Interest Rates and Balance of Payments
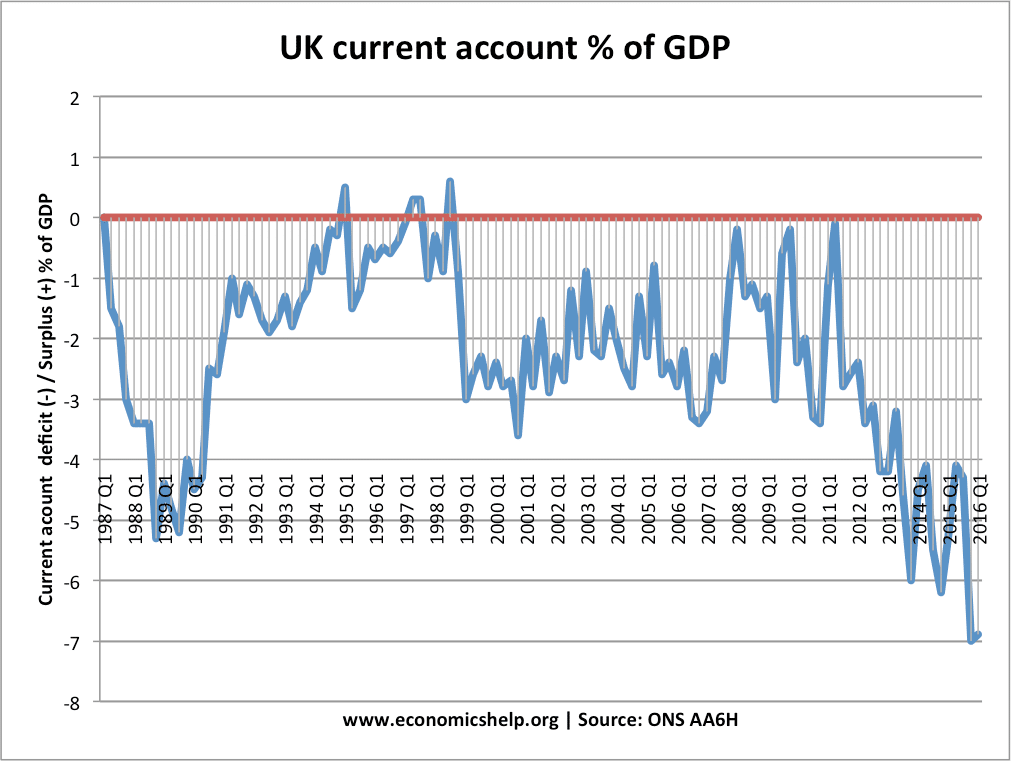
Readers Question: Interest Rates are increased by the governments to bring down inflation rates, this makes exports price competitive as well, as a result, exports increase. However, an increase in interest rates can lead to an appreciation of the currency as demand for the currency increases. So this again increases the price of exports as …