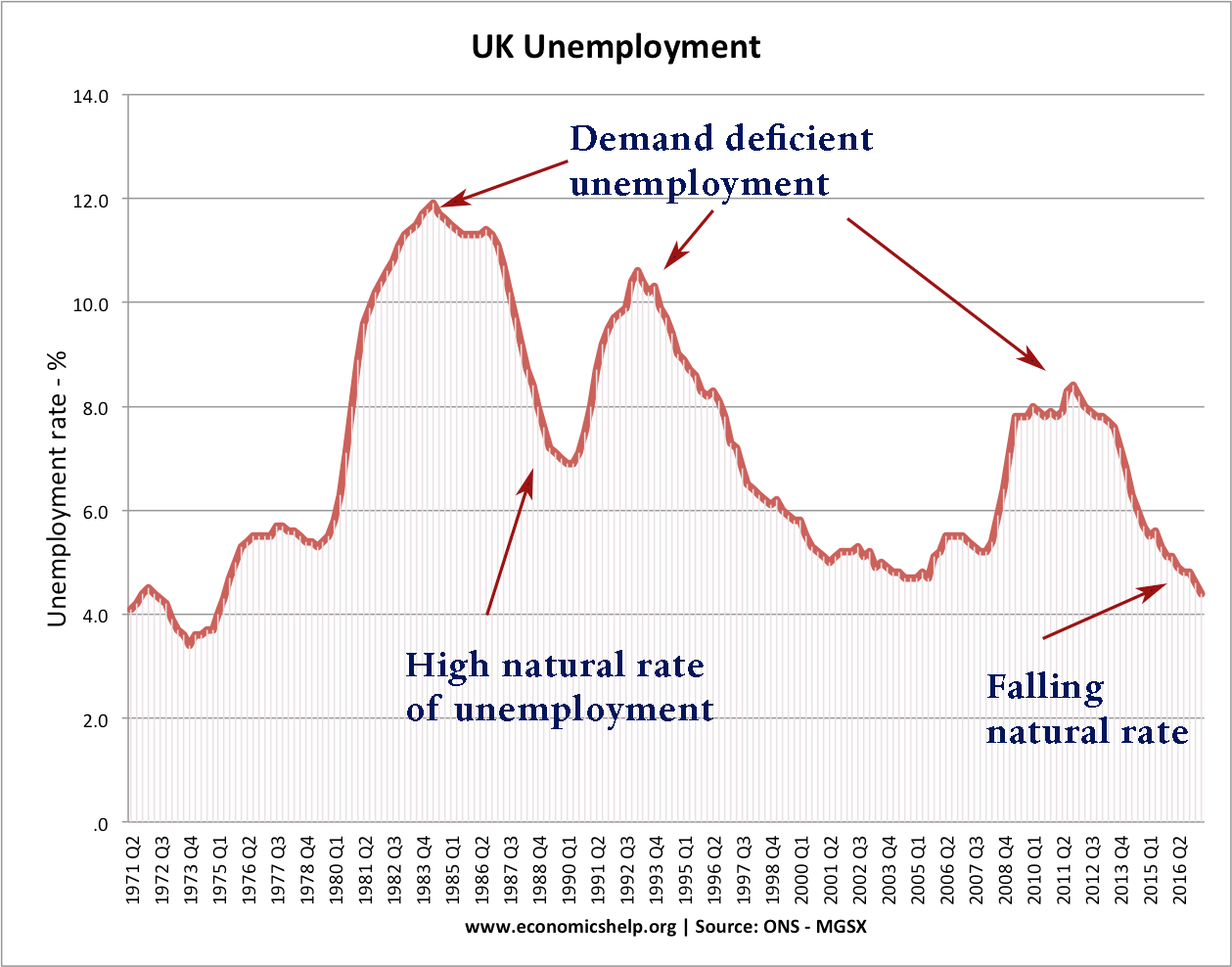
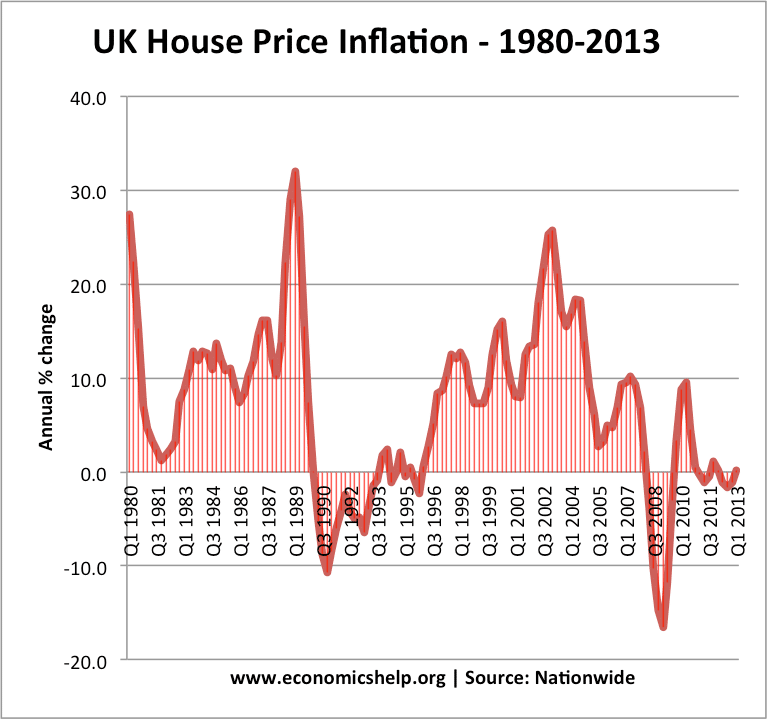
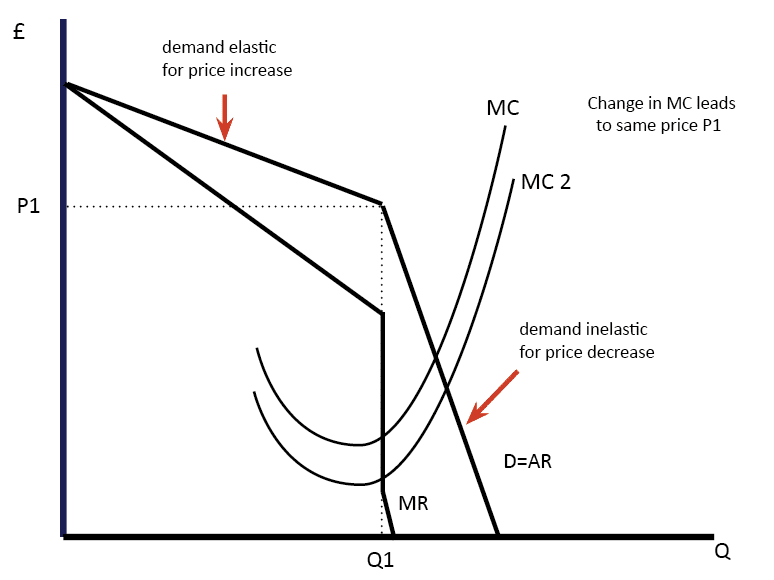
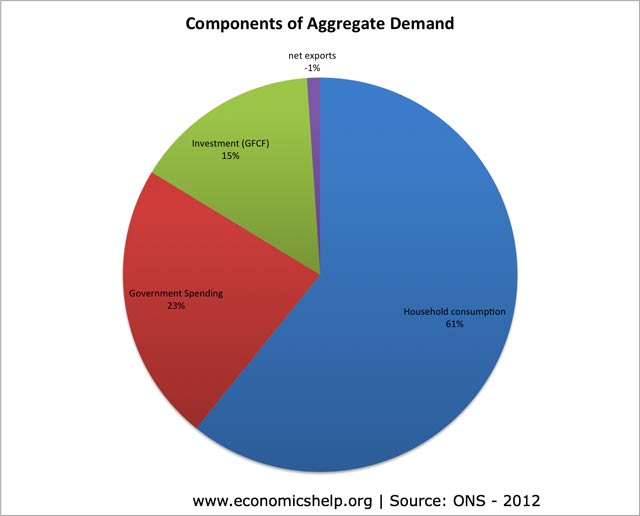
Should taxes on cigarettes be increased?
Q. Evaluate the economic case for and against the UK government further increasing the tax on tobacco in order to reduce smoking. Increasing tax will lead to a fall in demand, although this may only be a small effect because demand is price inelastic. People are addicted and there are no close substitutes. Cigarettes are …