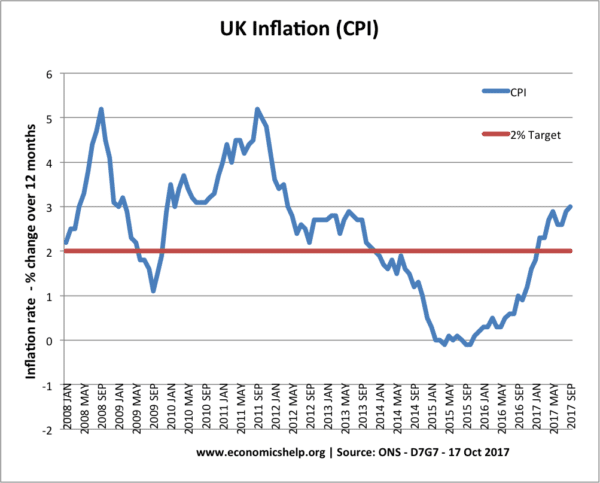
Should the government be concerned if the CPI rises to 5%?
Costs of Inflation
The Government set the MPC a target for CPI of 2.% +/-1. It believes inflation higher than 3.0% is potentially damaging to the economy.
- Decline in relative competitiveness. If inflation in the UK is higher than elsewhere, then UK goods will become uncompetitive leading to a fall in demand for UK exports. If there is a fall in demand for exports then there may be a deficit on the current account Balance of Payments. However, this may be offset by a devaluation that is likely to occur from high inflation.
- If the inflation was worldwide caused by an increase in the oil price (e.g. like in 2008), it may be necessary to revise the inflation target of 2% – or at least tolerate a higher inflation rate. The UK would not lose its competitive advantage because every country would have higher inflation. To reduce inflation could cause stagflation (lower growth and higher prices) In other words, it would be more harmful to reduce inflation than to tolerate a temporary spike in inflation.
- Depreciation in the exchange rate. If inflation is high there will be a devaluation of the exchange rate, This is something the govt wishes to avoid as it creates uncertainty amongst business and lower purchasing power of Sterling abroad.
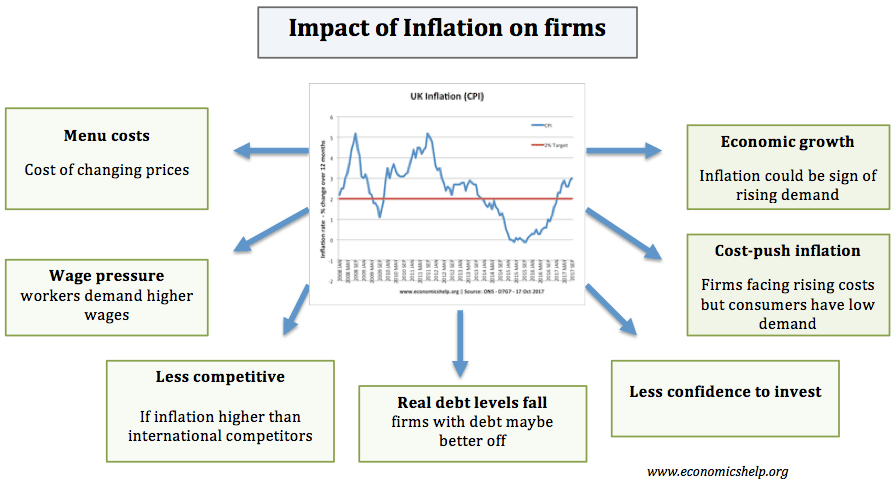
- Menu costs. Higher rates of inflation may cause menu costs, which means firms have to change price lists quite often. However, this is not that significant when inflation is only 5%. Modern technology has also made it easier for firms to change prices.
- Boom and bust economic cycles. If inflation is caused by unsustainable economic growth then the economic boom may be followed by a recession. To reduce inflation and keep inflation within the target, the B of E will have to increase interest rates; this causes problems because AD will fall causing lower growth. For example, in the late 1980s, the UK experienced demand-pull inflation from rapid economic growth – but this led to higher interest rates and the boom turning to bust.
- Creates uncertainty. Higher rates of inflation are disliked by business because it makes it more difficult to predict future costs. Therefore investment will be lower. Countries with lower inflation rates generally have poorer economic growth.
- A high rate of inflation would make it more difficult to join the Euro because it would breach the Maastricht criteria. If inflation in the UK was higher than Europe a single Monetary policy would be ineffective for the UK. These days, this is not really an issue for the UK as membership of the Euro is very unlikely.
- Redistribution. Inflation may cause redistribution of income from savers to borrowers. This is because inflation reduces the value of money. However, this will depend upon the rate of interest. E.g. if the interest rate was 8% and inflation 5%, savers would still have a real interest rate of 3%. However between 2009 – 17, interest rates in many countries were very low (0.5%) and this meant even small amounts of inflation (3-4%) led to a fall in the value of savings.
- Real wages It depends on whether wages are keeping up with inflation. If wages are increasing by 2% and inflation is 4% – then real wages would be falling. This happened in the UK between 2009-17.
- Hyperinflation. When inflation starts to rise at rapid rates, then inflation quickly becomes very destabilising for the economy. Countries with hyperinflation (Zimbabwe 2000s, Germany 1923) saw an economy devastated by the effects of changing prices. It causes instability and people lose their savings. See: costs of hyperinflation
Is inflation harmful to firms?
Costs of Low Inflation / Deflation
Should the govt be concerned with inflation falling below 2.0%?
- If prices are falling because AS shifts to the right because of new technology, this is beneficial for the economy, because growth is increasing and jobs should be being created.
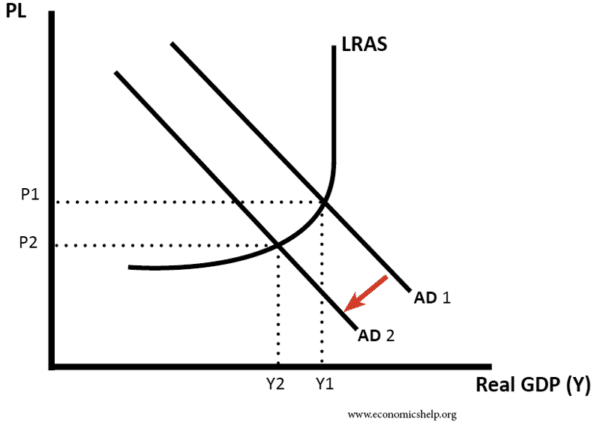
- If deflation is caused by falling AD then this is a serious economic problem because it indicates a recession with problems such as unemployment, lower output and a negative multiplier effect.
- Deflation can cause problems for the economy. It means that those who have debts will see the real value of debts increase, this will lead to lower consumer confidence and possibly lower AD and economic growth.
- Deflation makes monetary policy ineffective. This is because interest rates cannot be reduced below 0%.
- Companies cannot alter real wages easily because workers are very resistant to any cut in nominal wage wages. Therefore, real wages may rise.
- It is more difficult to set prices when there is deflation
Related