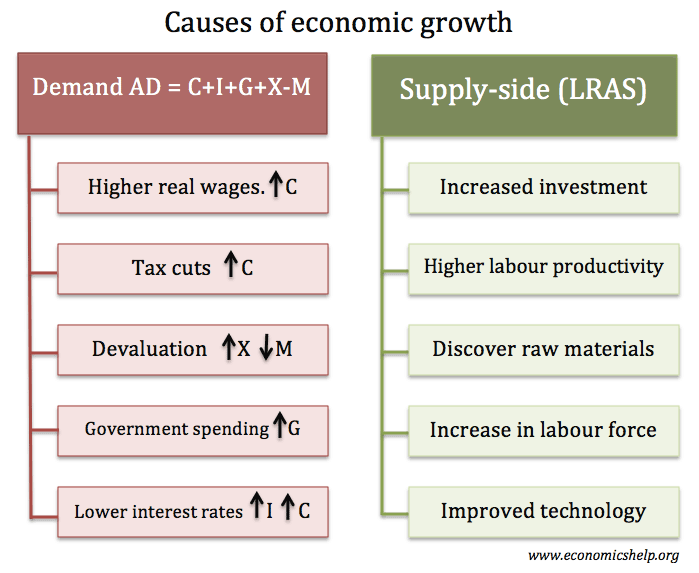
- Economic growth means an increase in real GDP. Economic growth means there is an increase in national output and national income.
- Economic growth is caused by two main factors:
- An increase in aggregate demand (AD)
- An increase in aggregate supply (productive capacity)
See latest stats on economic growth
Demand-side causes
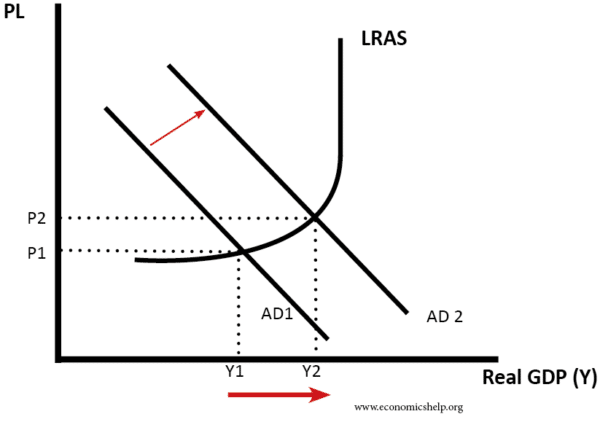
In the short term, economic growth is caused by an increase in aggregate demand (AD). If there is spare capacity in the economy, then an increase in AD will cause a higher level of real GDP.
AD= C + I + G + X- M
- C= Consumer spending
- I = Investment (gross fixed capital investment)
- G = Government spending
- X = Exports
- M = Imports
Graph showing increase in AD
1. Factors which affect AD
- Lower interest rates – Lower interest rates reduce the cost of borrowing and so encourages consumer spending and firms to invest. Lower interest rates also reduce mortgage payments and so increase the disposable income of consumers.
- Increased wages. Higher real wages increase disposable income and encourage consumer spending.
- Increased government spending (G). e.g. government investment on building new roads or increased spending on welfare benefits, which increase disposable income.
- Devaluation. A fall in the value of the exchange rate (e.g. Pound Sterling) makes exports cheaper and increases the quantity of exports (X). A depreciation also makes imports more expensive, reducing quantity of imports and making domestic goods relatively more attractive.
- Confidence. Increased consumer confidence encourages households to spend by either running down savings or taking out more personal credit. It enables higher spending (C)., which encourages spending (C).
- Lower tax. Lower income tax will increase the disposable income of consumers and increases consumer spending (C).
- Rising house prices. A rise in the price of houses creates a positive wealth effect. Homeowners who see a rise in the value of their houses will be more willing to spend (remortgaging house if necessary)
- Financial stability. If there is financial stability and banks are willing to lend, then firms will be more willing to invest and investment will increase aggregate demand.
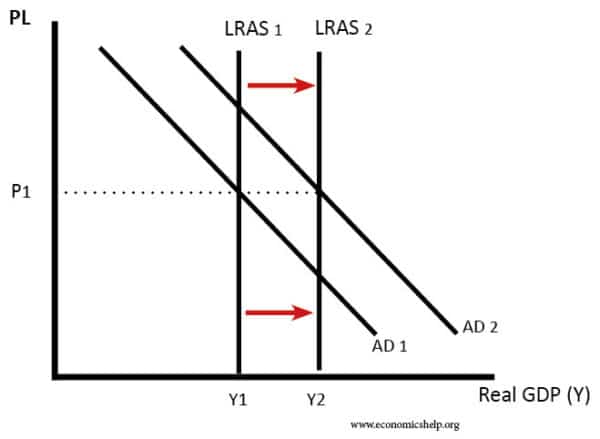
2. Long-term economic growth
This requires an increase in the long-run aggregate supply (productive capacity) as well as AD.
