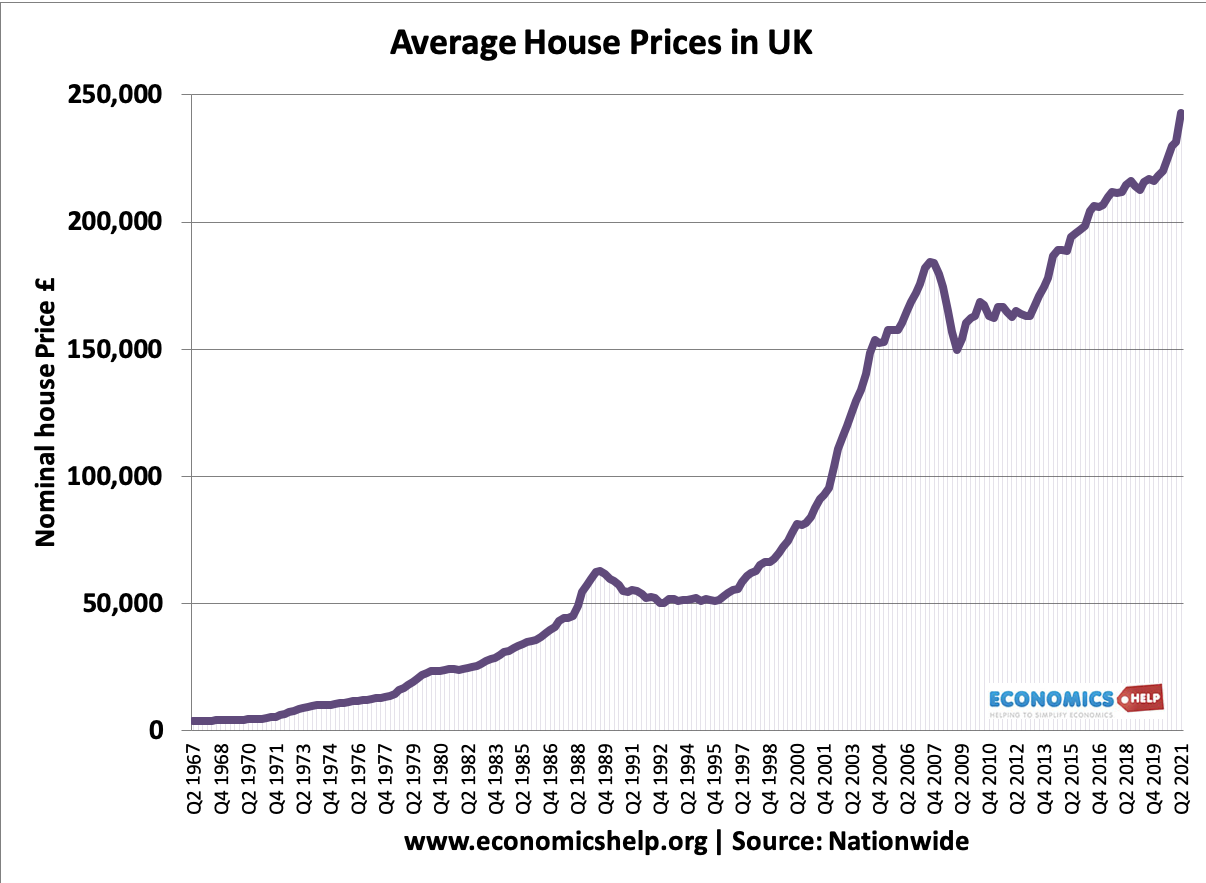
The Housing Market refers to the supply and demand for houses, usually in a particular country or region. A key element of the housing market is the average house prices and trend in house prices.
