Vertical integration occurs when two firms at different stages of production merge.
It involves going up or going down the supply chain.
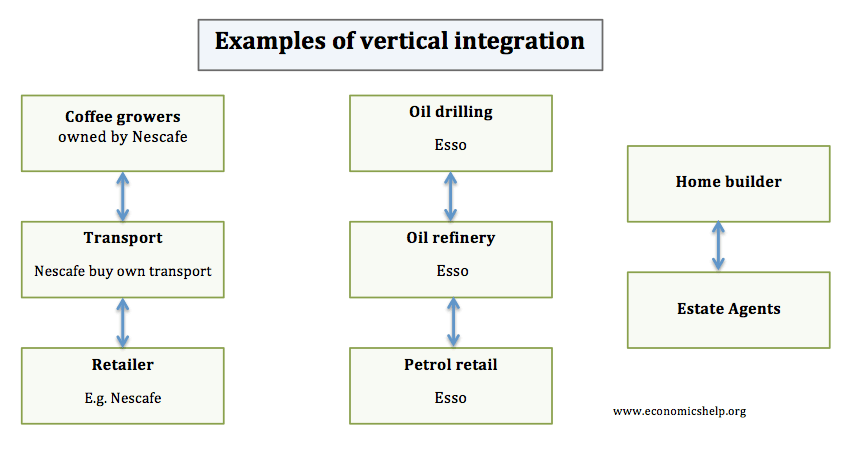
Example of vertical integration.
- Brewery merging with chain of pubs
- Software supplier merging with Computer firm
- Coffer grower merging with a coffee retailer such as Nescafe
- Car firm Renault merging with a tyre producer.
Advantages of Vertical Mergers
- Some economies of scale such as risk bearing economies, financial economies. Lower costs could lead to lower prices for consumers.
- The firm not subject to losing control of supply. e.g. they can’t be held to ransom by suppliers demanding higher price at a critical time.
- Maybe some overlap of technology and expertise. e.g. A bookshop may know what kind of books sell well so they can develop the right kind of paper and attractive design.
- Arguably the splitting up of the rail network created more confusion and less incentive to look after the track. It would make more sense for train operating companies to be responsible for the track as they would have a greater interest in maintaining it satisfactorily.
See also: Advantages of Mergers
Disadvantages of Vertical Mergers
- Vertical mergers will have fewer economies of scale because most of the production is at different stages of production. There is still scope for monopoly power.
- Also, a vertical merger can lead to monopsony power. e.g. tied pubs can charge a higher price to consumers and they have less choice of beer.
- Mergers can often create new problems of communication and coordination within the bigger more disparate firm. It can lead to diseconomies of scale where the new bigger firm is more inefficient. For example, if the new firm is quite profitable, there may be less accountability further down the supply chain.
- Discourage entry. If a supermarket owned a large share of dairy production in the UK, it could charge high prices to any new firm trying to enter the supermarket industry. Control over different stages of production becomes a barrier to entry.
- More on vertical integration