Definition of Deregulation
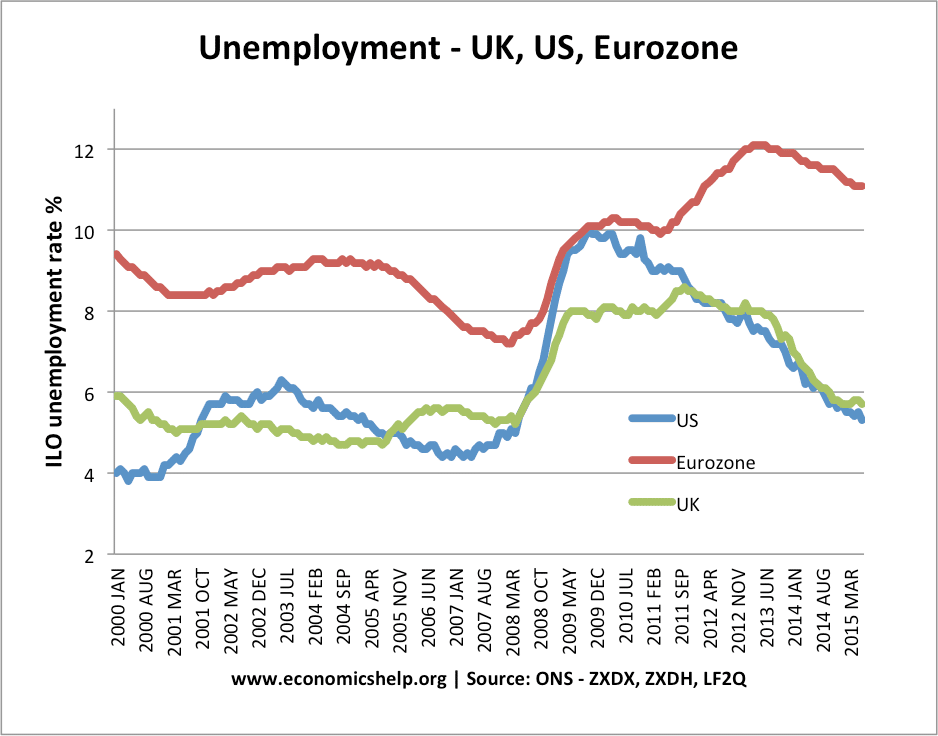
Deregulation involves removing government legislation and laws in a particular market. Deregulation often refers to removing barriers to competition. For example, in the UK, many industries used to be a state monopoly – BT, British Gas, British Rail, local bus services, Royal Mail. However, deregulation allowed new firms to enter these markets and reduce the …