Definitions related to housing market
- UK nominal house prices – actually monetary value – not adjusted for inflation
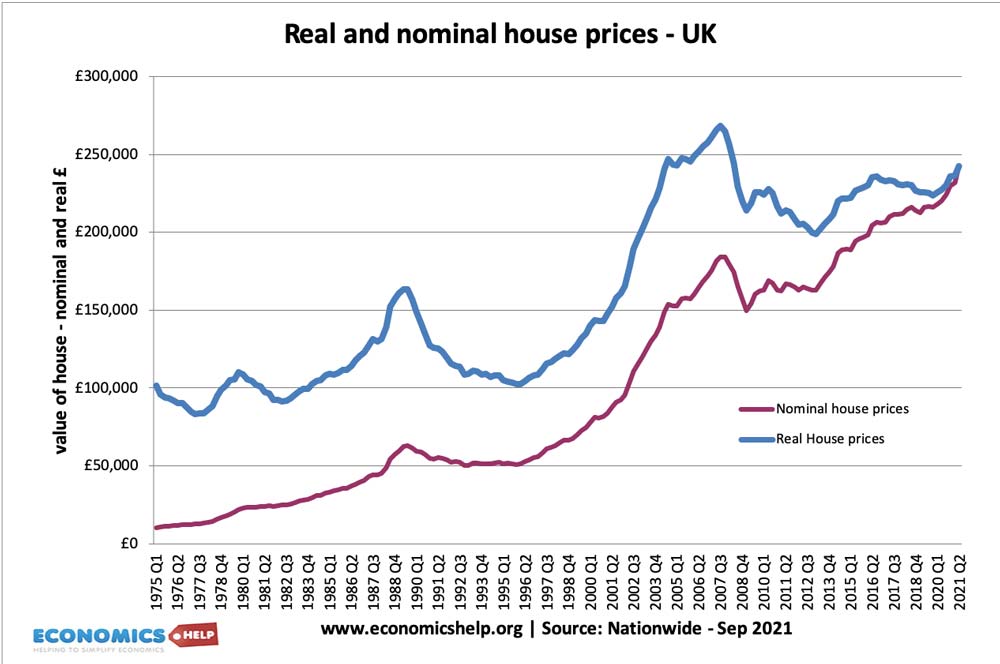
- Real house prices – house prices adjusted for inflation, e.g. if prices rise 10%, but inflation was 2%, then real house prices rose 8%
- Mortgage equity withdrawal – when homeowners re-mortgage house and take equity withdrawal.
- Affordability index – how much percentage of disposable income is needed to keep up with mortgage payments – rents.
- Buy to let – When investors buy houses with the intention of renting out the house to gain income from rent and hopefully capital gains.
- Capital gains – when investors see a rise in house prices
- Negative equity – when a homeowner has an outstanding mortgage bigger than the value of the home. If they sold their house, they would still owe money from the initial mortgage
- Real interest rates – nominal base rates – inflation rate
- Base rates – the interest rate set by the Bank of England; this base rate has a strong influence on the other interest rates in the economy. Banks will usually alter their lending rates in response to a change in the base rate.
- Fixed-rate mortgage – a mortgage where the interest rate is set for a number of years e.g. 2,5,10 years
- Variable-rate mortgage – a mortgage where the interest rate is linked to the Bank of England base rate and so mortgage payments will change with changes in the interest rate.
- Interest-only mortgage – when homeowners take out a mortgage which only involves paying the interest on the loan and not any principle on reducing the outstanding loan.
- Generation rent – the young population who cannot afford to buy, but have to rent.
Real house prices 1975 – 2015
A comparison between real house prices and nominal house prices.
