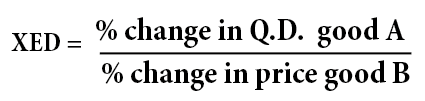Cross elasticity of demand
Cross elasticity of demand (XED) measures the percentage change in quantity demand for a good after a change in the price of another. For example: if there is an increase in the price of tea by 10%. and the quantity demanded for coffee increases by 2%, then the cross elasticity of demand = 2/10 = …