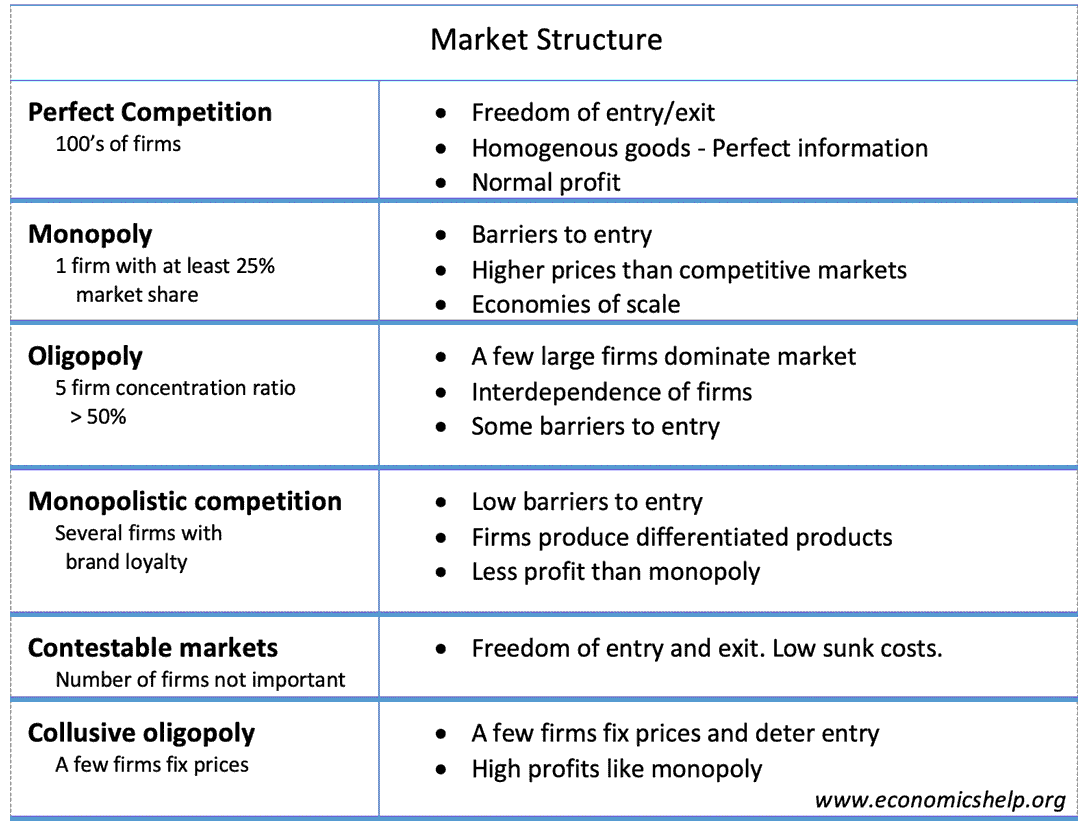
- Perfect competition – Many firms, freedom of entry, homogeneous product, normal profit.
- Monopoly – One firm dominates the market, barriers to entry, possibly supernormal profit.
- Oligopoly – An industry dominated by a few firms, e.g. 5 firm concentration ratio of > 50%. Interdependence of firms
- Oligopoly diagram
- Collusive behaviour – firms seek to form an agreement to increase prices.
- Kinked demand curve model – when prices are stable and firms compete on non-price competition.
- Monopolistic competition – Freedom of entry and exit, but firms have differentiated products. Likelihood of normal profits in the long term.
- Contestable markets – An industry with freedom of entry and exit, low sunk costs. The theory of contestability suggests the number of firms is not so important, but the threat of competition.
- Duopoly – where two firms dominate the market. For example, Pepsi and Coca Cola. Android vs Apple. A duopoly falls between a monopoly and oligopoly.
Related pages
- Mergers
- Objectives of firms
- Bertrand competition – (a competitive duopoly)