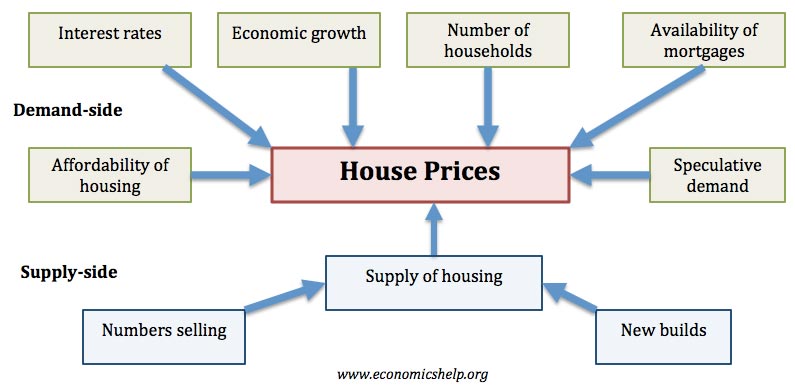
The Housing Market includes the following features
- Supply of housing – quantity of housing stock
- Demand for housing
- House prices
- Rented sector. Buy to let investment and demand from tenants
- Government intervention in the Housing market
Factors which affect the Housing Market
- Interest rates – which influence cost of variable mortgages
- State of mortgage industry – determines whether people are eligible for mortgages
- Economic growth, incomes and unemployment rates
- Population and demographic trends
Features of UK Housing Market
- The UK Housing Market is often volatile because of various factors.
- The UK Housing market has an influence on the wider economy. e.g. when house prices are falling, consumer spending tends to decrease.
- Because the housing market influences the economy and individual homeowners, it is important to try and be able to predict future movements in the housing market.
Homeownership rates
The main forms of housing tenure are
- Homeownership – either outright or through mortgage
- Private renters – renting from private landlords
- Social renters – people renting from local authorities and housing associations.
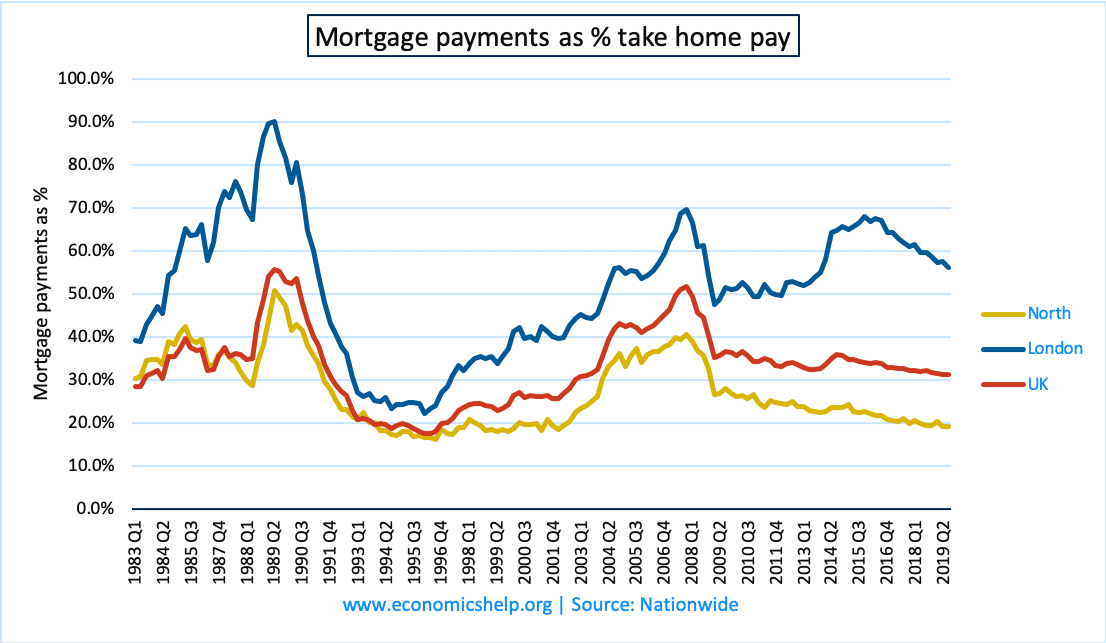
Affordability of housing
One measure of affordability is the percentage of take-home page that goes on a mortgage/ renting. This shows in the late 1990s housing affordability declined due to higher interest rates.
Related