Changes in price cause signals in the market mechanism.
For example, if there is an increase in demand this will lead to a higher price and a movement along the supply curve.
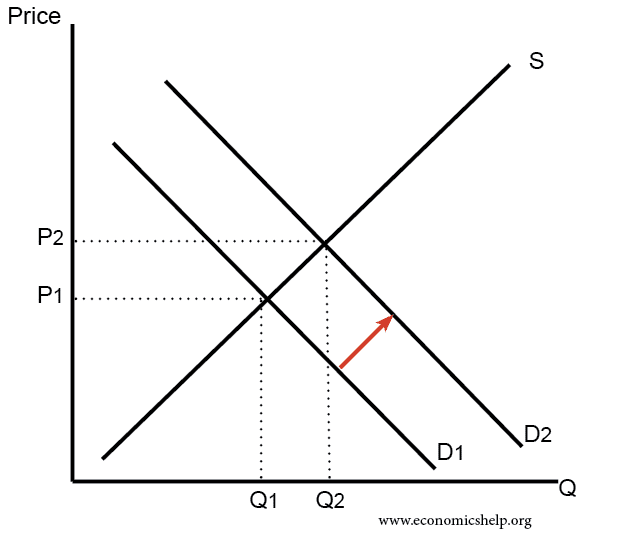
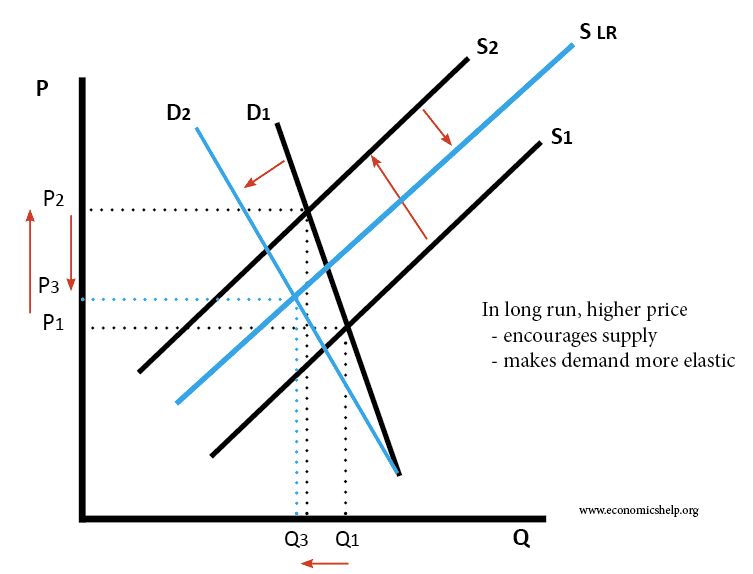
- However, in the long run, high prices act as an incentive for firms to supply more.
- Therefore firms will expand their production or new firms enter in the market. This will cause the supply curve to shift to the right.
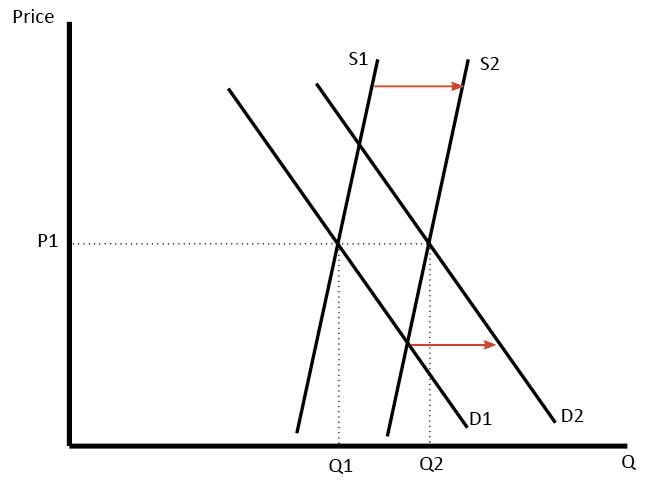
- For example, with an increase in demand for mobile firms, more firms entered the market. Therefore prices have not increased but stayed roughly the same.
