Should full employment be the primary macroeconomic objective?
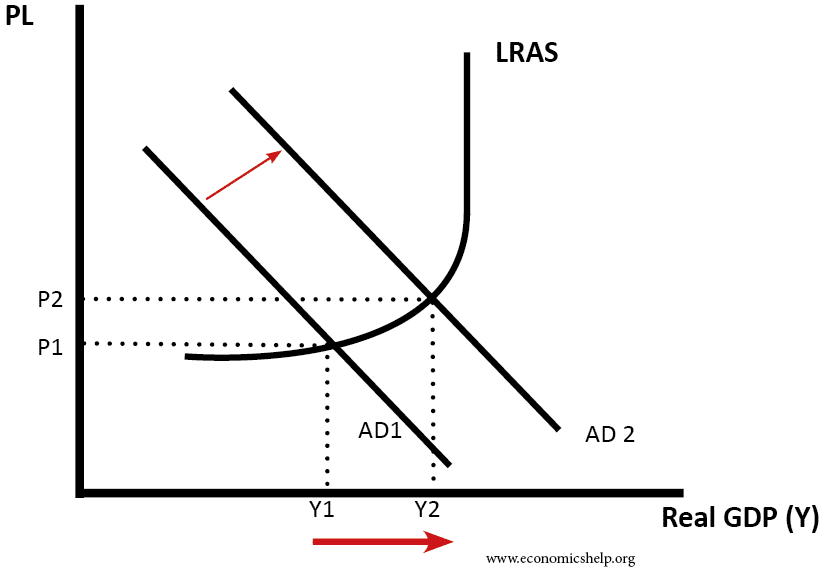
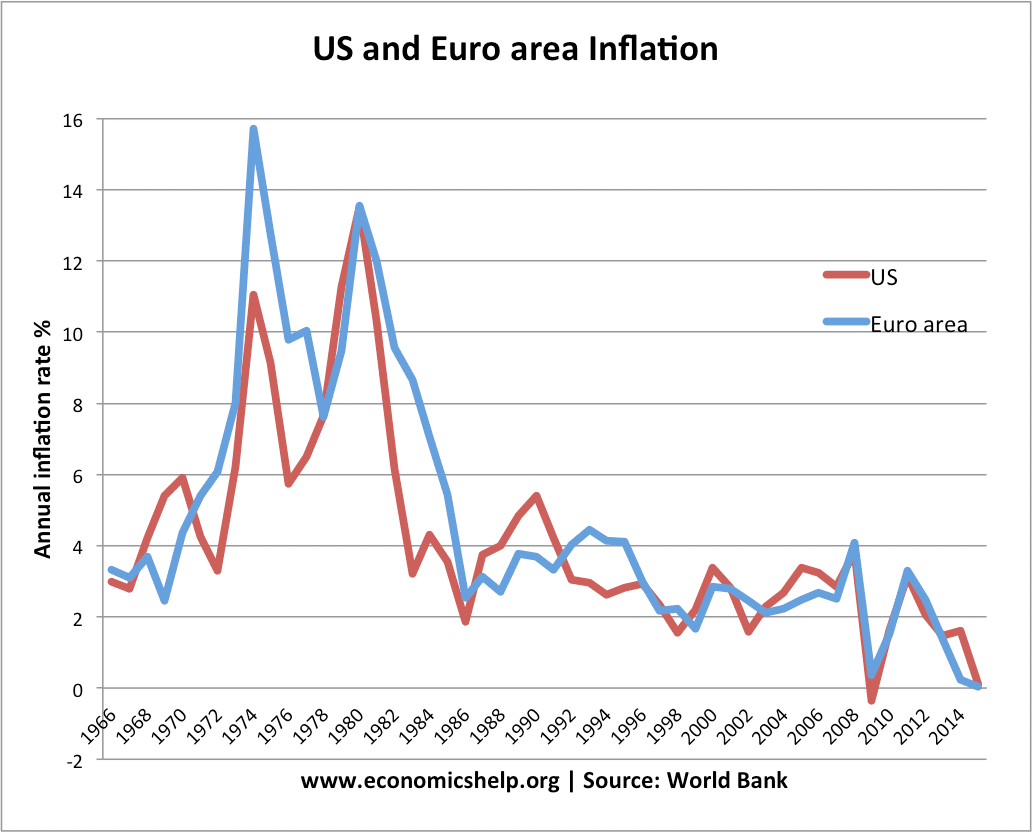
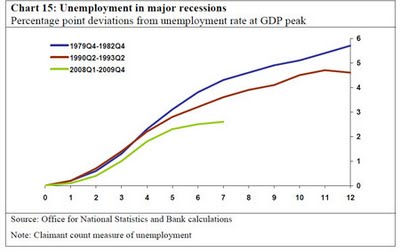
The main macroeconomic objectives of the government will include: low inflation, increasing the sustainable rate of economic growth full employment and balance of payments equilibrium. Full employment involves zero or very low unemployment. In practice, there will always be some frictional unemployment as people are looking for new jobs or leaving school. Economists suggest an …