Progressive tax
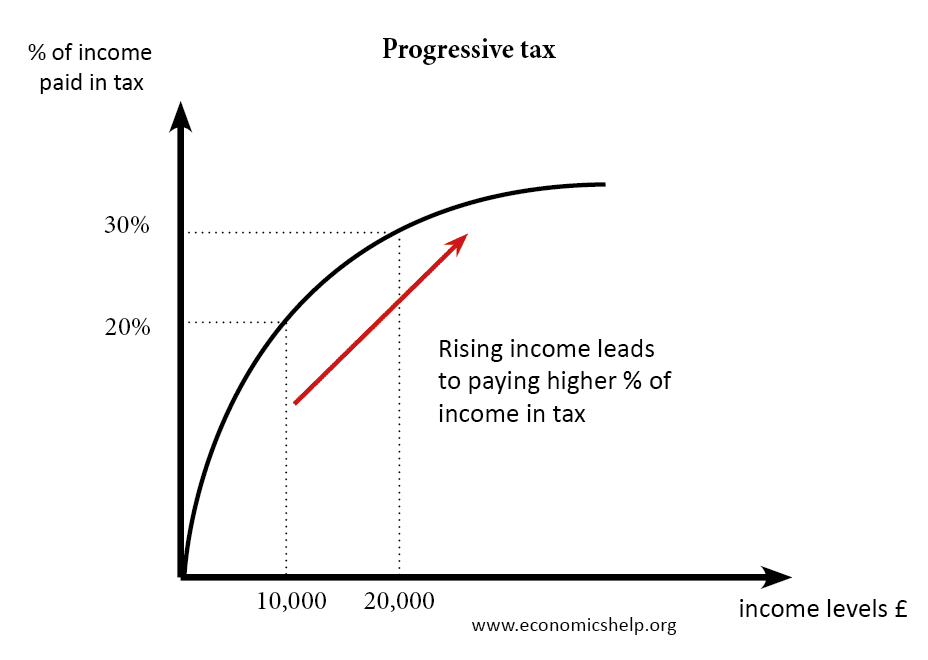
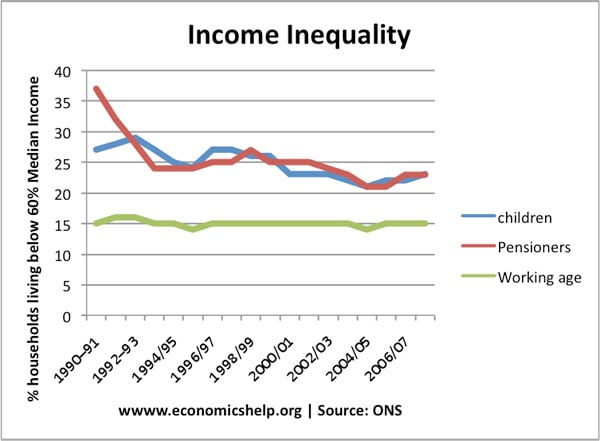
A progressive tax takes a higher percentage of tax from people with higher incomes. It means that the more a person earns, the higher his average rate of tax will be. In this case, the person earning £10,000 is paying 20% of their income in tax (total tax of £2,000) The person earning £20,000 is …