When the oil price tripled in the 1970s this encouraged new countries to start producing oil, e.g. it was now profitable for the UK to produce.
Also, in the short term demand for oil was inelastic (it was necessary). However, over time, consumers found alternatives to oil and demand become more price sensitive.
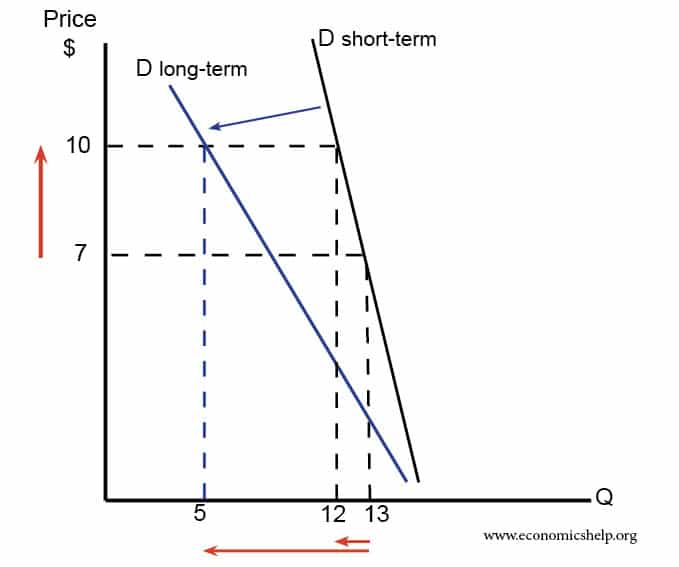
In the long term, demand becomes more price elastic as consumers have more time to find alternatives.
The effect of an increase in Costs
If a good becomes more expensive to produce, supply will shift to the left, and there will be a movement along the demand curve leading to lower demand.
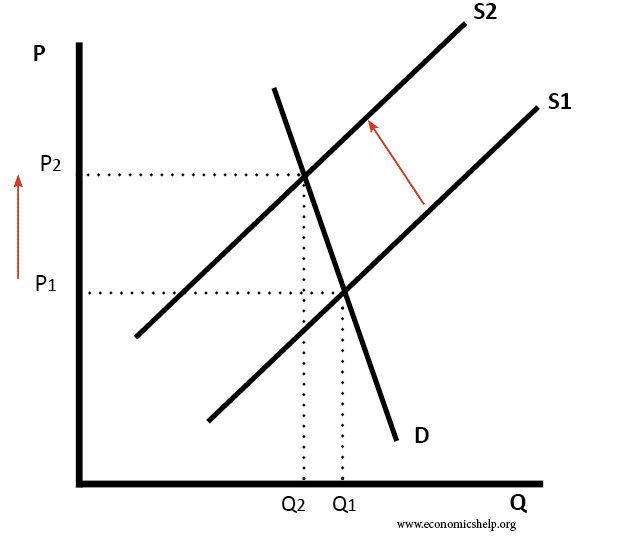
There will be an increase in demand for substitutes, for example if wool becomes more expensive then there will be an increase in demand for nylon.
- In the short term there may be not many substitutes. Therefore demand is quite inelastic, and demand only falls a little.
Long term effects of an increase in costs
- Demand falls by more. However, in the long run firms may develop alternatives so consumers will become more price sensitive (they could buy synthetic nylon. Therefore over time demand will be more elastic and fall by more.
- Higher price encourages new suppliers. If the price of wool rises, it becomes more profitable to produce wool. Therefore, in the long-term some farmers may respond by turning more farmland over to sheep production and so in long-term, new supplies of wool emerge.
Another example – higher oil price
For example if petrol became more expensive then in the short run demand would not fall very much. However, over time firms would develop more alternative such as electric cars or powdered solar cars, so demand becomes more price sensitive.
Also, over time, high oil prices may encourage new countries to produce oil (e.g. Russia, Venezuela, Antarctica)
Q. Should economists be concerned about the world running out of oil?
