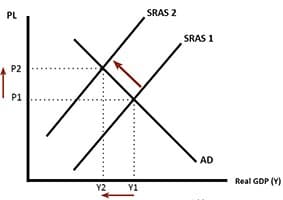
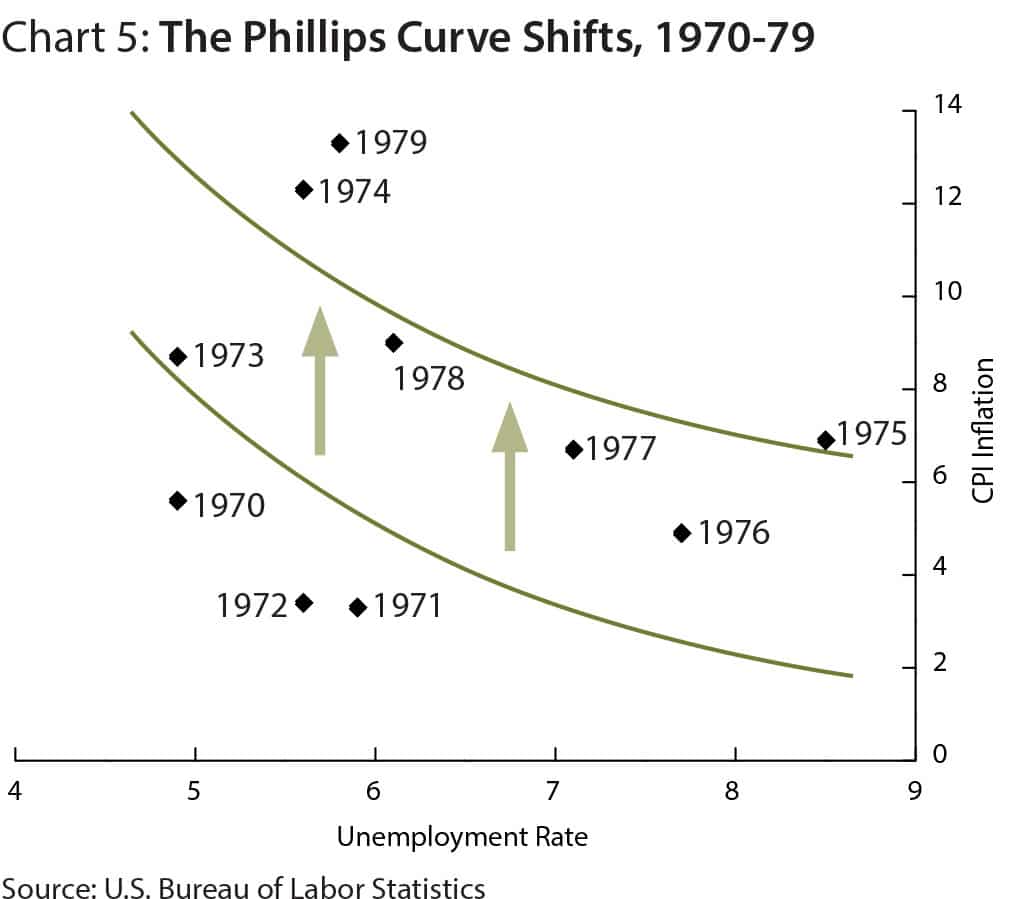
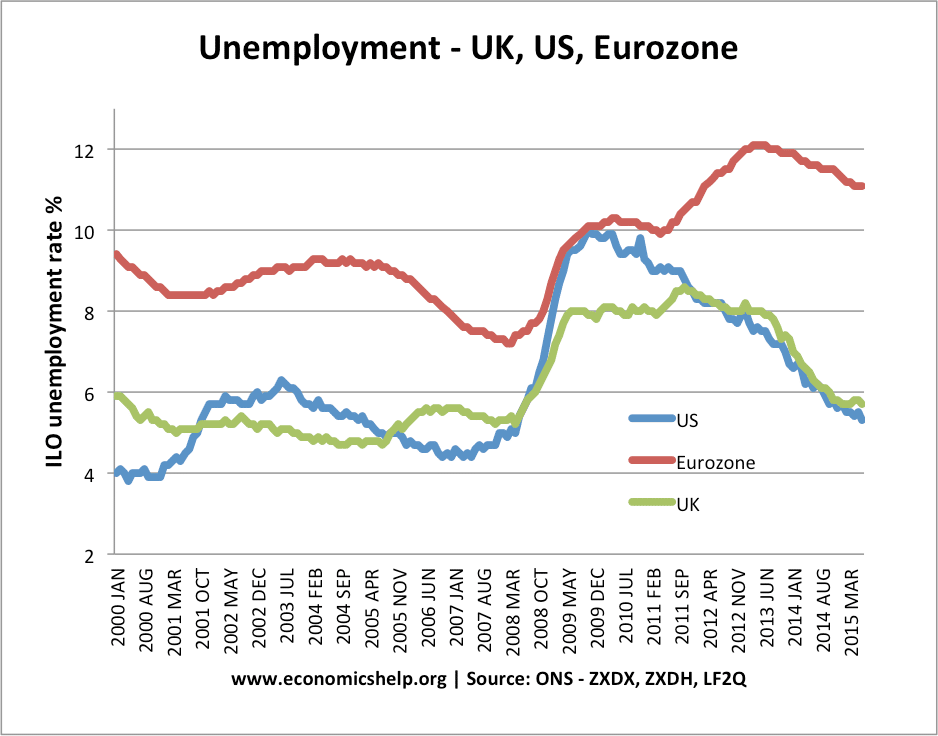
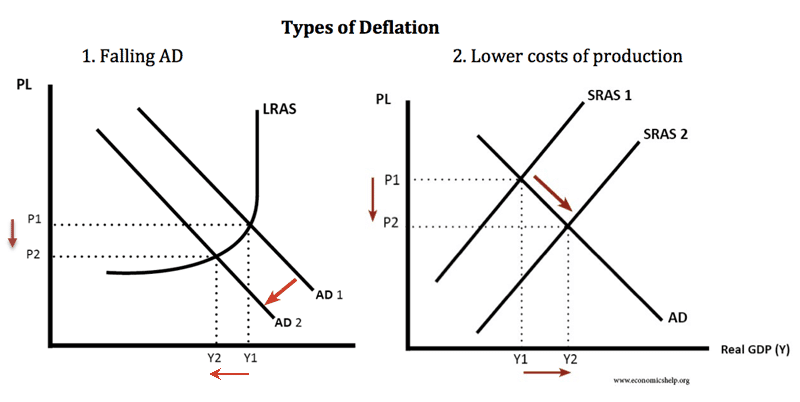
Bank of England
The Bank of England is responsible for managing UK monetary policy and maintaining the supply of money in the economy. The Bank of England is independent of the government. Although, the government can appoint members and set the inflation target. However, the Bank has a key role to play in the management of the economy …