Price regulation / restrictions
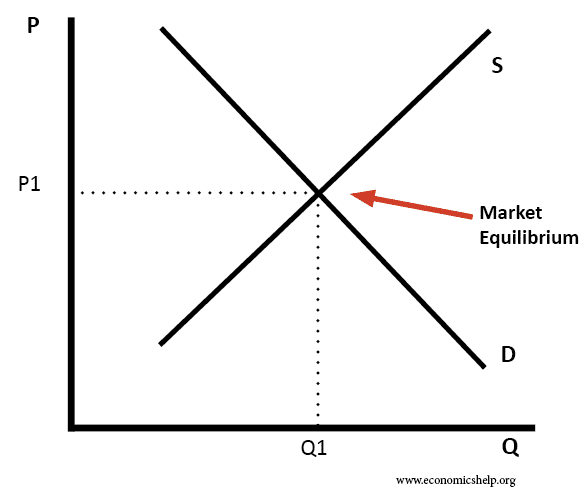
Readers question: Please tell me some products for which equilibrium price is not favourable for some producers and consumers which invite the state to impose price restriction. The equilibrium price is the price determined in a free market; the price determined by the interaction of supply and demand. Under what conditions could this market price …