The essence of profitability is a firms Revenue – Costs with revenue depending upon price and quantity of the good sold.
These factors will all determine the profitability of firms
1. The degree of competition a firm faces.
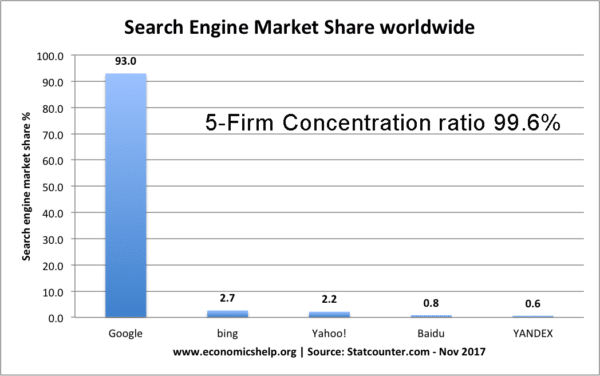
If a firm has monopoly power then it has little competition. Therefore demand will be more inelastic. This enables the firm to increase profits by increasing the price. For example, very profitable firms, such as Google and Microsoft have developed a degree of monopoly power, with limited competition.
- However, in theory, government regulation may prevent monopolies abusing their power, e.g. the OFT can stop firms colluding (to increase price) Regulators like OFGEM can limit the prices of gas and electricity firms.
2. If the market is very competitive, then profit will be lower. This is because consumers would only buy from the cheapest firms. Also important is the idea of contestability. Market contestability is how easy it is for new firms to enter the market. If entry is easy then firms will always face the threat of competition; even if it is just “hit and run competition” – this will reduce profits.
3. The strength of demand. For example, demand will be high if the product is fashionable, e.g. mobile phone companies were profitable during the period of rising demand and growth in the market. Products which have falling demand like Spam (tinned meat) will lead to low profit for the company. Some companies, like Apple, have successfully carved out strong brand loyalty making customers demand many of the new Apple products.
- However, in recent years, profits for mobile phone companies have fallen because the high profit encouraged oversupply, negating the increase in demand.
4. The state of the economy. If there is economic growth then there will be increased demand for most products especially luxury products with a high-income elasticity of demand. For example, manufacturers of luxury sports cars will benefit from economic growth but will suffer in times of recession.
5. Advertising. A successful advertising campaign can increase demand and make the product more inelastic demand. However, the increased revenue will need to cover the costs of the advertising. Sometimes the best methods are word of mouth. For example, it was not necessary for YouTube to do much advertising.
6. Substitutes, if there are many substitutes or substitutes are expensive then demand for the product will be higher. Similarly, complementary goods will be important for the profits of a company.
7. Relative costs. An increase in costs will decrease profits; this could include labour costs, raw material costs and cost of rent. For example, a devaluation of the exchange rate would increase the cost of imports, and therefore companies who imported raw materials would face an increase in costs. Alternatively, if the firm is able to increase productivity by improving technology then profits should increase. If a firm imports raw materials the exchange rate will be important. A depreciation making imports more expensive. However, a depreciation of the exchange rate is good for exporters who will become more competitive.
8. Economies of scale. A firm with high fixed costs will need to produce a lot to benefit from economies of scale and produce on the minimum efficient scale, otherwise average costs will be too high. For example in the steel industry, we have seen a lot of rationalisation where medium-sized firms have lost their competitiveness and had to merge with others.
9. Dynamically efficient. If a firm is not dynamically efficient then over time costs will increase. For example, state monopolies often had little incentive to cut costs, e.g. get rid of surplus labour. Therefore before privatisation, they made little profit, however with the workings and incentives of the market they became more efficient.
10. Price discrimination. If the firm can price discriminate it will be more efficient. This involves charging different prices for the same good so that the firm can charge higher prices to those with inelastic demand. This is important for airline firms.
11. Management. Successful management is important for the long-term growth and profitability of firms. For example, poor management can lead to a decline in worker morale, which harms customer service and worker turnover. Also, firms may suffer from taking wrong expansion plans. For example, many banks took out risky subprime mortgages, but this led to large losses. Tesco suffered from expanding into unrelated business, like garden centre. This led to over-stretching the company and losing sight of their core business.
12. Objectives of firms. Not all firms are profit maximising. Some firms may seek to increase market share, in which case profits will be sacrificed to gain market share. For example, this is the strategy of Walmart and to an extent Amazon.
13. Exchange rate. If a firm relies on exports, a depreciation in the exchange rate will increase profitability. A fall in the exchange rate makes exports cheaper to foreign buyers. Therefore, the firm can sell more or choose to have a bigger profit margin. If the firm imports raw materials, a depreciation will increase costs of production.
Related

1 thought on “Factors that affect the profitability of firms”
Comments are closed.