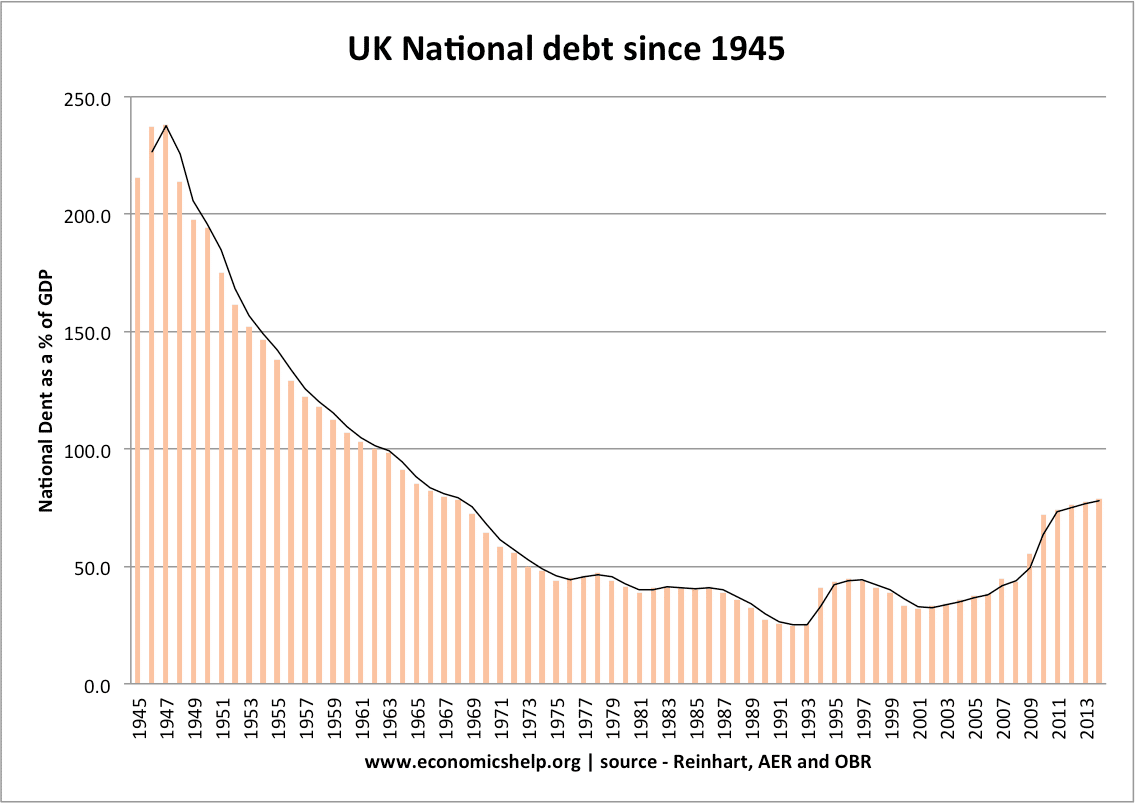
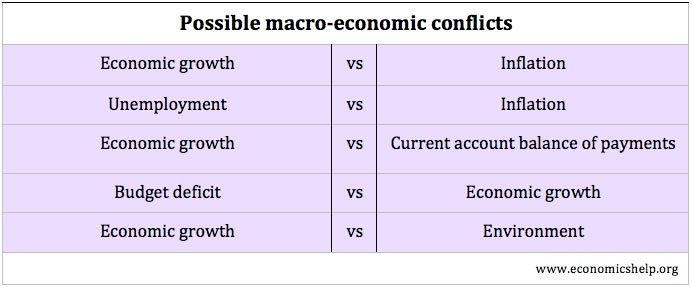
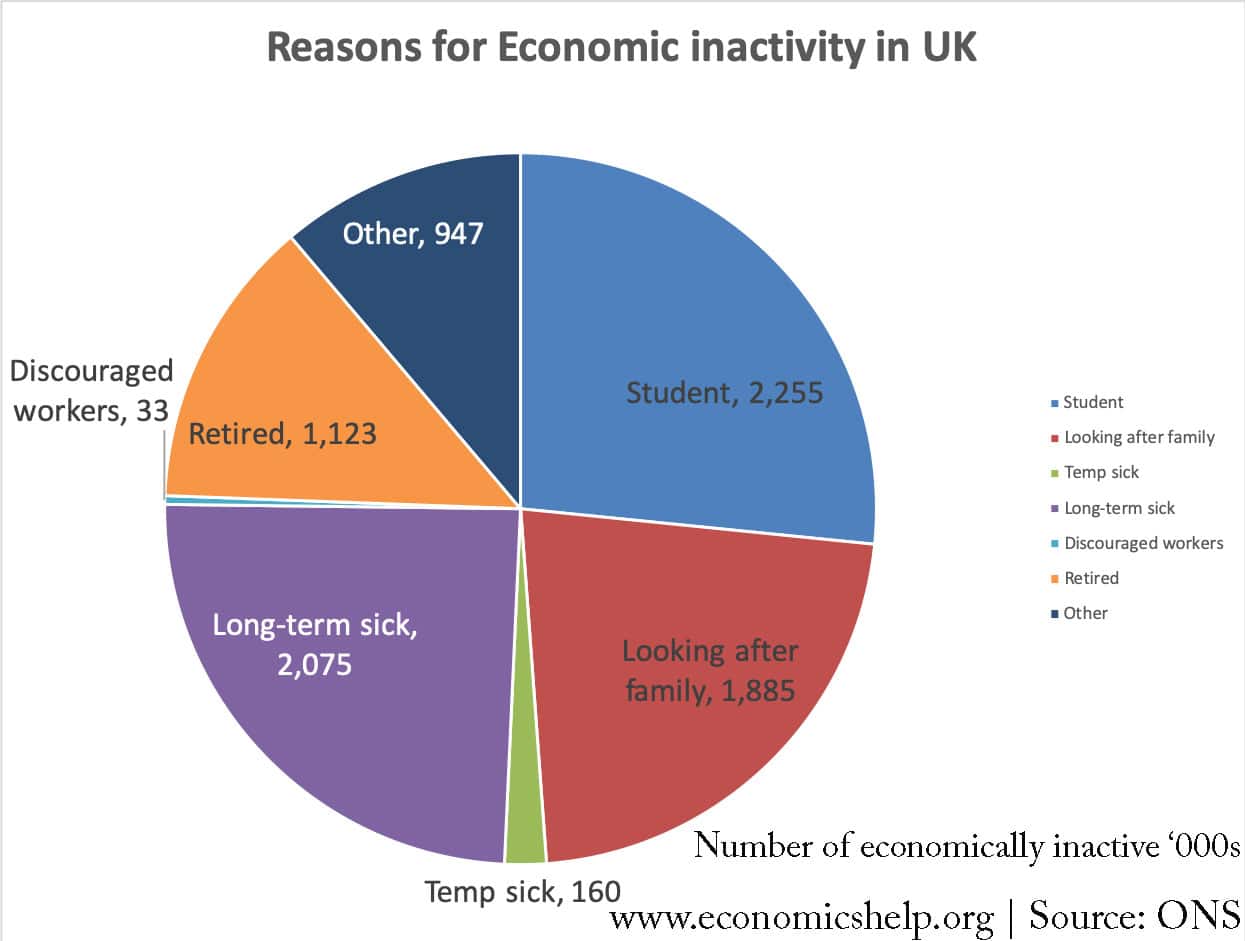
The Difference between Deficit and Debt
In terms of public spending, a deficit is the annual shortfall between spending and tax revenues. Debt is the total amount outstanding to holders of the government’s debt. Definition of deficit and debt Deficit refers to the annual borrowing requirement of the government. (often referred to as budget deficit – or annual net borrowing) Debt …