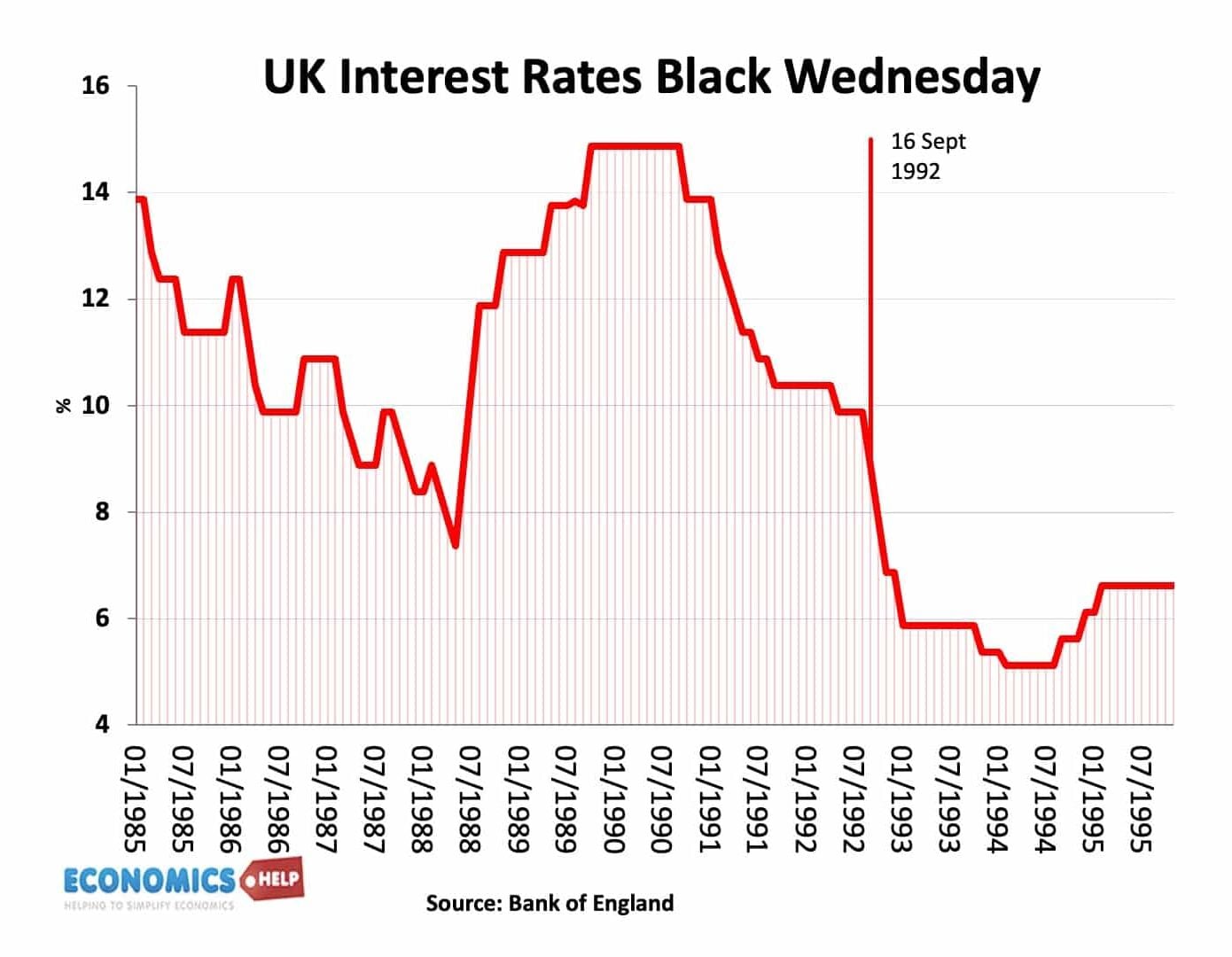
Bill of exchange
Definition for bill of exchange: A bill of exchange is a short dated security used to finance foreign trade. It can be cashed at any time by the supplier Examples – bills of exchange In the Commonwealth almost all jurisdictions have codified the law relating to negotiable instruments in a Bills of Exchange Act, e.g. …