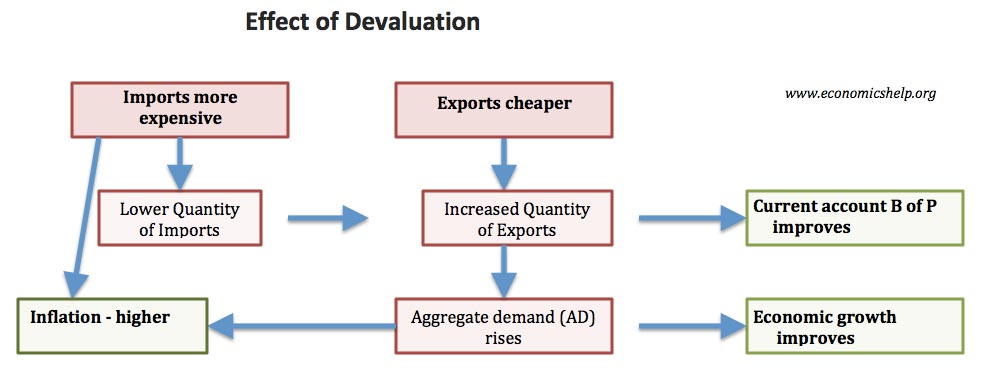
Effects of Globalisation on the UK Economy
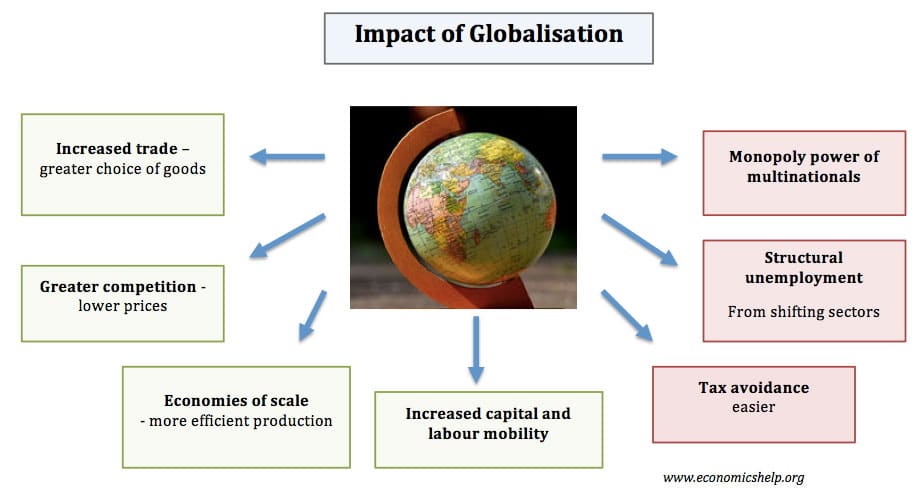
Globalisation involves the increased integration and interdependence of the global economy. It means there will be a rise in trade, and increase in movement of labour and capital. There are both pros and cons of globalisation. The benefits include greater competition, lower prices, economies of scale. Critics argue globalisation can leave many left behind due …