Relative poverty reflects the fact that some sections of society have an income far lower (e.g. 50% less) than the average salary. A national minimum wage is a legal requirement.
There are three levels of minimum wage, and the rates from April 2017 are:
- £7.50 for those over 25
Since the introduction of the NMW, many low paid workers have seen an increase in the hourly wage as firms are obliged to pay workers the statutory minimum wage. To some extent, this has helped reduce relative poverty, as the lowest paid workers have seen a significant increase in their weekly income. This is more prevalent in the North where wages tended to be lower; fewer jobs in the south have been affected by the NMW.
However, it is worth noting that the poorest sections of society tend to be those on benefits such as JSA (60% of the poorest tend to be unemployed) and incapacity benefits; therefore these groups will not benefit from a NMW. Also many on the NMW may be second income earners e.g. the wife of the main breadwinner. Therefore these households may be quite well off and would not classify as being relatively poor anyway. Therefore this is a limitation of the NMW in reducing poverty.
Another concern about the NMW is that it may cause unemployment. According to classical theory, an increase in the NMW will lead to real wage unemployment of Q3 –Q2.
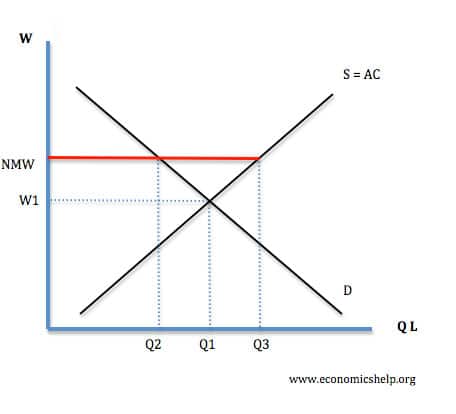
The extent of unemployment would depend upon the elasticity of demand for labour. If it was inelastic unemployment would only increase a little. However, If there was an increase in unemployment this would have the effect of increasing relative poverty rather than reducing it. This problem may be most likely to occur in industries with low-profit margins and regions where equilibrium wages tend to be low.
However, evidence suggests that UK labour markets are not perfectly competitive, but employers may have significant Monopsony power. This is especially true in part-time, temporary service sector jobs where workers have little union representation and few rights. If workers face monopsonists, a higher minimum wage may not cause unemployment, in some circumstances it may decrease.
Effect of Minimum Wage on a Monopsony
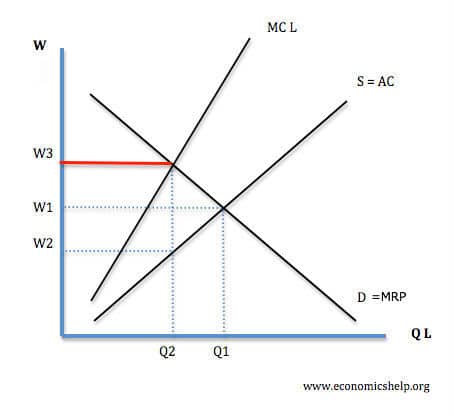
A Monopsonist will maximise profits at Q2 (because MRP = MC L) it will then pay a wage of W2. However, if a NMW raises to W 1 the demand for labour will increase to Q1 and employment increases. Unemployment will not increase until the wage rises above W2.
Empirical evidence suggests that increasing the NMW does not cause unemployment to increase suggesting this model is more accurate than the classical view. However, it will clearly depend upon how much the NMW is increased. It is also likely that some labour markets will be more competitive than others; therefore, the effect may differ for different industries.
Other positive benefits of the NMW include the fact it may increase the incentive for the unemployed to get a job rather than stay on benefits, however, the JSA is quite low, and the gap between benefits and work is quite high already. In conclusion, an increase in the NMW can help the low paid to increase their income, thereby reducing relative poverty to some extent. A significant concern about an increase is that in some labour markets it may cause real wage unemployment, therefore, increasing poverty. However, evidence suggests that the increase would have to be very significant for this to occur because many labour markets tend to be uncompetitive. There could also be a case for increasing the NMW more in the south where wages tend to be higher, thereby reducing relative poverty in the south.
Related