Diagram showing long-run economic growth
LRAS or potential growth can increase for the following reasons:
- Increased capital. e.g. investment in new factories or investment in infrastructure, such as roads and telephones.
- Increase in working population, e.g. through immigration, higher birth rate.
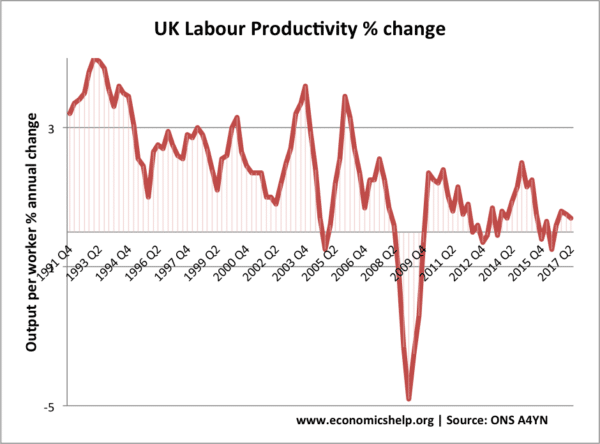
- Increase in labour productivity, through better education and training or improved technology.
more on labour productivity
- Discovering new raw materials. For example, finding oil reserves will increase national output
- Technological improvements to improve the productivity of capital and labour e.g. Microcomputers and the internet have both contributed to increased economic growth. In the future, economic growth may come from new technology such as Artificial intelligence (AI) which enables robots to take the place of human workers.
Other factors affecting economic growth
- Economic and political stability. Stability is important for reassuring firms it is a good idea to invest in increasing capacity. If we see a rise in uncertainty, confidence tends to fall and this can cause firms to delay investment.
- Low inflation. Low inflation is a good climate for encouraging business investment. High inflation increases volatility.
Periods of economic growth in UK
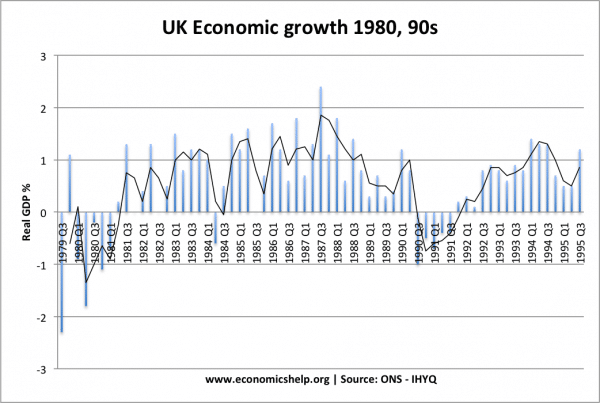
1980s boom
In the 1980s, the UK achieved rapid rates of economic growth, this was caused by
- Cuts in income tax, increasing disposable income, leading to higher spending and thereby stimulating business investment
- Boom in house prices, which caused a positive wealth effect, equity withdrawal and higher consumer spending.
- Rise in confidence, especially amongst south
- Low real interest rates, which made mortgages cheaper.
- See: UK economy in the 1980s
Period of great moderation 1992-2007
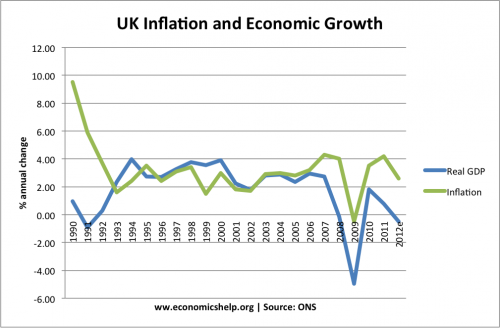
The longest period of economic expansion on record was from 1992 – 2007. This period of economic growth was caused by:
- Low global inflation, which created a period of economic stability.
- A rise in house prices, which helped increase consumer spending.
- Growth in productivity, helped by supply-side reforms.
- Inward investment helped create new jobs and better labour relations.
- See: Great moderation
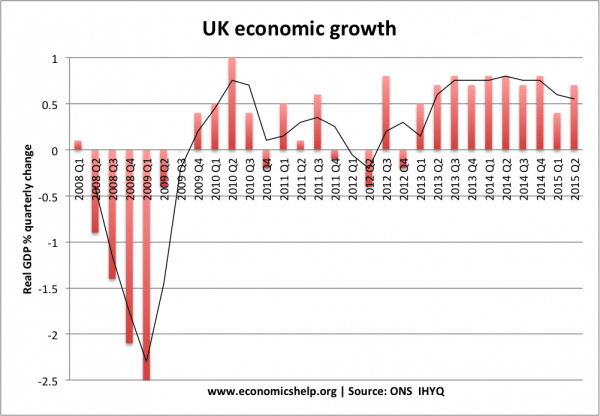
The great recession of 2008/09 caused by
- Credit crunch and fall in bank lending
- Rise in price of oil – reducing disposable income
- Fall in confidence
- Fall in house prices leading to the negative wealth effect.
- Global recession causing fall in export spending.
Related