Subsidies for positive externalities
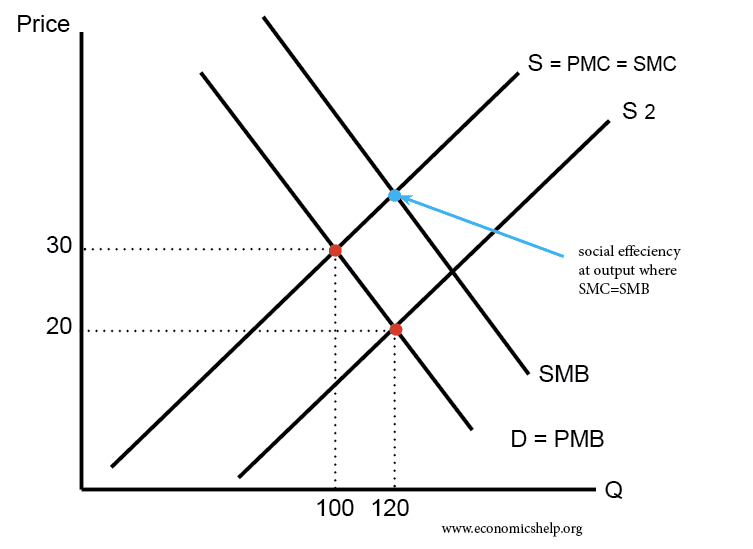
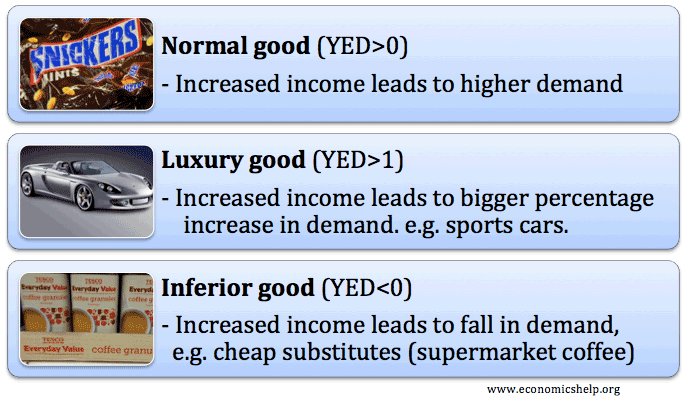
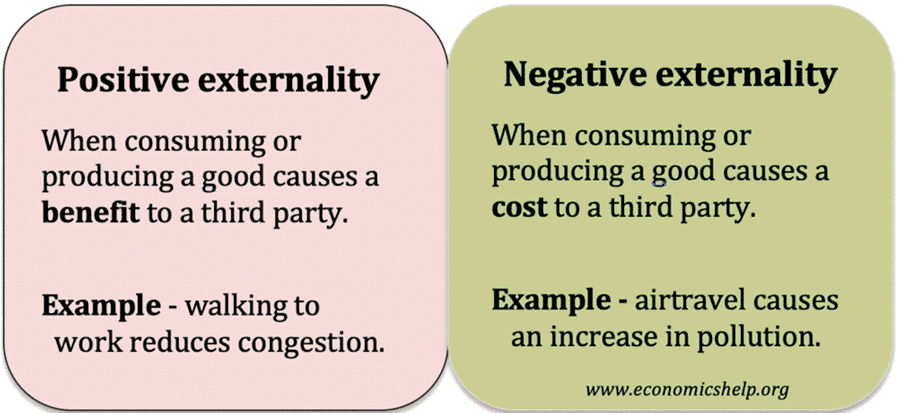
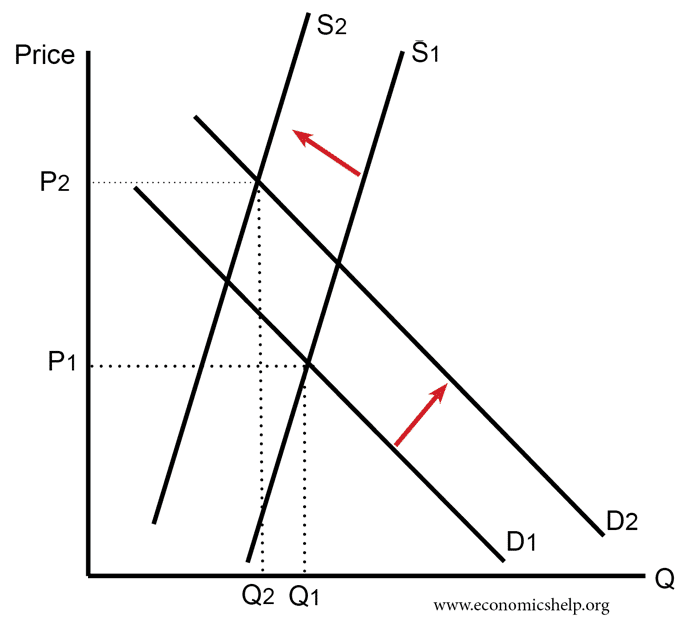
Subsidies involve the government paying part of the cost to the firm; this reduces the price of the good and should encourage more consumption. A subsidy shifts the supply curve to the right and can be justified for goods which offer benefits to the rest of society. What is the justification for subsidising goods with …