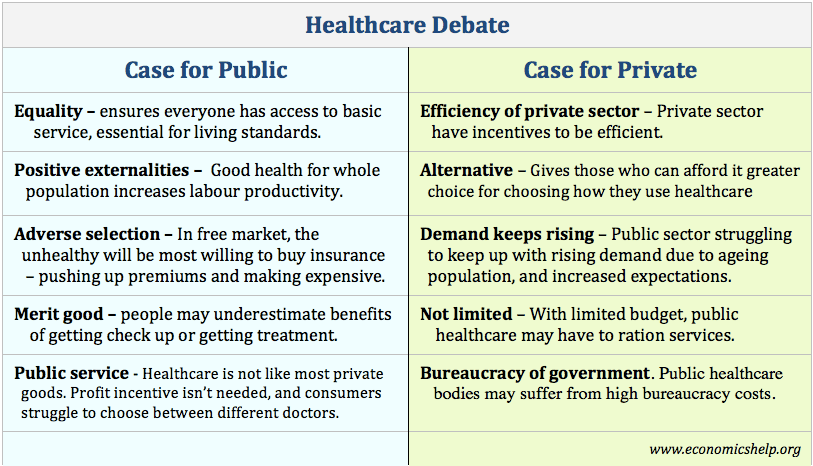
Although controversial, what are the potential advantages of privatising public services?
Firstly, privatising means outsourcing of public services to the private sector. For example, this might include
- Competitive tendering – where private companies are allowed to bid for the right to provide meals for hospitals.
- NHS outsourcing treatment to private hospitals. To deal with waiting lists, the NHS pays a private company like BUPA to treat an NHS patient.
- Encouraging more private sector health care, such as limiting the number of operations on the NHS. This effectively encourages people to pay privately for physio treatment, IV treatment.
- Last year the NHS in England spent £6.5bn on getting the private sector to see and treat patients. (6.1% of NHS budget) (2015)
Benefits of the private sector providing public services like the NHS
- Increased demands being placed on the public sector due to demographic changes. If more people went private this would enable the NHS to have shorter waiting lists.
- Provides consumers with more choice.
- When the price of treatment is zero, the demand escalates and the government struggle to meet the growing demand – which has been growing faster than inflation. If people have to pay for non-urgent treatments like physio, it will filter out less essential demand and enable the NHS to focus resources on more important treatments.
- If fewer people use the NHS it would enable the govt to lower taxes and reduce borrowing
- Private Sector has a profit incentive to cut costs and provide a more efficient service. The private sector will seek to provide a more efficient service. These incentives can be missing in a public body which doesn’t have the same profit incentive and the pressure from shareholders to cut costs and develop new ways of providing services.
- Private sector can be more innovative as it has a wider remit and willingness to try something new – which might enable better service
- Diseconomies of Scale in the NHS. Large public bodies can become bureaucratic and inefficient, leading to higher overall costs.
- An ageing population is causing demand for health care to grow much faster than the willingness to pay taxes.
- Many ‘private’ health care companies are actually non-profit making trusts which put any surplus back into healthcare treatment.
Problems of Privatising Public Services
- Private Sector may cut costs by reducing quality of service, e.g employing fewer cleaners will lead to dirtier hospitals
- May increase inequality as people on lower incomes cannot afford these rationed treatments such as physiotherapy.
- The private sector is not necessarily more efficient in providing health care. One study found that in comparisons between health care systems, publically funded healthcare systems offer lower average per capita costs – as there is a greater pressure to ration scarce resources. Source: “Comparisons of Health Care Systems in the United States, Germany and Canada” (2012) PMC
“the medical care system [in Canada] provides its residents with access to all “medically necessary hospital and physician services” at a fraction of the per capita cost of the U.S system [1]
- Health is a merit good and will be underprovided in a free market.
- Private companies have a greater willingness to raise the price of drugs and make use of their monopoly power. Private insurance also leads to moral hazard – with doctors willing to prescribe expensive drugs with little benefit because the cost is borne by private insurance companies – who in turn just increase insurance premiums.
- With regard to healthcare, choice is a limited factor as patients lack suitable information about different treatments and will have less knowledge than doctors about the best place to go. Choice can even be harmful as patients choose non-optimal medical choice.
Related