- Definition of market equilibrium – A situation where for a particular good supply = demand. When the market is in equilibrium, there is no tendency for prices to change. We say the market-clearing price has been achieved.
- A market occurs where buyers and sellers meet to exchange money for goods.
- The price mechanism refers to how supply and demand interact to set the market price and amount of goods sold.
- At most prices, planned demand does not equal planned supply. This is a state of disequilibrium because there is either a shortage or surplus and firms have an incentive to change the price.
Market equilibrium
Market equilibrium can be shown using supply and demand diagrams
In the diagram below, the equilibrium price is P1. The equilibrium quantity is Q1.
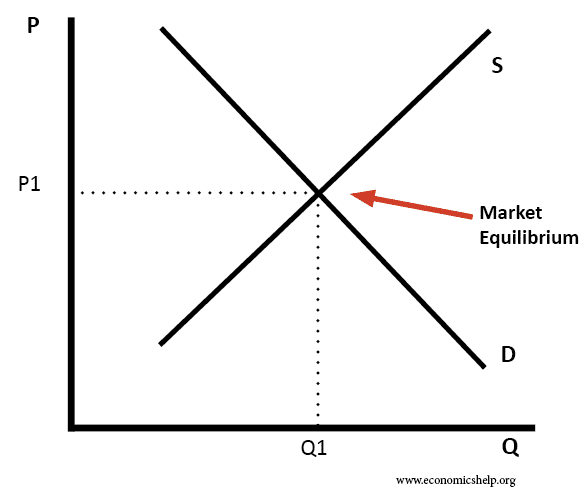
If price is below the equilibrium
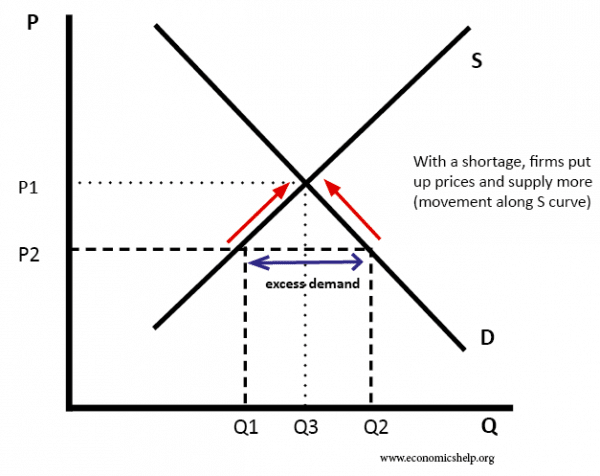
- In the above diagram, price (P2) is below the equilibrium. At this price, demand would be greater than the supply. Therefore there is a shortage of (Q2 – Q1)
- If there is a shortage, firms will put up prices and supply more. As price rises, there will be a movement along the demand curve and less will be demanded.
- Therefore the price will rise to P1 until there is no shortage and supply = demand.
If price is above the equilibrium
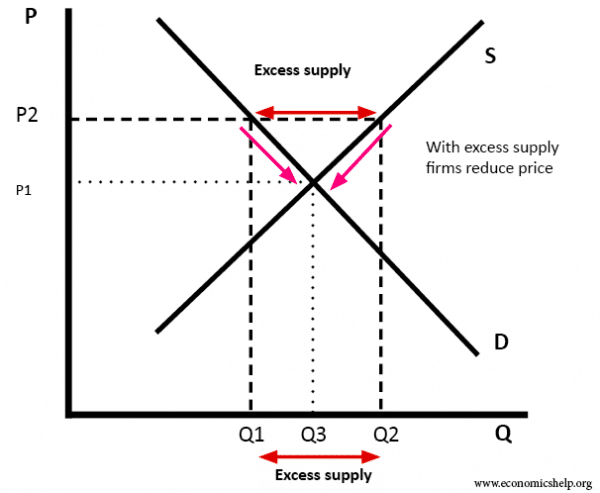
- If price was at P2, this is above the equilibrium of P1. At the price of P2, then supply (Q2) would be greater than demand (Q1) and therefore there is too much supply. There is a surplus. (Q2-Q1)
- Therefore firms would reduce price and supply less. This would encourage more demand and therefore the surplus will be eliminated. The new market equilibrium will be at Q3 and P1.
Movements to a new equilibrium
- Increase in demand
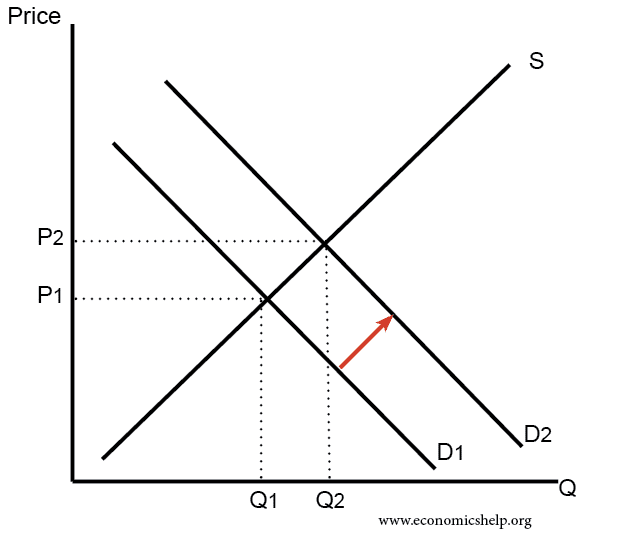
If there was an increase in income the demand curve would shift to the right (D1 to D2). Initially, there would be a shortage of the good. Therefore the price and quantity supplied will increase leading to a new equilibrium at Q2, P2.
2. Increase in supply
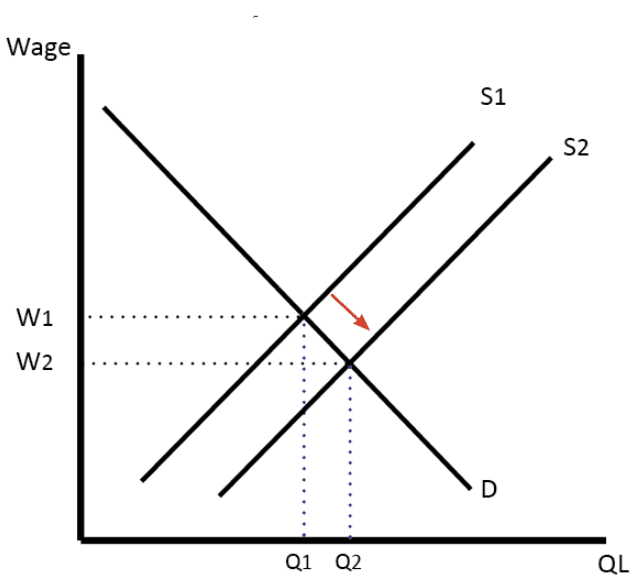
An increase in supply would lead to a lower price and more quantity sold.
Related posts
- Finding market equilibrium with equations
- Price mechanism in the long-term
- Economic rent and transfer earnings
- The economics of the price of coffee
First published 28 Nov 2010. Last updated 28 Nov 2019
