How to work out output, price and profit from monopoly equations.
Readers Question: A monopolist operates under a production technology which allows the production of any output level at a constant average cost of $5 per unit. This monopolist sells into two distinct markets the demand curves for which are: P1=55-Q1 (for market one) and Q2 = 70 – 2P2 (for market 2). If this monopolist operates so as to maximize total profit then calculate:
(i) Total output;
(ii) The quantity sold in each market;
(iii) The price charged in each market;
(iv) The monopolist’s total profit.
The Demand Curve equals the average revenue curve.
We need to find out the Marginal revenue Curve
The Marginal Revenue curve is twice as steep.
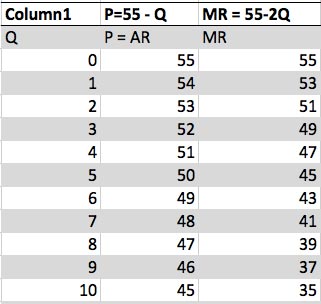
- If Q.D = 55 – P1(AR).
- P = 55 – Q
- MR = 55 -2Q1
The next step is to work out profit maximisation.
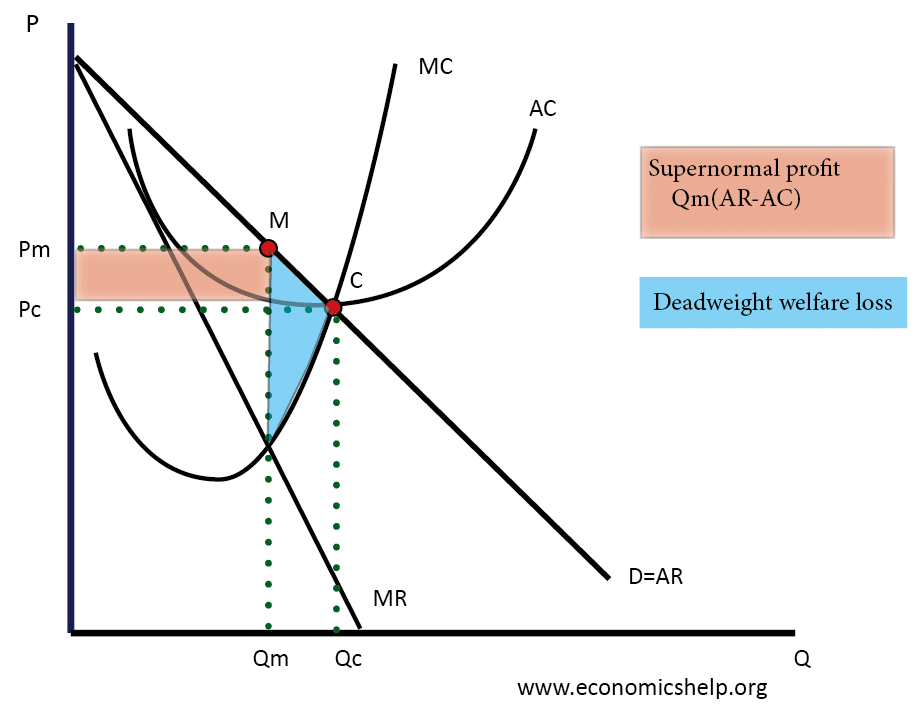
Profit Maximisation for a Monopolist
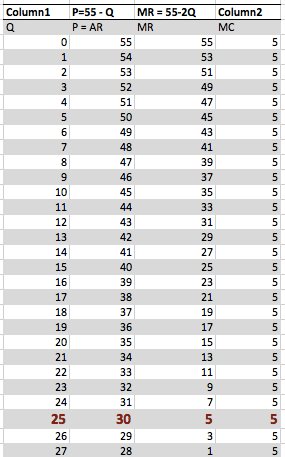
- Profit Maximisation occurs where MR=MC
- MC = $5 (a constant average cost means the MC=AC)
- MR = 55 -2Q
Therefore,
- 5 = 55 – 2Q
- 2Q = 50
- Q = 25
- P = 55 – Q
- P = 30
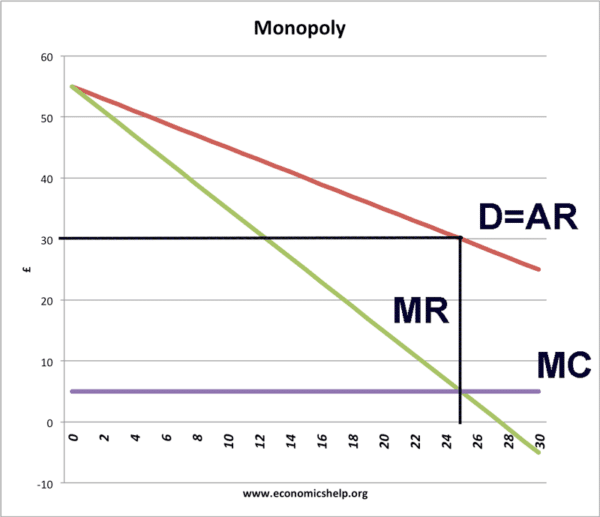
Example using diagram
Profit maximisation at Q = 25. Price = 30
To Calculate Profit for A Monopoly
Profit = Total revenue – Total Cost
Total Revenue = 25*30 = 750
Total Cost = 5 * 25 = 125
- Therefore, total profit for this section is = 625 (assuming there is no fixed cost)
Related

Thank you!
I had a similar question due tomorrow, and you’ve been a lifesaver. I was completely lost before 🙂
Hi, i have some questions to ask you about economics,
i want to know the best website talking about Economics, becuase i want to study be internet
sincerely yours,
pueng khammala ( teacher from Souphanouvong University , Luang Prabang province, Laos)
it is nice in a glance..but more clarfication is needed.
What is channel pricing?
how is MR twice steep as AR curve?
yawnnnnnnn