Definition of Positive Externality: This occurs when the consumption or production of a good causes a benefit to a third party. For example:
- When you consume education you get a private benefit. But there are also benefits to the rest of society. E.g you are able to educate other people and therefore they benefit as a result of your education. (positive consumption externality)
- A farmer who grows apple trees provides a benefit to a beekeeper. The beekeeper gets a good source of nectar to help make more honey. (positive production externality)
- If you walk to work, it will reduce congestion and pollution; this will benefit everyone else in the city.
Social Benefit
- With positive externalities, the benefit to society is greater than your personal benefit.
- Therefore with a positive externality the Social Benefit > Private Benefit
- Remember Social Benefit = private benefit + external benefit.
Diagram of Positive Externality (consumption)
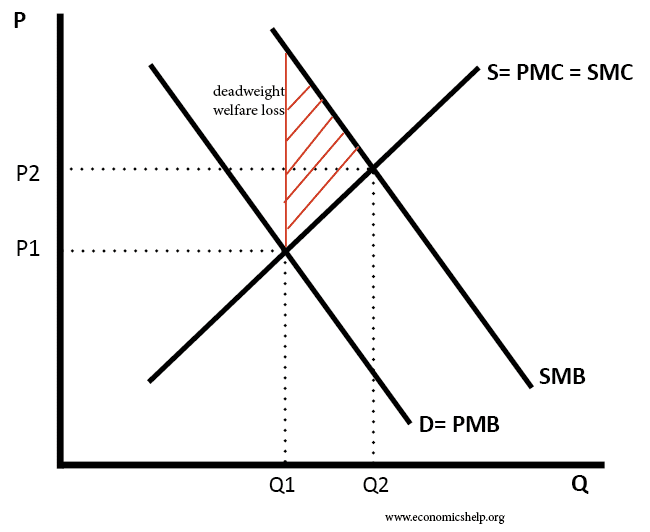
- In this case, the social marginal benefit of consumption is greater than the private marginal benefit. For example, if you take a train, it reduces congestion for other travellers.
- In a free market, consumption will be at Q1 because demand = supply (private benefit = private cost )
- However, this is socially inefficient because at Q1, social marginal cost < social marginal benefit. Therefore there is under-consumption of the positive externality.
- Social efficiency would occur at Q2 where social cost = social benefit
For example, in a free market without government intervention, there would be an under-consumption of education and public transport.
Examples of positive externalities (consumption)
- Good architecture. Choosing a beautiful design for a building will give benefits to everybody in society.
- Buying flowers for front garden gives benefits to others who walk past
- Consuming a healthy diet ultimately will benefit others in society because less health care costs, higher productivity
- Education or learning new skills. With better education, you are more productive and can gain more skills. But, also the rest of society benefits from your new skills.
Positive externality (production)
- This occurs when a third party benefits from the production of a good. For example, building a train station may provide shelter for the homeless when it is raining.
- If a company develops new technology, such as a database programme, this new technology can be implemented by other firms who will gain a similar boost to productivity.
- Tim Berners Lee who developed the World Wide Web, made it freely available, creating a very large positive externality.
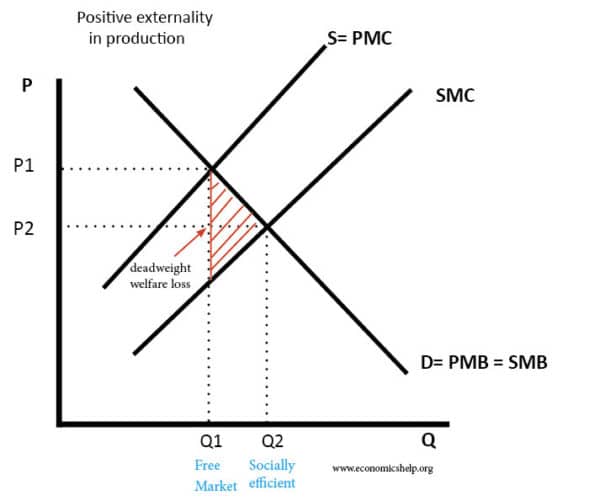
Diagram of positive externality in production
- Because there are positive externalities in production, the social marginal cost of production is less than the private marginal cost of production.
- In a free market, a firm will ignore benefits to third parties and will produce at Q1 (free market outcome)
- However, the socially efficient level will be at Q2 (where social marginal cost = social marginal benefit)
More examples of positive externalities
- Getting a vaccination provides a benefit to other people in society because you do not spread infectious diseases.
- A decision to stop smoking causes benefits to other people in society who longer suffer passive smoking.
- Switching from conventional farming to organic farming helps the environment as there are fewer chemicals in the environment.
- Picking up litter makes the environment nicer for everyone.
Dealing with positive externalities
Positive externalities lead to under-consumption and market failure. Government policies to increase demand for goods with positive externalities include
- Rules and regulations – minimum school leaving age
- Increasing supply – the government building of council housing to increase the stock of good quality housing.
- Subsidy to reduce price and encourage consumption, e.g. government subsidy for rural train services.
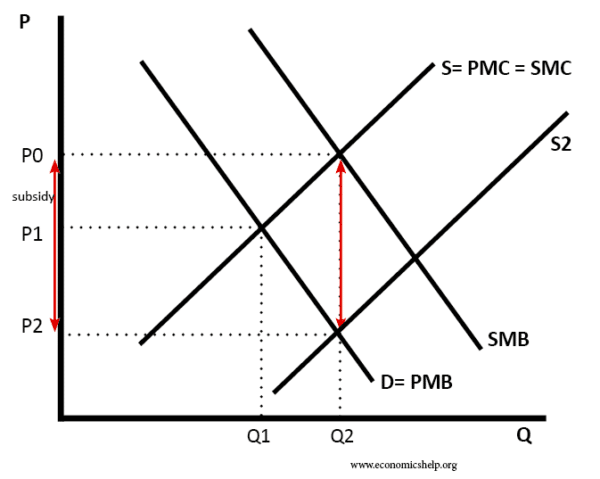
Diagram to show the effect of subsidy on good with positive externalities
A subsidy of P0-P2 shifts supply curve to the right (S2) and the new quantity demand will be Q2 (where SMB=SMC)
In this case, the subsidy has overcome the market failure. Though government intervention itself could be subject to government failure.
- More detail at: Subsidy on positive externality
Which diagram to draw?
Either (production or consumption externality) is acceptable to show the principle of positive externalities. Generally, I advise using the positive externalities of consumption. To simply economics for some students (who often get confused by these diagrams), I will only teach one positive externality diagram. (consumption)
Extra How to define externalities?
A reader asks the question if a farmer switches from conventional to organic farming is this really a positive externality?
“Conventional and organic farming both have negative externalities. One has less than the other, but switching doesn’t mean a positive externality, it just means a reduction or even mitigation of a negative externality. In the same way driving an electric car is not a positive externality.”
Related
- Positive externalities in the housing market – examples of positive externalities in the housing market, such as improved local communities, improved public health and better environmental standards.
- Subsidy on positive externality
- Negative externality
- Should we pay to see the doctor?
Last updated: 10th July 2019, Tejvan Pettinger, www.economicshelp.org, Oxford, UK

1 thought on “Positive Externalities”
Comments are closed.