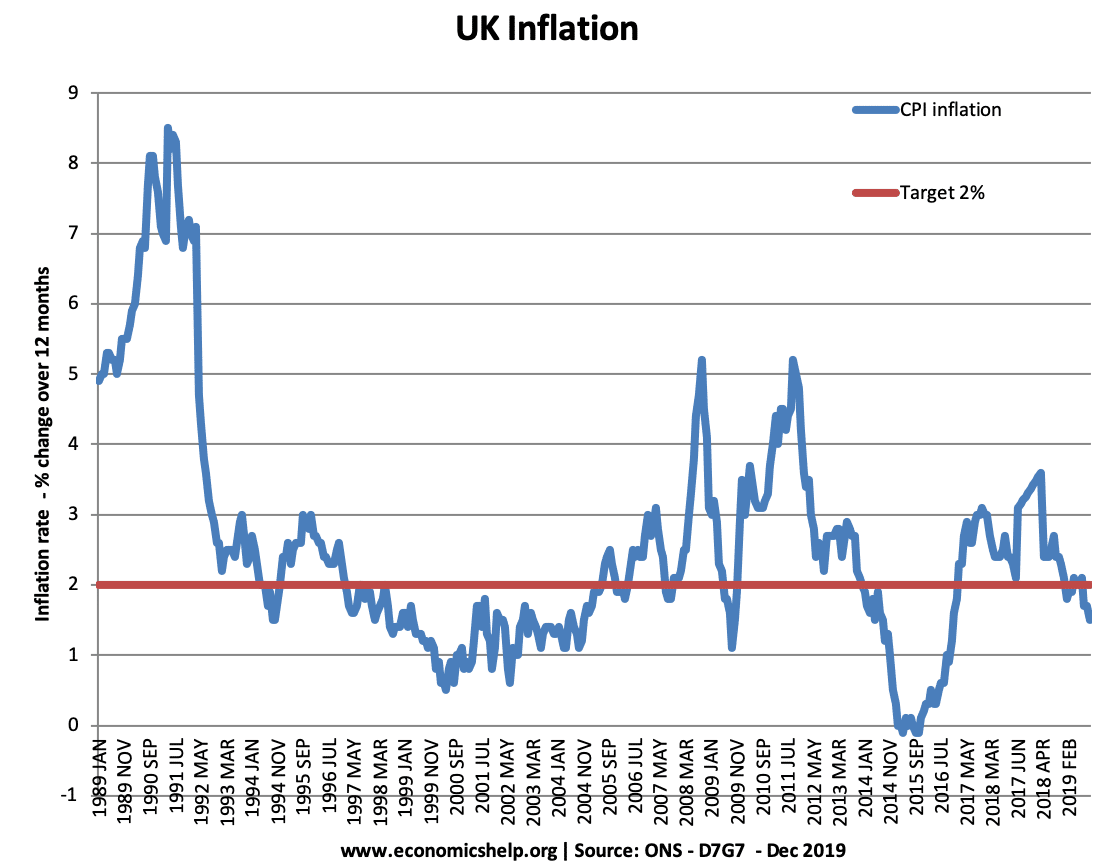
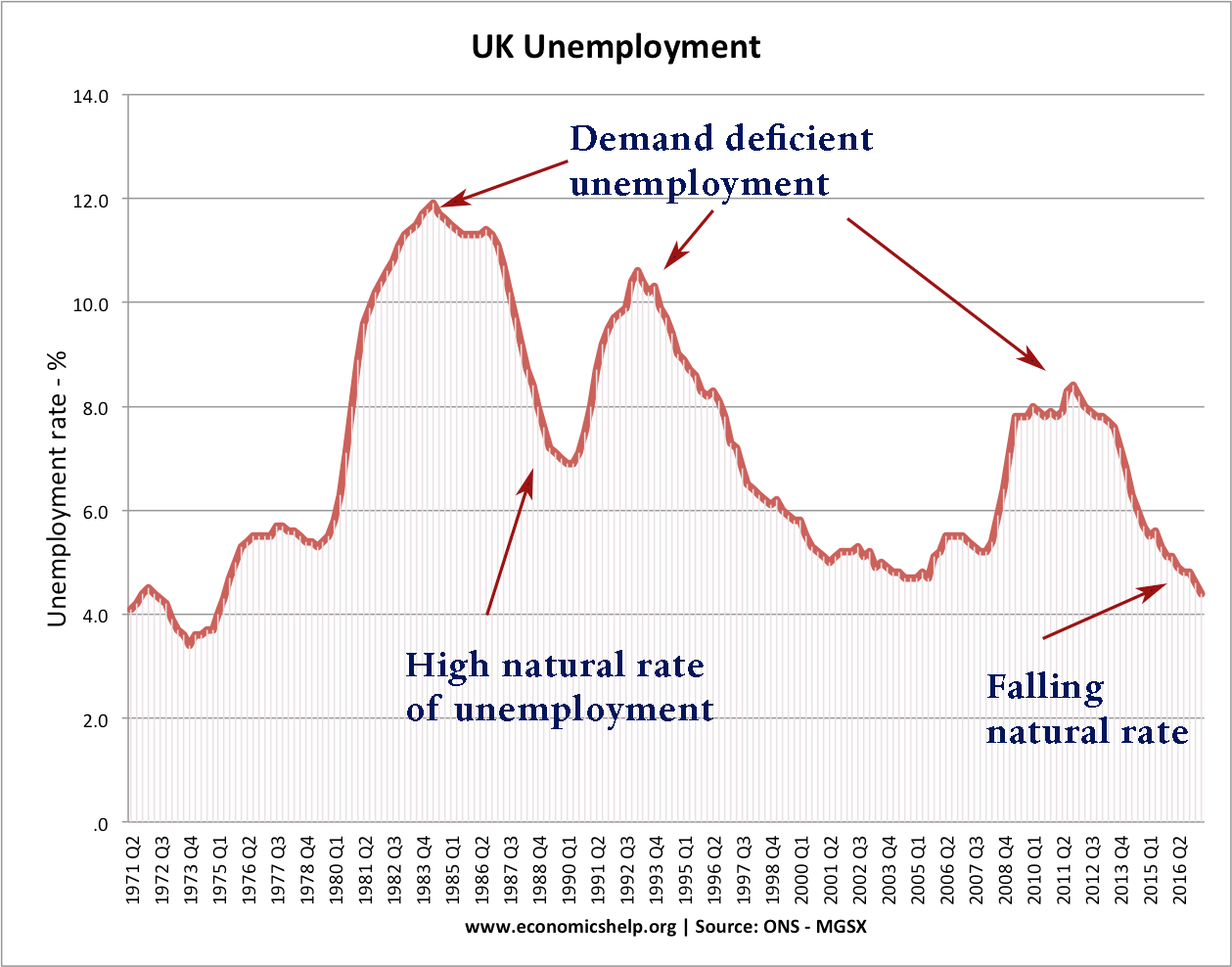
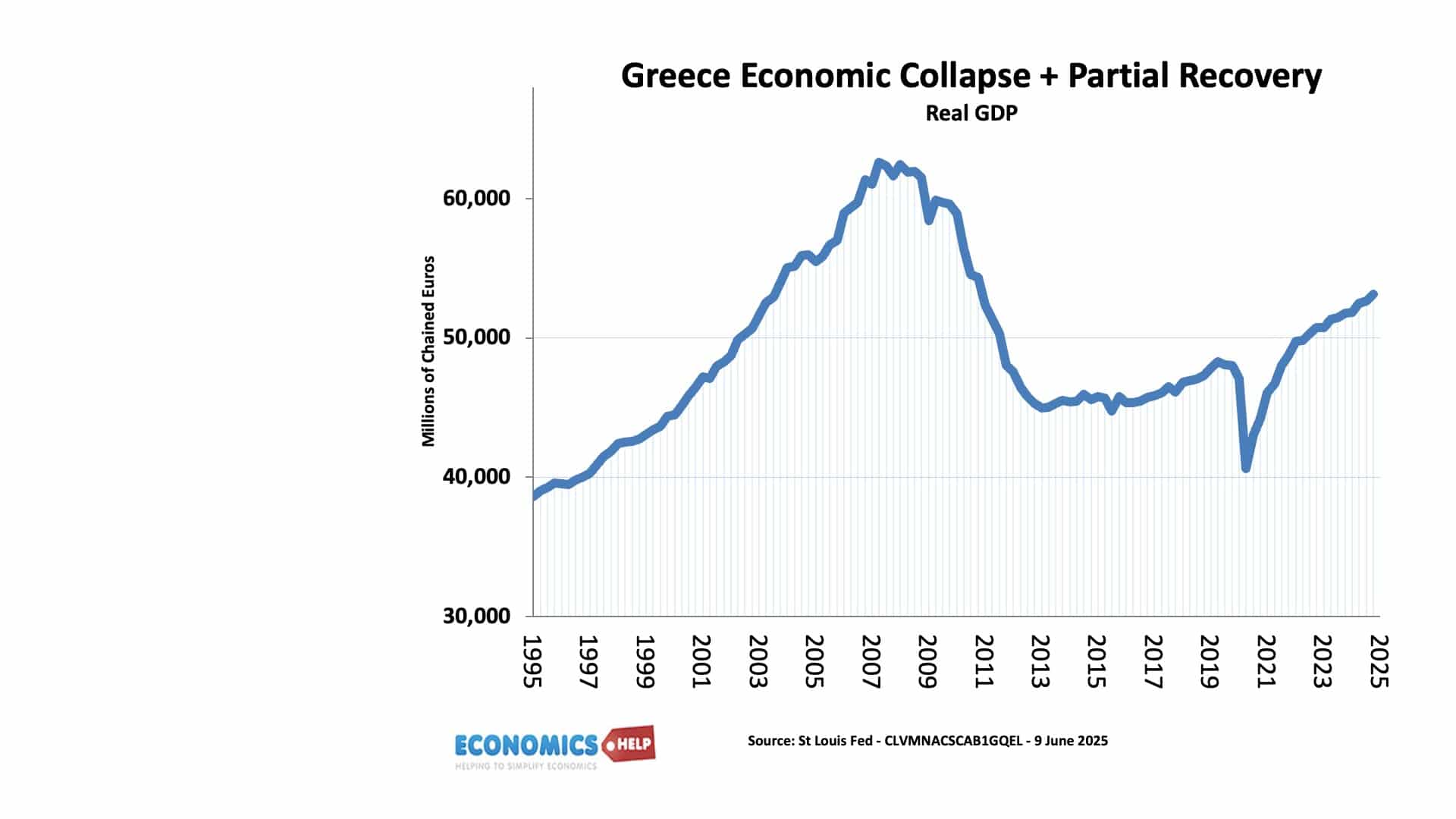
The Law of Demand for Housing
Yesterday, I wrote this piece on the demand for housing Usual demand curve Basically we noted the phenomena that rising house prices often cause an increase in demand and falling house prices cause lower demand. This seems to contradict the basic law of demand. But, I suggested this was due to shifts in the demand …