Factors of Production – definition and explanation
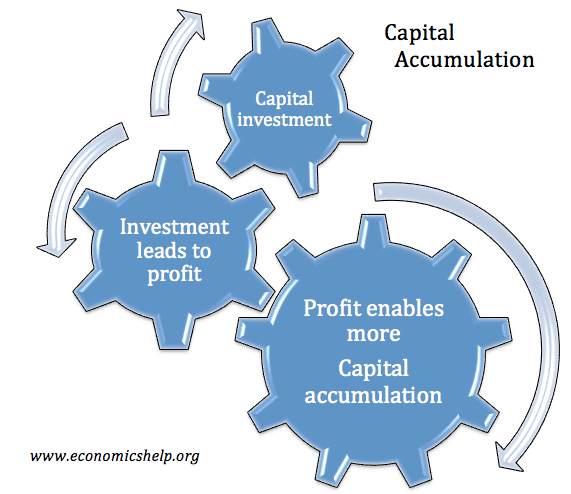
Factors of production refer to the different elements that are used in producing goods and services. Factors of production are inputs into the productive process. The four main factors of production are: Land – this is raw materials available from mining, fishing, agriculture Capital – This is a manufactured item used to aid production, for …