Explanation of why government intervention to try and correct market failure may result in government failure.
Summary
Market failure is a socially inefficient allocation of resources in a free market. Market failure can occur for various reasons
Government failure occurs when government intervention results in a more inefficient and wasteful allocation of resources. Government failure can occur due to:
- Poor incentives in public sector
- Lack of information
- Bureaucracy and administration costs higher in public sector
- Decisions taken for political reasons
Example of government intervention in transport
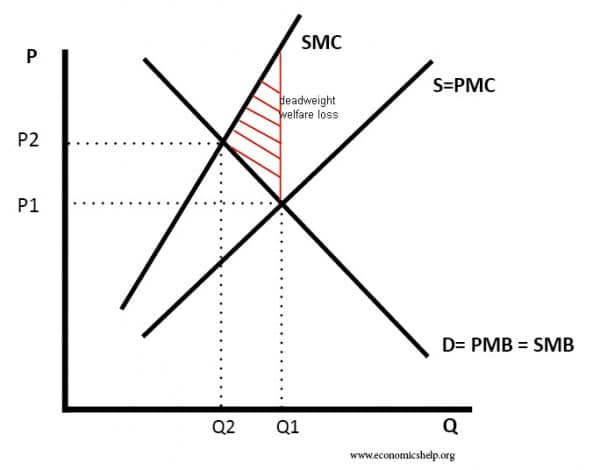
Transport is prone to market failure as it is a good with significant externalities. For example, driving a car into a city causes congestion and pollution – two negative externalities. Therefore, we get a social inefficient allocation of resources – congestion and time wasted by business and commuters.
The free market output is at Q1, but social efficiency is at Q2.
To respond to this problem, the government may try to intervene in the economy. For example, it could raise taxes and build a new highway, which travels into the city. In theory, this should reduce congestion and help solve the market failure. However, in building a new inter-city highway, there may be government failure.
Unintended consequences. As a result of building the new highway, it may encourage more people to buy a car and live further out of the city. In this case, increasing supply has an effect on increasing demand in the long-term. After 5 or 10 years, the levels of congestion can end up being as bad as before the government spent all the money in building the new road. But, in addition to the failure to solve congestion, the government have increased levels of pollution and wasted public funds on a scheme that has failed to tackle the problem.
The government may undertake such a scheme due to poor planning. A new highway may be a popular political idea in the short-term by residents keen to beat traffic jams. However, the politicians fail to explain the potential drawbacks of more congestion in the long-term.
Example of Subsidy for loss-making firm
The government may be worried that if a large steel plant closes down, it will result in unemployment. This unemployment will be a type of market failure as the unemployed steelworkers may struggle to gain employment in new areas. As a result, the government uses public funds to give a subsidy to the steel plant and keep the firm in business.
However, government subsidies to failing business can lead to government failure.
If firms become used to receiving a government subsidy, they may feel fewer incentives to cut costs and transform the business – they become reliant on subsidies and the government ends up wasting public funds on supporting inefficient firms. In the long-run, consumers end up paying higher taxes and higher prices for steel
Example of Market failure in agriculture – CAP
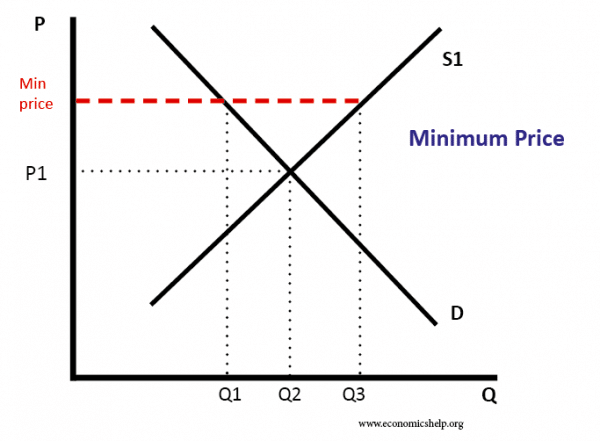
Minimum price caused supply to be greater than demand. The EU had to buy the surplus Q3-Q1
Governments often intervene in agricultural markets. The argument is that agriculture is prone to market failure. Supply can be volatile and in certain years farmers are left with lower incomes. Therefore, to stabilise food supply and farm incomes, the government have intervened. The EEC implemented a Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) which involved guaranteeing a minimum price for agricultural produce.
However, this also required import tariffs to keep the minimum prices protected from international competition.
The problem with this policy is that it had unintended consequences. As farmers had a guaranteed minimum price, it created an incentive for them to produce as much as possible. It was guaranteed the government would buy any surplus.
- Farmers started using more artificial fertilisers to maximise yields.
- The EU had to keep buying more an more surplus food, which was stored in big depositories (known as wine lakes, butter mountains)
- The food was either destroyed or dumped on world markets (causing lower income for farmers in developing economies)
Therefore, in order to overcome the market failure of volatile prices for farmers, the EU created a system where:
- The price of food was higher than it should have been.
- Tax revenue was used to buy surplus food that was not needed.
- The environment was damaged by farmers trying to maximise yields.
- The EU experienced retaliatory tariffs from other countries in response to high agricultural tariffs on food.
- At its peak the CAP took 70% of the EU budget – money that could have been better spent elsewhere.
Example Monopoly
Monopoly leads to market failure because firms are in a position to increase prices at the expense of the consumer and be more inefficient. To prevent an increase in Monopoly power, the Competition Commission can block mergers; however, some mergers could have benefits e.g. economies of scale and more research and development. If the government blocked all mergers this may be harmful to the economy
Further reading