A product market refers to a place where goods and services are bought and sold
A factor market refers to the employment of factors of production, such as labour, capital and land.
Product market
- Demand for product markets comes primarily from households
- The main sellers of goods are different kinds of firms.
- Demand for goods is a direct demand. The good is bought for its intrinsic use.
- The market facilitates the exchange of goods and services in the economy. It is based on a voluntary transaction across a wide range of places.
Product markets rely on the operation of supply and demand to determine prices
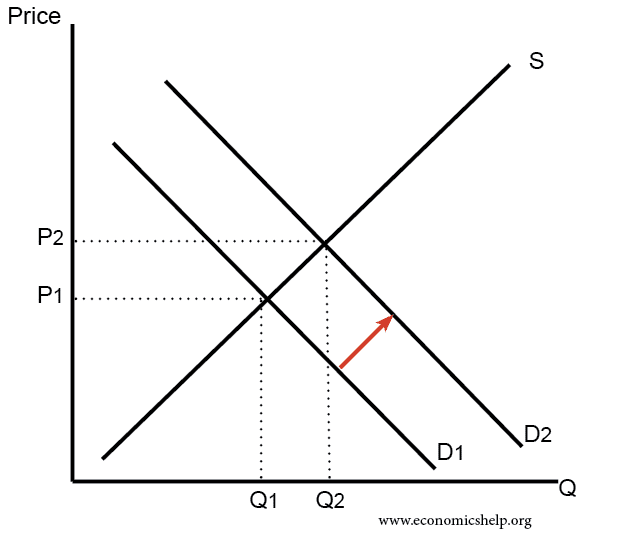
In this case, an increase in demand can lead to an increase in the price of the product.
Examples of Product markets

- Farmer’s market selling vegetables direct to the public
- Fish market
- Supermarkets selling a range of goods in a convenient place.
- Amazon.com – Offering the direct sale of goods, and marketplaces for intermediaries
- Ebay.com – Offering individuals the opportunity to sell goods.
Factor markets
The factor market is a place where factors of production (land, labour, capital) are bought and sold.
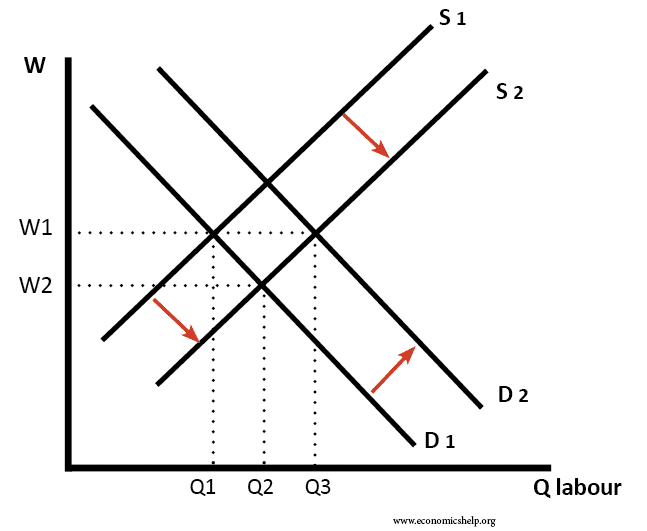
In this case, an increase in supply of labour and demand for labour leads to an increase in Q of workers and wages staying at W1.
- Demand for labour and capital is a derived demand. Firms need to employ more workers when there is greater demand for the product that they make.
- If demand for takeaway coffee rises, then Starbucks will need to employ more coffee workers (baristas)
- If there is an increase in demand for private dental treatment, there will be an increase in demand for dentists and this will push up the price of dental treatment and also the wage of dentists.
Examples of Factor Markets

- A labour exchange where firms post available jobs.
- Modern equivalents include websites/apps for job seekers.
- Commercial real estate agents, making available office space to rent
Interaction of product and factor markets
- Increase in demand for product leads to increased demand for factors of production
Example – mobile phones and lithium batteries
The rise in demand for mobile phones and other mobile devices has led to a strong rise in demand for lithium. Lithium is used in the batteries.
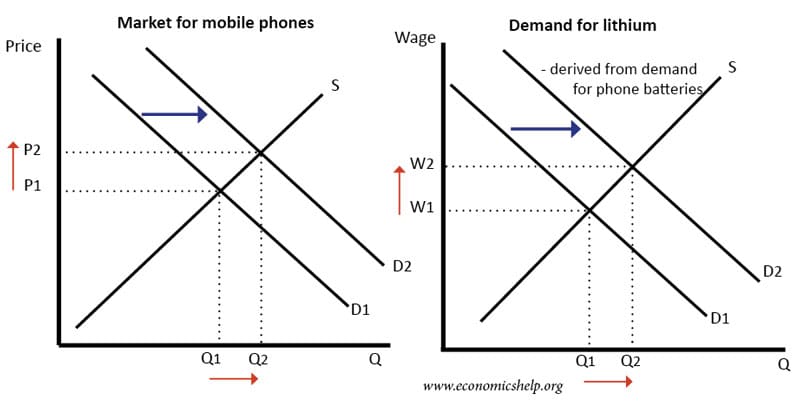
2. Increase in demand for labour (factor market) leads to increased demand for products.
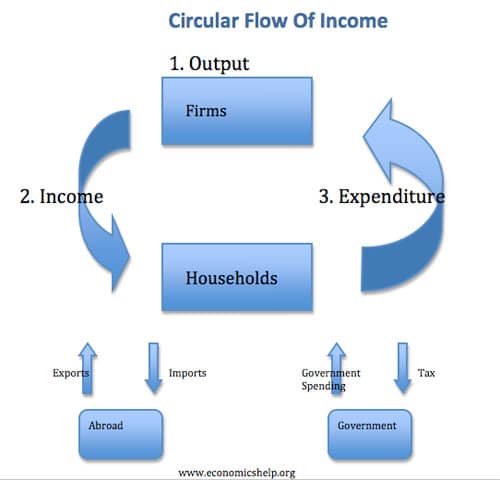
If firms employ more workers and pay higher wages then this leads to an increase in household income. This enables them to purchase more goods and services. It represents a circular flow of income.
Related
