Perfect competition is a market structure with:
- Freedom of entry and exit
- Perfect information/knowledge
- Many firms
- The price is set by the industry supply and demand.
- Firms are price takers; this means their demand curve is perfectly elastic. If they set a higher price, nobody would buy because of perfect knowledge. Therefore firms have an elastic demand curve.
- In the long-run firms in perfect competition will make normal profits.
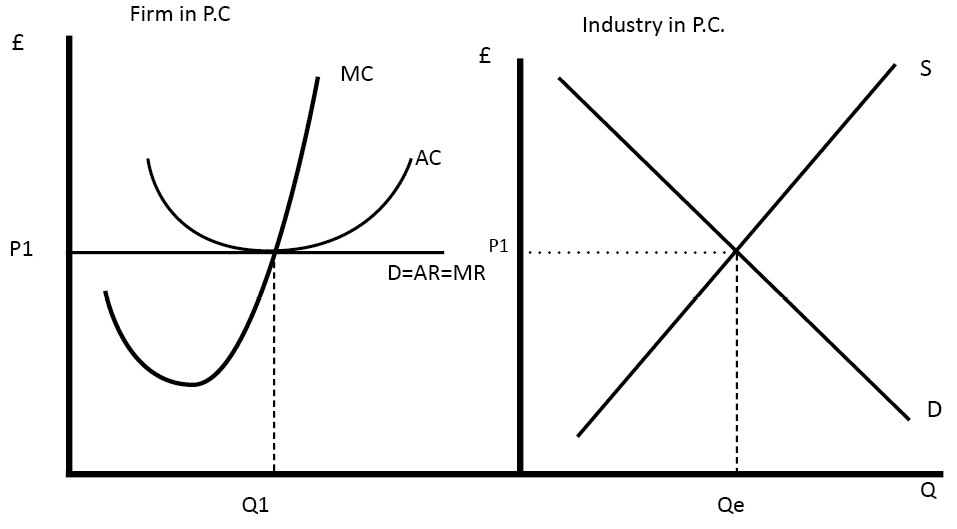
Diagram of Perfect Competition
- The market price is set by the supply and demand of the industry (diagram on right)
- This sets the market equilibrium price of P1.
- Individual firms (on the left) are price takers. Their demand curve is perfectly elastic.
- A firm maximises profit at Q1 where MC = MR
- At this price firms make normal profits – because average revenue (AR) = average cost (AC)
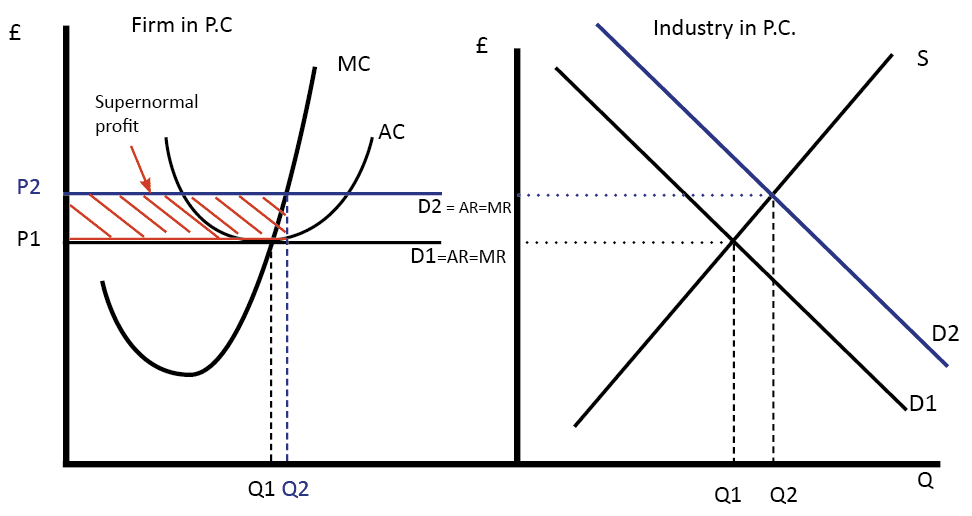
Changes in Perfect Competition equilibrium
- Market demand rises from D1 to D2 causing the price to rise from P1 to P2.
- Due to the rise in price to P2, profits are now maximised at Q2.
- A firms marginal cost (MC) curve is effectively its supply curve
- At Q2, (P, AR is greater than ATC) and therefore the firm now makes supernormal profit.
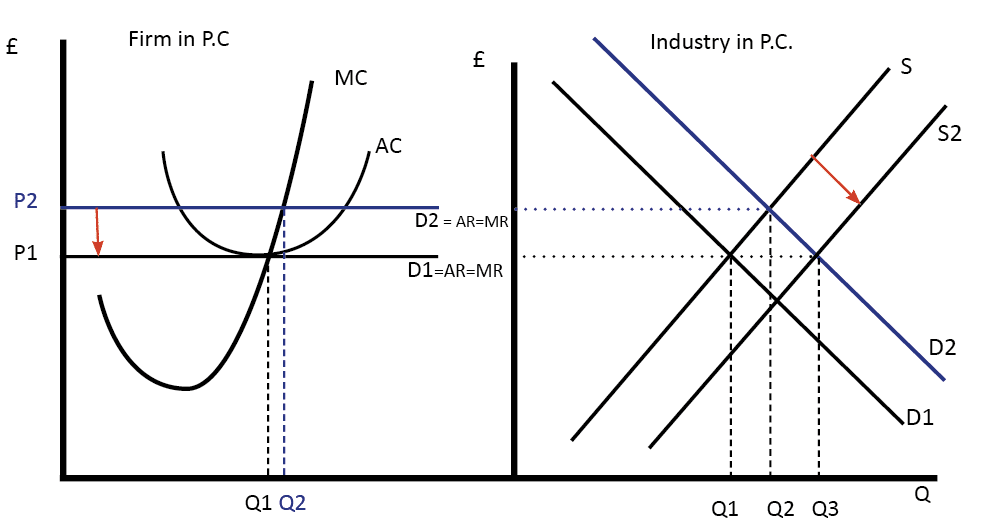
Perfect competition in the long run
- However, the supernormal profit encourages more firms to enter the market.
- New firms enter (supply increases from S1 to S2) until the price falls to P1.
- With price at P1, profits are maximised at Q1 and normal profits are made once again (AR=AC).
Effect of a fall in demand
- If there was a fall in market demand, the price would fall.
- Now firms would make a loss, and some will go out of business causing the supply curve to shift to the left.
- The supply curve will fall until price rises back to a level which gives normal profit.
Perfect competition in the real world?
Some markets are close to perfect competition, for example
- Foreign exchange markets
- Farmers market with many farmers and buying selling vegetables.
More on

I would like to be help on on how to explain and sketch the graphs
Hi Lindiwe can you please explain why the equilibrium position will not remain fixed in the Short run graph of Perfect Competition
Brief but effective, thank a lot for the post.
I have need only perfect compition in short run normal profit, super normal profit, loss super or super normal losss with daigrams and features and in real life use of perfect competition short run
does a producer in perfect market influence price
It depends
Price depand on demand if demand fell down then price rise .if price fell down then demand rise .
Yes
Thanks a lot for the diagram though it needs further explanation on MC,AC,PC and RC.
i just a material form this site and please how do i get the references to add to my work
So educative. I am learning alot from this website- economics help.
Thanks alot this really helps.
Thank you very much for your help and it’s helpful
excellent analysis of the diagrams. rarely described like this in most secondary school economics text books
Where or How do we get economic profit in firm in pc
Under Wich condition a firm can get a profit