
- If the marginal utility of the last item is positive – then total utility will be increasing
- If the marginal utility of the last consumption is negative – total utility will be falling
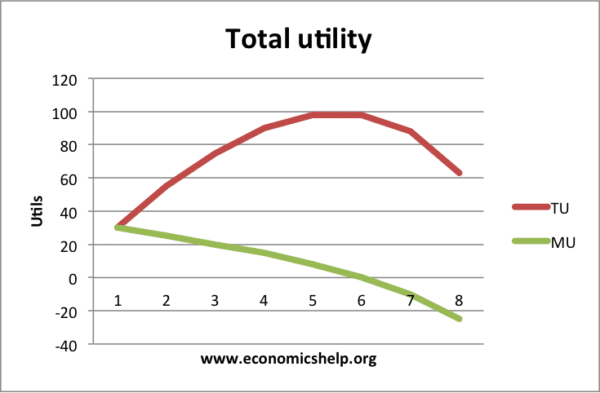
Example of Marginal and Total Utility for Icecream consumption
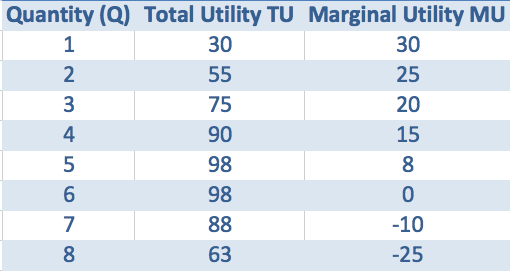
- Total utility starts to fall when marginal utility is negative
This shows the law of diminishing marginal utility of consumption. If you eat too many ice-creams, you start to get negative utilty and the total satisfaction starts to decline
Consumption decisions
The decision of how much to consume also depends on the marginal cost of production.
Related