The Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) was designed to give farmers a guaranteed income and also to guarantee food supplies. This was achieved with minimum prices and import tariffs. However, the system of target prices. led to various economic problems.
CAP
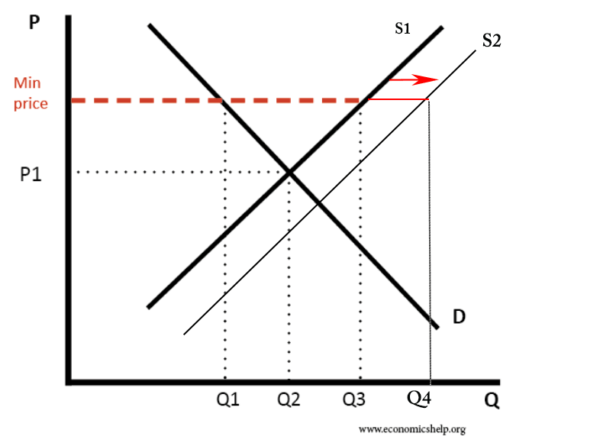 CAP led to massive oversupply (Q4-Q1)
CAP led to massive oversupply (Q4-Q1)
Problems of CAP included
- High prices for consumers
- Incentives for farmers to oversupply
- Expensive to buy food that was not used
- Over-supply encouraged excess use of fertilisers that was bad for the environment.
- Minimum prices required import tariffs on imports from abroad. This led to trade disputes and tariffs on EU exports
Reforms
Reforms have centred on solutions to the oversupply of food. This has involved.
1. Quotas.
Quotas were put on milk to reduce the problem of oversupply. However, the problem with this was that it is difficult to control the fertility of cows so the supply of milk under or overshot the quotas. This caused a lot of hardship for farmers, who had often to through milk away.
Milk quotas were due to end in 2000 but they will continue until at least 2008. However, the quota has been reduced by 2.4% and min price for milk reduced by15%
2. Set Asides
This involves encouraging or giving financial incentives to farmers to take land out of use. This has the following advantages
- Reduces Excess supply
- Is good for world farmers and trade negotiations
- Reduces the cost of buying surpluses for the EU
- Better for the environment.
However
- Is still costly for the EU to pay farmers to produce nothing
- Is an inefficient allocation of resources
- Farmers tend to choose the least fertile land to take out of use.
3. MacSharry Reforms
- AN Extension of the Set Aside programme. To qualify for income support farmers have to agree to set aside 15% of their land
- (Farmers were given subsidies equal to the price reduction * by the average yield* the amount of hectares )
- Reducing the Target Price for Cereals by 29% and giving farmers instead direct income support
- Incentives given to farmers who switched to less intensive farming methods
Recent reforms on CAP have focused on
- Further cuts in minimum prices and shift of subsidy to direct income support for farmers.
- Subsidy related to environmental protections.
- Phase-out price support and replace it with direct income support.
- Payments conditional on farmers making environmental improvements to their land
- There would be a maximum ceiling of 300,000 Euros per farm thereby reducing the amount going to large farms.
- More money given to rural development and less to direct income support
- These are very important given the expansion in the East of the EU
Advantages of CAP Reforms
- Prices are brought closer to world levels, improving trade negotiations with other trading blocks. World farmers will benefit from higher prices and being able to export more to the EU
- Consumers will pay lower prices.
- Better for the environment because set-asides are encouraged and intensive farming discouraged. Farmers are rewarded for considering the environment this is an important issue in attempting to overcome market failure in farming which used to occur.
- This is very important with the expansion of the EU into the East, many E. European countries have large and inefficient farming sectors therefore reform of CAP causes greater urgency.
Disadvantages of CAP Reforms
- Still costly for the EU to subsidise farmers
- The policy still benefits the biggest and richest farmers most because income support depends upon how many acres a farmer has. In 1991 MacSharry proposed putting a ceiling on individual payments to farmers but this was blocked for political reasons
- There still remain tariff barriers with non-EU country and some target prices. The reforms have therefore not gone far enough.
Related
