Economic goods – definition and examples
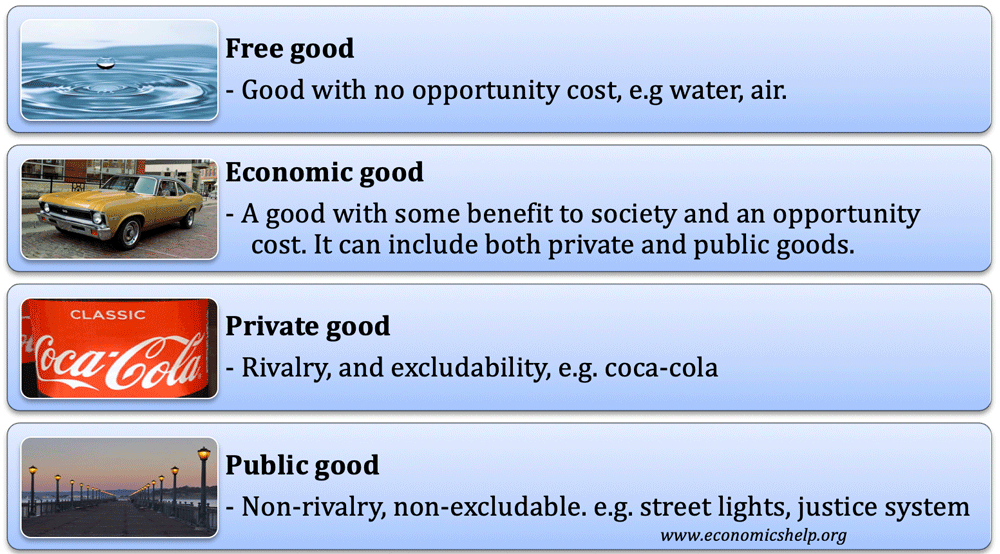
Definition An economic good is a good or service that has a benefit (utility) to society. Also, economic goods have a degree of scarcity and therefore an opportunity cost. This is in contrast to a free good (like air, sea, water) where there is no opportunity cost – but abundance. Free goods cannot be traded …